Less symptomatic patients have a higher viral load when diagnosed and may carry a higher virus shedding risk potential, possibly representing an important overlooked population for infection containment, reports The American Journal of Pathology
Credit: The American Journal of Pathology
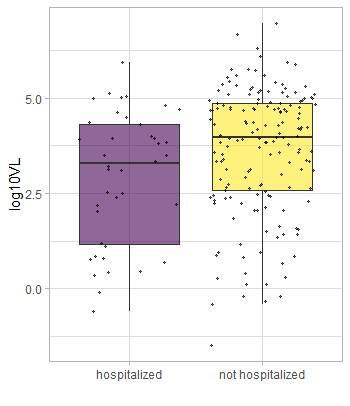
Philadelphia, July 14, 2020 – In a retrospective study, investigators from New York University Langone Health found that the quantity of SARS-CoV-2 (viral load) collected from patients in the emergency department is significantly higher in patients with fewer or milder symptoms who did not require hospitalization–the opposite of what might be expected. Reporting in The American Journal of Pathology, published by Elsevier, they also found that a patient’s history of cancer and cardiovascular disease is associated with higher viral loads even after adjusting for age.
The study was designed to determine possible associations between the viral load measured in patients positive for SARS-CoV-2 and their clinical parameters including severity of symptoms, hospital admission vs direct discharge, length of hospitalization, admission to the intensive care unit, length of need for oxygen support, and overall survival.
“It appears that the viral load peaks in the early stages of the disease. Although it is not associated with the duration of symptoms, their severity or outcome, it appears that the viral load is an important epidemiological surrogate marker of infectivity in mildly symptomatic and asymptomatic non-hospitalized patients, explained co-lead investigator Paolo Cotzia, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology, and Assistant Director, Center for Biospecimen Research and Development, NYU Langone Health, New York City, NY, USA.
“Whether the viral load in these patients stays the same or changes in later stages of the disease remains to be investigated and could provide further insights on the dynamics of viral replication.”
Two hundred and five patients who visited the emergency department at a New York City tertiary care center with confirmed COVID-19 were included in the study. Nasopharyngeal samples were taken at the time of diagnosis. One hundred and sixty-five patients were discharged from the emergency department, and 40 patients were hospitalized. Non-hospitalized patients were younger overall, and other characteristics were similar across the group. The median duration from symptom onset to sample collection for the hospitalized group was five days compared with three days for the discharged patients.
Investigators found that the initial viral load was significantly lower in patients who required hospitalization compared to those who were discharged. The association remained significant even after adjustment for age, sex, race, body mass index, and other existing medical conditions. They also found that a higher viral load was associated with shorter duration of symptoms in all patients and was not associated with disease severity.
Co-lead investigator George Jour, MD, Assistant Professor, Department of Pathology and Department of Dermatology, Associate Director Molecular Pathology, NYU Langone Health, New York City, NY, USA, observed, “Another important finding of our study is that the initial nasopharyngeal viral load reflects the time from onset of symptoms and duration of symptoms. We found that higher viral loads are seen in mild rather than in severe disease because they appear to reflect the time lapsed from the onset of infection. Furthermore, higher viral loads correlate with the presence of cancer or cardiovascular diseases.”
Although diagnostic viral load seems to have no prognostic utility for predicting outcomes from COVID-19, the investigators say it may be an important surrogate marker in mildly symptomatic, non-hospitalized patients. Their results support the concept that such patients may represent important sources of the virus. “Our study should increase awareness and should prompt the adherence to strict recommendation of social distancing and mask usage to avoid transmission,” the investigators concluded.
###
Media Contact
Eileen Leahy
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




