Credit: Radiological Society of North America
OAK BROOK, Ill. (June 24, 2020) – In recent weeks, a multisystem hyperinflammatory condition has emerged in children in association with prior exposure or infection to SARS-CoV-2. A new case series published in the journal Radiology examines the spectrum of imaging findings in children with the post-COVID-19 inflammatory condition known in the U.S. as Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C).
The array of findings includes airway inflammation and rapid development of pulmonary edema, coronary artery aneurysms, and extensive intra-abdominal inflammatory changes.
In April 2020, Evelina London Children’s Hospital in London, U.K., experienced a surge of children with a multi-system hyperinflammatory syndrome. The children had a variety of symptoms, including fever, headaches, abdominal pain, rash and conjunctivitis. Clinical features and lab findings shared some similarities to those of Kawasaki disease–which causes inflammation in the walls of blood vessels–Kawasaki-disease shock syndrome or toxic-shock syndrome, although atypical and more severe.
“Our hospital saw an unprecedented cluster of children presenting with MIS-C, a new hyperinflammatory syndrome in children related to the current COVID-19 pandemic–the recognition of which led to a national alert,” said the study’s lead author, Shema Hameed, M.B.B.S., consultant pediatric radiologist at Evelina London Children’s Hospital.
For the study, researchers performed a retrospective review of clinical, laboratory and imaging findings of the first 35 children under age 17 who were admitted to the pediatric hospital that met the case definition for MIS-C. The children were admitted from April 14 to May 9, 2020, and included 27 boys and eight girls, with a median age of 11 years old.
The most common clinical presentation was fever, found in 33 (94%) of the children, gastrointestinal symptoms including abdominal pain, vomiting and diarrhea in 30 (86%) of the children, rash (13 or 37%) and conjunctivitis (9 or 26%). Twenty-one children (60%) were in shock. Clinical status was severe enough to warrant management in the pediatric intensive care unit in 24 of 35 children (69%), of which 7 (20%) required mechanical ventilation and 20 (57%) inotropic support.
Two children required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) due to severe myocardial dysfunction. Lab tests revealed that all of the children had abnormal white blood cell counts.
The study identified a pattern of imaging findings in post COVID-19 MIS-C, including airway inflammation, rapidly progressive pulmonary edema, coronary artery aneurysms and extensive abdominal inflammatory changes within the right iliac fossa.
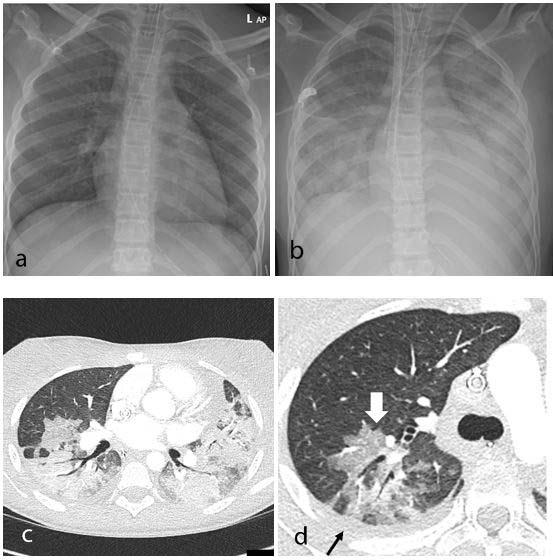
All 35 children underwent chest X-ray due to fever, sepsis or features of multisystem inflammation. Nineteen X-rays were abnormal, the most common finding being that of bronchial wall thickening.
The predominant findings on chest CT were basal consolidation, or part of the lung filling with fluid; and collapsed lung with pleural effusions, or build-up of fluid in the outer membranes of the lungs.
Abdominal ultrasound findings included inflammatory changes within the right iliac fossa, with mesenteric fat stranding, lymphadenopathy and bowel wall thickening, as well as free fluid in the pelvis.
“As pediatric radiologists, we were interested in the emerging pattern of imaging findings that we observed in these children,” Dr. Hameed said. “Our intention is to bring these findings to the attention of the wider radiological community.”
The authors advise that future studies should include a larger group of patients, ideally utilizing multi-center databases to assess the radiological findings alongside the complex clinical course of these young patients.
###
“Spectrum of Imaging Findings on Chest Radiograph, US, CT, and MRI Images in Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C) Associated with COVID-19.” Collaborating with Dr. Hameed were Heba Elbaaly, Catriona E. L. Reid, Rui M. F. Santos, Vinay Shivamurthy, James Wong and K. Haran Jogeesvaran.
Radiology is edited by David A. Bluemke, M.D., Ph.D., University of Wisconsin School of Medicine and Public Health, Madison, Wisconsin, and owned and published by the Radiological Society of North America, Inc. (https:/
RSNA is an association of radiologists, radiation oncologists, medical physicists and related scientists promoting excellence in patient care and health care delivery through education, research and technologic innovation. The Society is based in Oak Brook, Illinois. (RSNA.org)
For patient-friendly information on pediatric imaging, visit RadiologyInfo.org.
Media Contact
Linda Brooks
[email protected]




