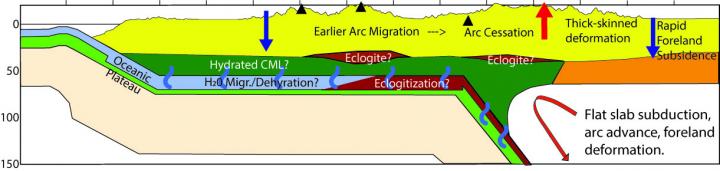
Credit: Lara Wagner, Carnegie Institution for Science
A $2.7 million multi-disciplinary, multi-institutional NSF-Frontiers of Earth Science grant has been awarded to a team led by Carnegie’s Lara Wagner to study an active flat slab in Colombia. A flat slab is produced when a tectonic plate descends to depths of about 30 to 60 miles (~50-100 km) then flattens and travels horizontally for hundreds of miles before descending farther into Earth’s mantle. Flat slabs are unlike standard subduction, in which a tectonic plate descends more steeply beneath another plate directly into the Earth.
Because flat slabs travel horizontally directly beneath the overriding continents for hundreds of miles, they have more extensive effects on the continental crust including mountain building far from plate boundaries, ore formation, and geochemical modifications that can affect the long-term stability of the overriding plate. Furthermore, large earthquakes within flat slabs, such as the Magnitude 7.1 Mexico City earthquake that occurred in 2017 or the Magnitude 8 earthquake in Peru that occurred this May can cause extensive damage far from plate boundaries, where earthquakes are uncommon and local communities are therefore less prepared.
Unlike previously studied flat slabs, the Colombian flat slab has broken into two parts, one of which has recently sunk back down into the mantle to resume a normal subduction geometry. By comparing the still-existing flat slab region to the recently foundered flat slab region, the researchers will be able to study the initial migration and cessation of volcanism, the development of modern analogues to the Rocky Mountains called basement cored uplifts, the formation of ore deposits, and ultimately the return to normal arc volcanism–the complete flat slab cycle.
The coordinated multi-disciplinary approach, with co-principal investigators Brian Horton and Thorsten Becker at the University of Texas-Austin and Christy Till at Arizona State University includes funding for a 70-station, 2-year seismic deployment across much of central Colombia. The grant has a major education and outreach component to be led by the Carnegie Academy for Science Education (CASE). Teachers from Washington, D.C., Austin, and Phoenix will go into the field, which will help them prepare bilingual educational lesson plans, multimedia, and web materials on the Earth sciences.
###
Caption: Unlike standard subduction, in which a tectonic plate descends beneath another plate into Earth, flat slab subduction is a process in which a tectonic plate descends to depths of about 30 to 60 miles ( ~50-100 kilometers, light blue, green, and beige) then flattens and travels horizontally for hundreds of miles before descending farther into Earth’s mantle. Image courtesy Lara Wagner, Carnegie Institution for Science
Media Contact
Lara Wagner
[email protected]




