Credit: Karolinska Institutet.
Disorders of the cells’ energy supply can cause a number of serious diseases, but also seem to be connected to ageing. More research is needed on mitochondrial function to find future treatments. A new study involving researchers at Karolinska Institutet shows how an important molecule inside the mitochondria affects their function in mice and fruit flies. The study, which is published in Science Advances, adds valuable knowledge on formerly relatively unexplored protein modifications.
In each cell of the body is an organ called the mitochondrion, which converts nutrients in our food to energy. Mitochondria are an essential part of the metabolism, and when things go wrong we can develop serious diseases.
Mitochondrial dysfunction is the hallmark of a group of rare genetic disorders but can also be observed in common diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, neurodegenerative diseases and the normal ageing process.
More research is needed on mitochondria and how they communicate with the rest of the cell if scientists are to find new therapeutic approaches to improve mitochondrial function.
Researchers at Karolinska Institutet, the Max-Planck Institute for Biology of Ageing in Cologne and the University of California San Diego have now studied how the methylation of proteins affects different mitochondrial processes.
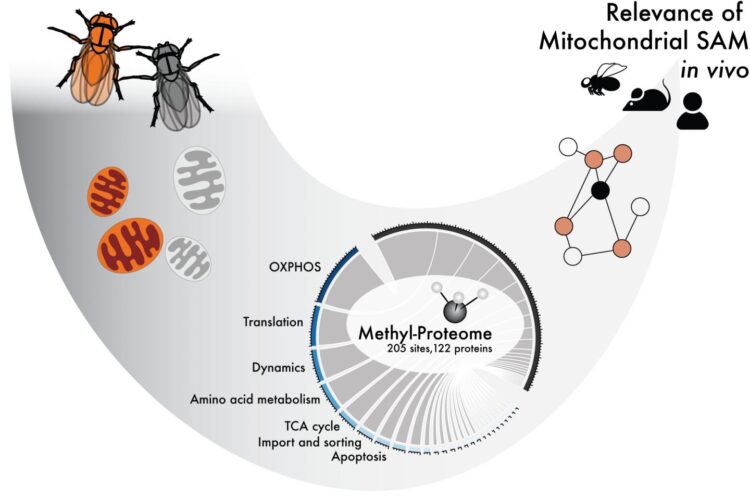
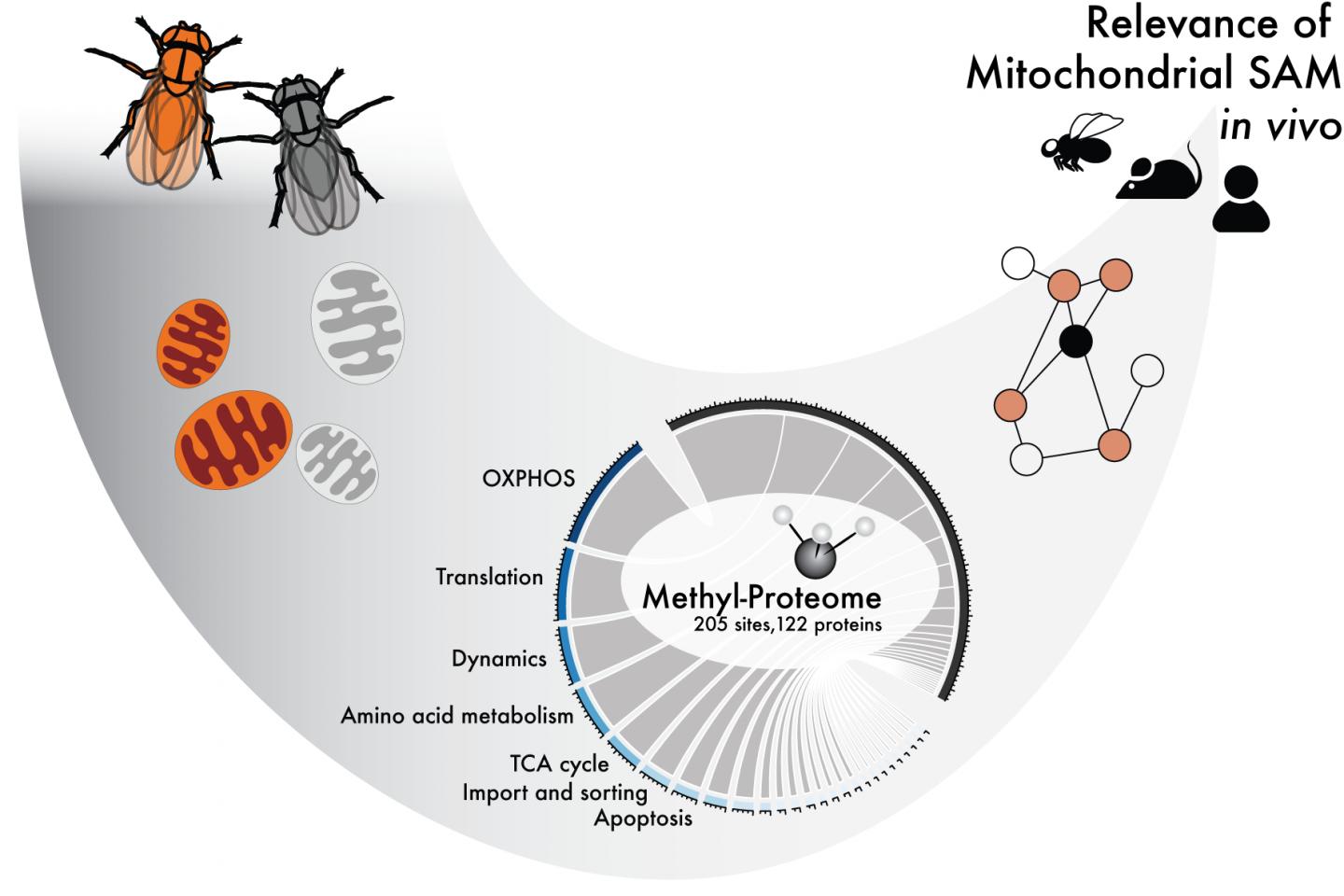
Methylation is a chemical modification in which a methyl group (CH3) is added to a molecule, thereby potentially affecting its function. S-Adenosylmethionine (SAM), also known as AdoMet, is the main methyl group donor within the cell, including inside of mitochondria.
“We’re interested in studying this particular molecule since the production of SAM changes in cancer and when we age,” says Anna Wredenberg, researcher at the Department of Medical Biochemistry and Biophysics, Karolinska Institutet.
