Credit: Professor Sumio Ohtsuki
A Japanese research team has developed a cyclic peptide (a chain of amino acids bonded circularly) that enhances blood-brain barrier (BBB) penetration. By attaching the cyclic peptide to the surface of nanoparticles, research and development of new drug nanocarriers for drug delivery to the brain becomes possible.
Unlike blood circulation to the peripheral organs in the body, the BBB prevents various substances, including many drugs, from moving from the blood into the brain. Biopharmaceuticals and macromolecular drugs are attracting attention as new treatments for previously untreatable diseases and for improving outcomes. However, these high molecular weight drugs are unable to penetrate the BBB. Technologies that can deliver them to the brain would bring significant progress in the development of medications that act on the brain.
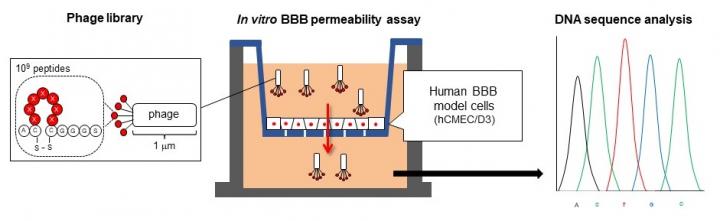
Aiming to develop technologies applicable to various drugs, a research team from Kumamoto University, Japan worked on developing a cyclic peptide able to penetrate the BBB. In their search to find a peptide with the desired function, they turned to viruses called phages. From a phage library listing cyclic peptides with 109 types of amino acid sequences, the researchers searched for phages able to penetrate human BBB model cells and analyzed their sequences. Since the size of a phage (about 1,000 nanometers) is larger than macromolecular drugs, the scientists expected that these cyclic peptides would also allow drug penetration into the BBB.
Of the two new cyclic peptides they discovered, one promoted phage penetration not only in human BBB model cells but also in monkey and rat BBB model cells. Furthermore, this phage could be found in the brain of a mouse 60 minutes after intravenous injection. In additional experiments, the researchers modified liposomes by adding the cyclic peptide to the surface of liposomes thereby creating 150 nanometer-sized artificial nanoparticles. When this modified liposome was injected intravenously into a mouse, it was also detected in the brain 60 minutes later showing that the new cyclic peptide facilitates penetration of phage and liposome nanoparticles through the BBB allowing for delivery into the brain.
“Liposomes are nanocarrier that can encapsulate various substances. The liposome whose surface has been modified with this new cyclic peptide can be used as a nanocarrier to bypass the BBB. A way to deliver macromolecular drugs to the brain has been opened,” said Professor Ohtsuki. “We expect this research to contribute significantly toward the development of drugs for central nervous system diseases, including Alzheimer’s disease.”
###
This research was posted online in the “Journal of Controlled Release” on 2 March 2020.
[Source]
Yamaguchi, S., Ito, S., Masuda, T., Couraud, P.-O., & Ohtsuki, S. (2020). Novel cyclic peptides facilitating transcellular blood-brain barrier transport of macromolecules in vitro and in vivo. Journal of Controlled Release, 321, 744-755. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.03.001
Media Contact
J. Sanderson & N. Fukuda
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




