Study looks beneath surface to see how oxides, gases interact
Credit: Binghamton University, State University of New York
BINGHAMTON, N.Y. – New research led by faculty at Binghamton University, State University of New York, could aid cleaner energy technologies.
The atomic reaction between gases and oxides is a key piece for many technological puzzles. It can lead to benefits such as better catalysts to enable cleaner energy technologies, or to problems like corrosion.
Understanding those interactions isn’t always easy, though, and often doesn’t go beyond the surface — quite literally.
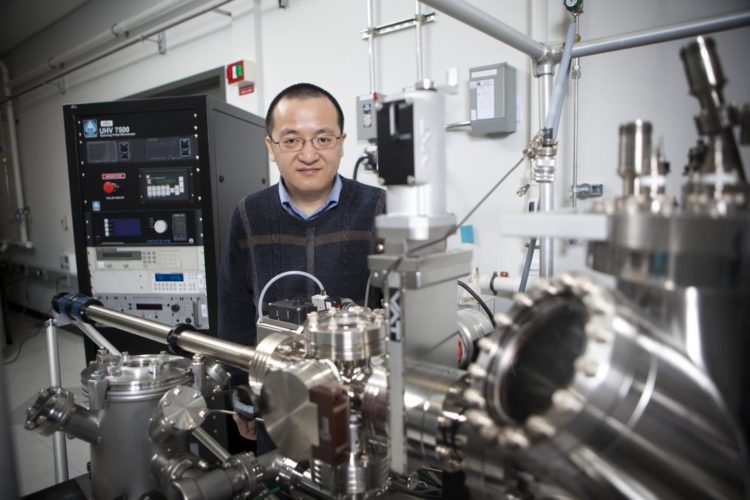
A team from Binghamton University, the Brookhaven National Laboratory and the National Institute of Standards and Technology — led by Professor Guangwen Zhou from the Thomas J. Watson School of Engineering and Applied Science’s Department of Mechanical Engineering — has a new way to look deeper into how gas molecules affect the atoms beneath the surface of a material.
The material studied is cupric oxide, a copper oxide that many researchers are interested in because it is more abundant and affordable than noble metals such as silver, gold and platinum, and it is used for numerous processes such as methanol production.
For the paper “Surface-reaction induced structural oscillations in the subsurface,” published earlier this month in Nature Communications, Zhou and his fellow researchers (including Binghamton PhD students Xianhu Sun, Wenhui Zhu, Dongxiang Wu, Chaoran Li, Jianyu Wang, Yaguang Zhu and Xiaobo Chen) examined the reaction between hydrogen and copper oxide using atomic-scale transmission electron microscopy.
The technique allowed them to see the surface and subsurface simultaneously and in real time, showing that structural oscillations are induced in the subsurface by loss of oxygen from the oxide surface.
“This study shows how the reaction from the surface propagates to deeper atomic layers. We look at it from a cross-section so we can see atoms both in the top layer and subsurface layers more clearly,” said Zhou, who teaches as part of the Materials Science and Engineering Program and also is the associate director of Binghamton’s Institute for Materials Research.
This new study is funded by the Department of Energy, in the hope that the results can lead to better catalysts, improved batteries, longer-lasting vehicles and other higher-quality products.
“If we know these reaction mechanisms, we can design better materials,” Zhou said. “We can’t care just about the surface but also the deeper layers if we want to understand the process better.”
###
Media Contact
John Brhel
[email protected]
607-240-9786
Related Journal Article
http://dx.