By completely removing SAM from the mitochondria of fruit flies and mice, the researchers have been able to study which processes in the mitochondria are dependent on methylation.
“Earlier studies have shown that both SAM and cellular energy levels drop during ageing. Our study suggests a link between these two pathways by demonstrating that low SAM levels can influence mitochondrial energy production.”
The study has identified which of the mitochondrial proteins are methylated and how methylation affects them, and how these modifications might affect mitochondrial function. The researchers also demonstrate the physiological consequences of the lack of such changes. However, several questions still need answering.
“Our study has provided an indication that some modifications can be modulated by diet, but we need to continue examining if we can change the pathological process for the better,” says Anna Wredenberg. “So far we’ve only looked at protein changes, but other molecules can also be modified by intra-mitochondrial SAM. We have to study these modifications to get a better understanding of the role it plays.”
###
The study was financed by the Swedish Research Council, the European Research Council, the Knut and Alice Wallenberg Foundation, the Max Planck Society and the Ragnar Söderberg Foundation. There are no reported conflicts of interest.
Publication: “The One-Carbon Pool Controls Mitochondrial Energy Metabolism via Complex I and Iron-Sulfur Clusters”, Florian A. Schober, David Moore, Ilian Atanassov, Marco F. Moedas, Paula Clemente, Akos Vegvari, Najla El Fissi, Roberta Filograna, Anna-Lena Bucher, Yvonne Hinze, Matthew The, Erik Hedman, Ekaterina Chernogubova, Arjana Begzati, Rolf Wibom, Mohit Jain, Roland Nilsson, Lukas Kall, Anna Wedell, Christoph Freyer, Anna Wredenberg. Science Advances, online 19 February 2021.
Media Contact
Press Office
[email protected]