Every time you make a memory, somewhere in your brain a tiny filament reaches out from one neuron and forms an electrochemical connection to a neighboring neuron.A team of biologists at Vanderbilt University, headed by Associate Professor of Biological Sciences Donna Webb, studies how these connections are formed at the molecular and cellular level.
The filaments that make these new connections are called dendritic spines and, in a series of experiments described in the April 17 issue of the Journal of Biological Chemistry, the researchers report that a specific signaling protein, Asef2, a member of a family of proteins that regulate cell migration and adhesion, plays a critical role in spine formation. This is significant because Asef2 has been linked to autism and the co-occurrence of alcohol dependency and depression.
“Alterations in dendritic spines are associated with many neurological and developmental disorders, such as autism, Alzheimer’s disease and Down Syndrome,” said Webb. “However, the formation and maintenance of spines is a very complex process that we are just beginning to understand.”
Neuron cell bodies produce two kinds of long fibers that weave through the brain: dendrites and axons. Axons transmit electrochemical signals from the cell body of one neuron to the dendrites of another neuron. Dendrites receive the incoming signals and carry them to the cell body. This is the way that neurons communicate with each other.
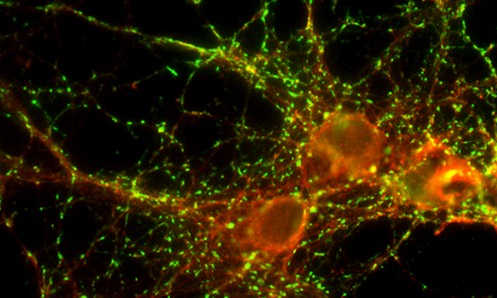
Fluorescent microphotograph of neurons. The green dye stains for a specialized synaptic protein and the red dye stains for actin, the polymeric protein that forms microfilaments and is a major component in the cytoskeleton. (Adam Wegner, Webb Lab / Vanderbilt)
As they wait for incoming signals, dendrites continually produce tiny flexible filaments called filopodia. These poke out from the surface of the dendrite and wave about in the region between the cells searching for axons. At the same time, biologists think that the axons secrete chemicals of an unknown nature that attract the filopodia. When one of the dendritic filaments makes contact with one of the axons, it begins to adhere and to develop into a spine. The axon and spine form the two halves of a synaptic junction. New connections like this form the basis for memory formation and storage.
Autism has been associated with immature spines, which do not connect properly with axons to form new synaptic junctions. However, a reduction in spines is characteristic of the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease. This may help explain why individuals with Alzheimer’s have trouble forming new memories.
The formation of spines is driven by actin, a protein that produces microfilaments and is part of the cytoskeleton. Webb and her colleagues showed that Asef2 promotes spine and synapse formation by activating another protein called Rac, which is known to regulate actin activity. They also discovered that yet another protein, spinophilin, recruits Asef2 and guides it to specific spines.
“Once we figure out the mechanisms involved, then we may be able to find drugs that can restore spine formation in people who have lost it, which could give them back their ability to remember,” said Webb.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by Vanderbilt University.