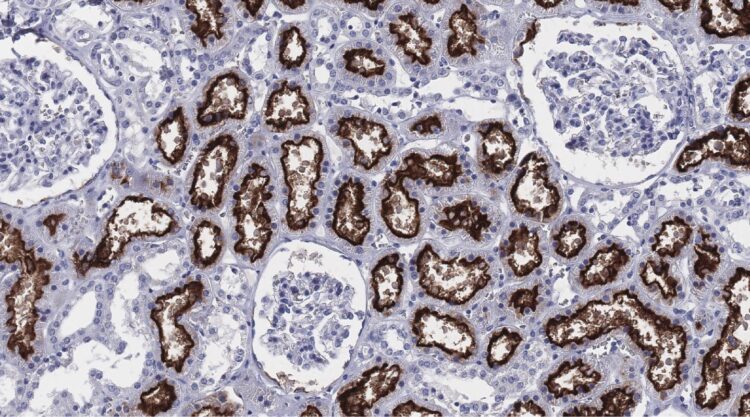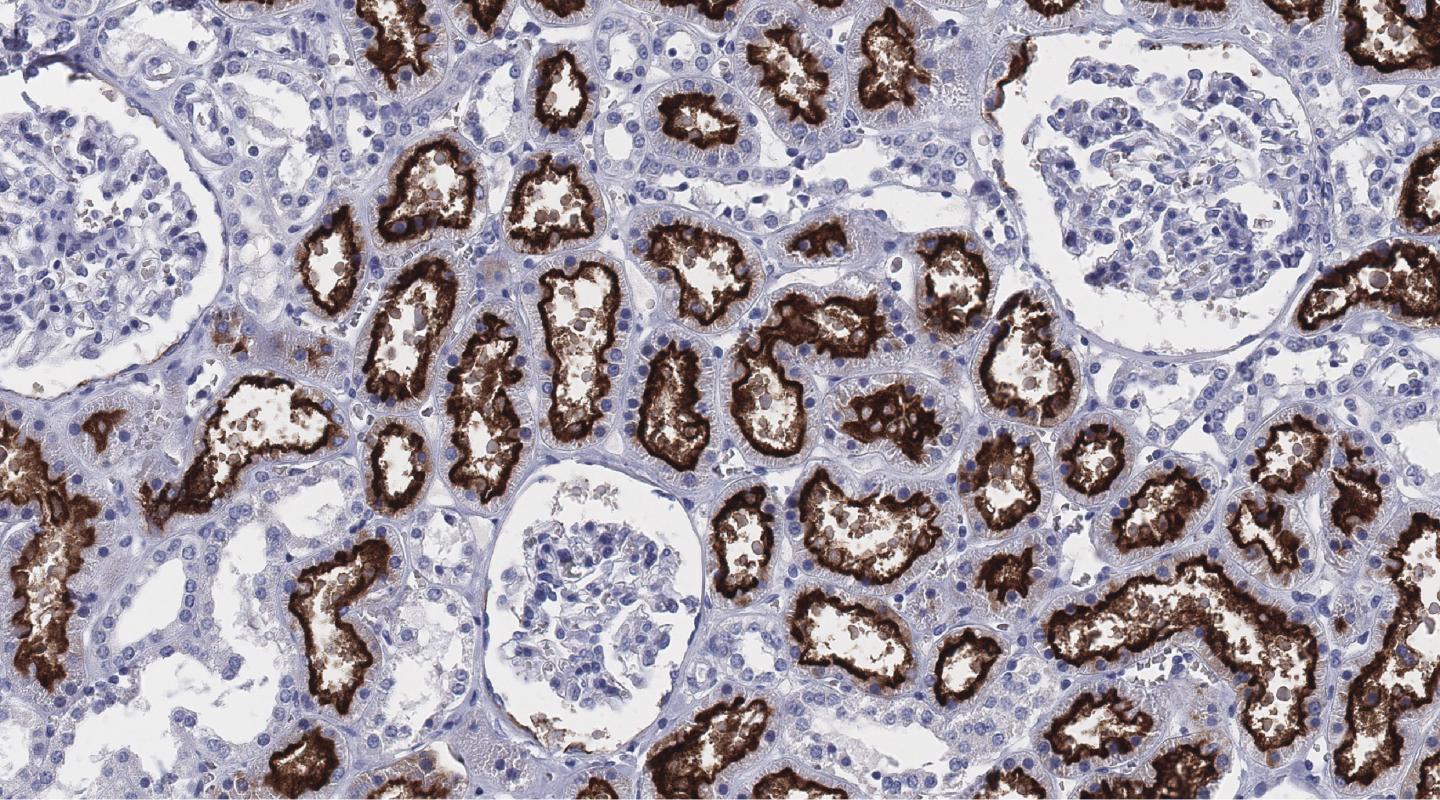
Credit: The Human Protein Atlas programme
Researchers at Uppsala University have described the presence, throughout the human body, of the enzyme ACE2. This is thought to be the key protein used by the SARS-CoV-2 virus for host cell entry and development of the disease COVID-19. In contrast to previous studies, the study shows that no or very little ACE2 protein is present in the normal respiratory system. The results are presented in Molecular Systems Biology.
