National Eye Institute researchers developed and validated an artificial-intelligence-based method to evaluate patients with Stargardt, an eye disease that can lead to childhood vision loss. The method quantifies disease-related loss of light-sensing retina cells, yielding information for monitoring patients, understanding genetic causes of the disease, and developing therapies to treat it. The findings published today in JCI Insight.
Credit: NEI
National Eye Institute researchers developed and validated an artificial-intelligence-based method to evaluate patients with Stargardt, an eye disease that can lead to childhood vision loss. The method quantifies disease-related loss of light-sensing retina cells, yielding information for monitoring patients, understanding genetic causes of the disease, and developing therapies to treat it. The findings published today in JCI Insight.
“These results provide a framework to evaluate Stargardt disease progression, which will help control for the significant variability from patient to patient and facilitate therapeutic trials,” said Michael F. Chiang, M.D., director of the NEI, which is part of the National Institutes of Health.
About 1 in 9,000 people develop the most common form of Stargardt, or ABCA4-associated retinopathy, an autosomal-recessive disease caused by variants to the ABCA4 gene, which contains genetic information for a transmembrane protein in light-sensing photoreceptor cells. People develop Stargardt when they inherit two mutated copies of ABCA4, one from each parent. People who have just one mutated copy of ABCA4 are genetic carriers, but do not develop the disease. More rare forms of Stargardt are associated with variants of other genes.
Yet even among patients who all have ABCA4 gene variants, there can be a wide spectrum in terms of age of onset and disease progression. One patient may have very early loss of light-sensing photoreceptors throughout the retina, while another may be a teenager with involvement limited to the fovea, the area of the retina that provides the sharpest central vision one needs to read and see other fine details. Still, another patient may reach mid-life with no vision loss.
“Different variants of the ABCA4 gene are likely driving the different disease characteristics, or phenotypes. However, conventional approaches to analyzing structural changes in the retina have not allowed us to correlate genetic variants with phenotype,” said the study’s co-leader, Brian P. Brooks, M.D., Ph.D., chief of the NEI Ophthalmic Genetics & Visual Function Branch. Dr. Brooks co-led the study with Brett G. Jeffrey, Ph.D., head of the Human Visual Function Core of the NEI’s Ophthalmic Genetics and Visual Function Branch.
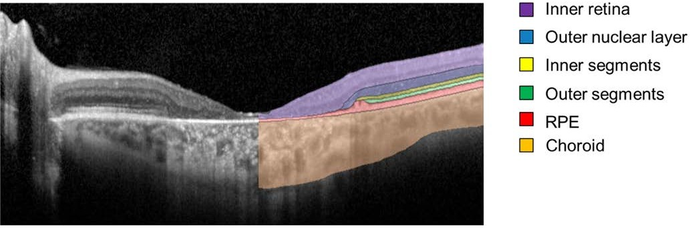
The researchers followed 66 Stargardt patients (132 eyes) for five years using a retinal imaging technology called spectral-domain optical coherence tomography (SD-OCT). The cross-sectional, 3D SD-OCT retinal images were segmented and analyzed using deep learning, a type of artificial intelligence in which huge amounts of imaging data can be fed into an algorithm, which then learns to detect patterns that allow the images to be classified.
Using the deep-learning method, the researchers were able to quantify and compare the loss of photoreceptors and various layers of the retina according to the patient’s phenotype and ABCA4 variant.
Specifically, the researchers zeroed in on the health of photoreceptors in an area known as the ellipsoid zone – a feature of the photoreceptor inner/outer segment border that is diminished or lost due to disease. The researchers also examined the outer nuclear layer in the immediate region surrounding the area of ellipsoid zone loss.
They found that the loss of the ellipsoid zone (a measure of severe photoreceptor degeneration), and thinning of the outer nuclear layer beyond those areas (a measure of subtle photoreceptor degeneration), followed a predictable temporal and spatial pattern. On the basis of that predictability, they could generate a way of classifying the severity of 31 different ABCA4 variants.
Importantly, they also found that photoreceptor degeneration was not limited to the area of the ellipsoid zone loss. Instead, progressive photoreceptor layer thinning – subtle to the physician’s eye, but quantitatively measurable – was evident in areas distant to the ellipsoid zone loss boundary. This represented the actual leading front of the disease, suggesting that it would be an area to monitor closely to determine if a new therapy was having an effect.
“We now have sensitive structural outcome measures for Stargardt disease, applicable to a wide range of patients which is essential for forging ahead with therapeutic trials,” Jeffrey said.
The study was funded by the NEI Intramural Research Program. The study was conducted at the NIH Clinical Center, ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01736293.
For more information about Stargardt disease, visit https://www.nei.nih.gov/learn-about-eye-health/eye-conditions-and-diseases/stargardt-disease
Reference:
Pfau M, Cukras CA, Huryn LA, Zein WM, Ullah E, Boyle MP, Turriff A, Chen MA, Hinduja AS, Siebel HEA, Hufnagel RB, Jeffrey BG, Brooks BP. “Photoreceptor degeneration in ABCA4-associated retinopathy and its genetic correlates,” published in press review February 25, 2022 in JCI Insight. 2022;7(2):e155373.https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.155373.
##
NEI leads the federal government’s research on the visual system and eye diseases. NEI supports basic and clinical science programs to develop sight-saving treatments and address special needs of people with vision loss. For more information, visit https://www.nei.nih.gov.
About the National Institutes of Health (NIH): NIH, the nation’s medical research agency, includes 27 Institutes and Centers and is a component of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. NIH is the primary federal agency conducting and supporting basic, clinical, and translational medical research, and is investigating the causes, treatments, and cures for both common and rare diseases. For more information about NIH and its programs, visit https://www.nih.gov/.
NIH…Turning Discovery Into Health®
DOI
10.1172/jci.insight.155373
Method of Research
Observational study
Subject of Research
People
Article Title
NIH study classifies vision loss and retinal changes in Stargardt disease
Article Publication Date
25-Jan-2022
COI Statement
The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.




