Researchers led by the University of Tsukuba devise a new approach to show how ghost-like neutrinos helped shape the Universe
Credit: University of Tsukuba
Tsukuba, Japan – Computer simulations have struggled to capture the impact of elusive particles called neutrinos on the formation and growth of the large-scale structure of the Universe. But now, a research team from Japan has developed a method that overcomes this hurdle.
In a study published this month in The Astrophysical Journal, researchers led by the University of Tsukuba present simulations that accurately depict the role of neutrinos in the evolution of the Universe.
Why are these simulations important? One key reason is that they can set constraints on a currently unknown quantity: the neutrino mass. If this quantity is set to a particular value in the simulations and the simulation results differ from observations, that value can be ruled out. However, the constraints can be trusted only if the simulations are accurate, which was not guaranteed in previous work. The team behind this latest research aimed to address this limitation.
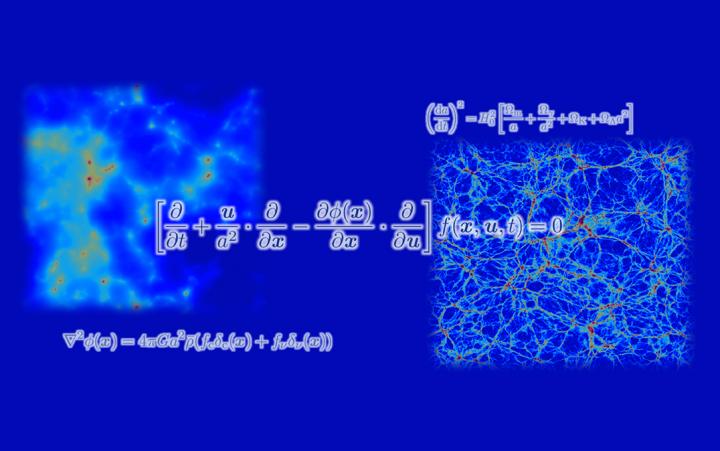
“Earlier simulations used certain approximations that might not be valid,” says lead author of the study Lecturer Kohji Yoshikawa. “In our work, we avoided these approximations by employing a technique that accurately represents the velocity distribution function of the neutrinos and follows its time evolution.”
To do this, the research team directly solved a system of equations known as the Vlasov-Poisson equations, which describe how particles move in the Universe. They then carried out simulations for different values of the neutrino mass and systemically examined the effects of neutrinos on the large-scale structure of the Universe.
The simulation results demonstrate, for example, that neutrinos suppress the clustering of dark matter–the ‘missing’ mass in the Universe–and in turn galaxies. They also show that neutrino-rich regions are strongly correlated with massive galaxy clusters and that the effective temperature of the neutrinos varies substantially depending on the neutrino mass.
“Overall, our findings suggest that neutrinos considerably affect the large-scale structure formation, and that our simulations provide an accurate account for the important effect of neutrinos,” explains Lecturer Yoshikawa. “It is also reassuring that our new results are consistent with those from entirely different simulation approaches.”
###
This work represents a milestone in simulating the Universe and paves the way for further exploration of how neutrinos influence the formation and growth of the large-scale structure. For instance, the new simulation approach could be used to study the dynamics of neutrinos and unconventional types of dark matter. Ultimately, it might lead to a determination of the neutrino mass.
The article, “Cosmological Vlasov-Poisson Simulations of Structure Formation with Relic Neutrinos: Nonlinear Clustering and the Neutrino Mass,” was published in The Astrophysical Journal at DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/abbd46
Media Contact
Naoko Yamashina
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