The article presents a large-scale, systematic evaluation of angiotensin I converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) expression in more than 150 cell types, at both messenger RNA (mRNA) and protein levels, and reports that ACE2 is expressed only at very low levels, if at all, in respiratory epithelial cells.
“Considering the clinical manifestations of COVID-19, with acute respiratory distress syndrome and extensive damage to the lung parenchyma, the results highlight the need for further study of the biological mechanisms responsible for COVID-19 infection and disease progression,” says Dr Cecilia Lindskog, senior author of the paper and Head Director of the Human Protein Atlas tissue team at Uppsala University.
A full understanding of susceptibility to SARS-CoV-2 infection and its progression to a severe and sometimes deadly disease calls for study of the SARS-CoV-2 entry receptors and their cell-type-specific expression in human tissues, at both mRNA and protein levels. It has been suggested that SARS-CoV-2 employs the enzyme ACE2 for host cell entry, and that penetration of SARS-CoV-2 via this receptor would explain the severe clinical manifestations observed in various tissues and organs, including the respiratory system.
The study by Hikmet et al. presents a comprehensive update on ACE2 expression throughout the human body, at both mRNA and protein levels. Consistently high expression was found in the intestines, kidney, gallbladder, heart, male reproductive organs, placenta, eye and vascular system. In the respiratory system, however, expression was limited, and in a subset of cells in a few individuals there was no or only low expression.
“Previous studies have indicated that ACE2 protein is highly expressed in the human lung. But these expression profiles have not been reliably presented along with tissues and organs from the entire human body, or based on several different datasets at mRNA and protein levels,” Lindskog says.
“Here, in contrast to previous studies, we were able to confidently show that no ACE2 protein is present, or that it occurs at only very low levels, in the normal respiratory system.”
Immunohistochemical analysis of 360 normal lung samples from an extended patient cohort was based on the Human Protein Atlas (HPA) resource. Two different antibodies, which were stringently validated, were used.
“The HPA programme has devoted considerable efforts to introducing and implementing a new concept for enhanced validation of antibodies, using strategies recommended by the International Working Group for Antibody Validation (IWGAV). Such strategies are crucial for determining whether the antibody staining corresponds to true protein expression,” says Professor Mathias Uhlén, Director of the HPA consortium and co-author of the paper.
In a News & Views article published along with the ACE2 paper, Nawijn et al. acknowledge the importance of the study and discuss potential explanations for the low expression in the respiratory system. Recent studies suggest that ACE2 could be an interferon-induced gene, leading to upregulation during SARS-CoV-2 infection. It is proposed that ACE2 may first enter and infect eye conjunctiva and cells in the upper airways, and that this is followed by ACE2 upregulation due to the antiviral response, enabling the SARS-CoV-2 to spread and infect the lung parenchyma. It has also been suggested that smoking may increase ACE2 expression in the respiratory system.
“Further studies addressing the dynamic regulation of ACE2, and to confirm whether the low ACE2 expression in the human respiratory system is sufficient for SARS-CoV-2 infection or whether other factors are needed for host cell entry, are urgently needed,” Lindskog says.
###
The Human Protein Atlas
The Human Protein Atlas (HPA) programme, based at the Science for Life Laboratory in Stockholm, Sweden, started in 2003. Its aim is to map all the human proteins in cells, tissues and organs using integration of various omics technologies, including antibody-based imaging, mass spectrometry-based proteomics, transcriptomics and systems biology. There is open access to all the data in this knowledge resource, so that scientists in academia and industry alike can freely use the data to explore the human proteome.
The Human Protein Atlas programme, which has already contributed to several thousand publications in the fields of human biology and disease, has been selected by ELIXIR (http://www.
Media Contact
Cecilia Lindskog
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.