Credit: Mitra lab/CSHL, 2019
Traumatic brain injuries (TBI), including concussions, can be caused by anything from sports injuries to battlefield trauma. And they can have fatal or lasting effects. The results of a severe concussion–problems with thinking, memory, movement, emotions–are clear. The causes, or underlying pathological mechanisms, were not.
A new study questions the ongoing hypothesis that the blunt force behind a traumatic brain injury causes nerve damage, or axonal injury. A team of researchers, including Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory professor Partha Mitra, found greater signs of blood vessel damage than nerve damage after performing post mortem scans on an injured brain. The findings could influence the treatment of and development of new drugs for TBI.
“Nerve damage following traumatic brain injuries has been a majority point of view, and therapy as well as drug development has been targeted towards that,” Mitra said. “The idea is that if the mechanism is actually different, therapeutic intervention may also be different.”
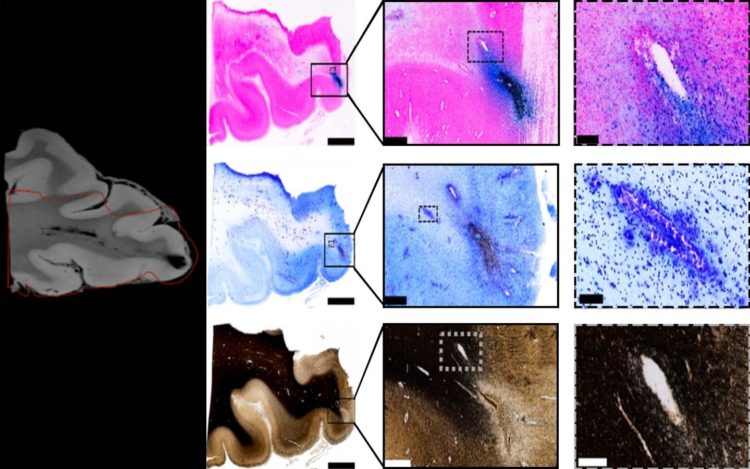
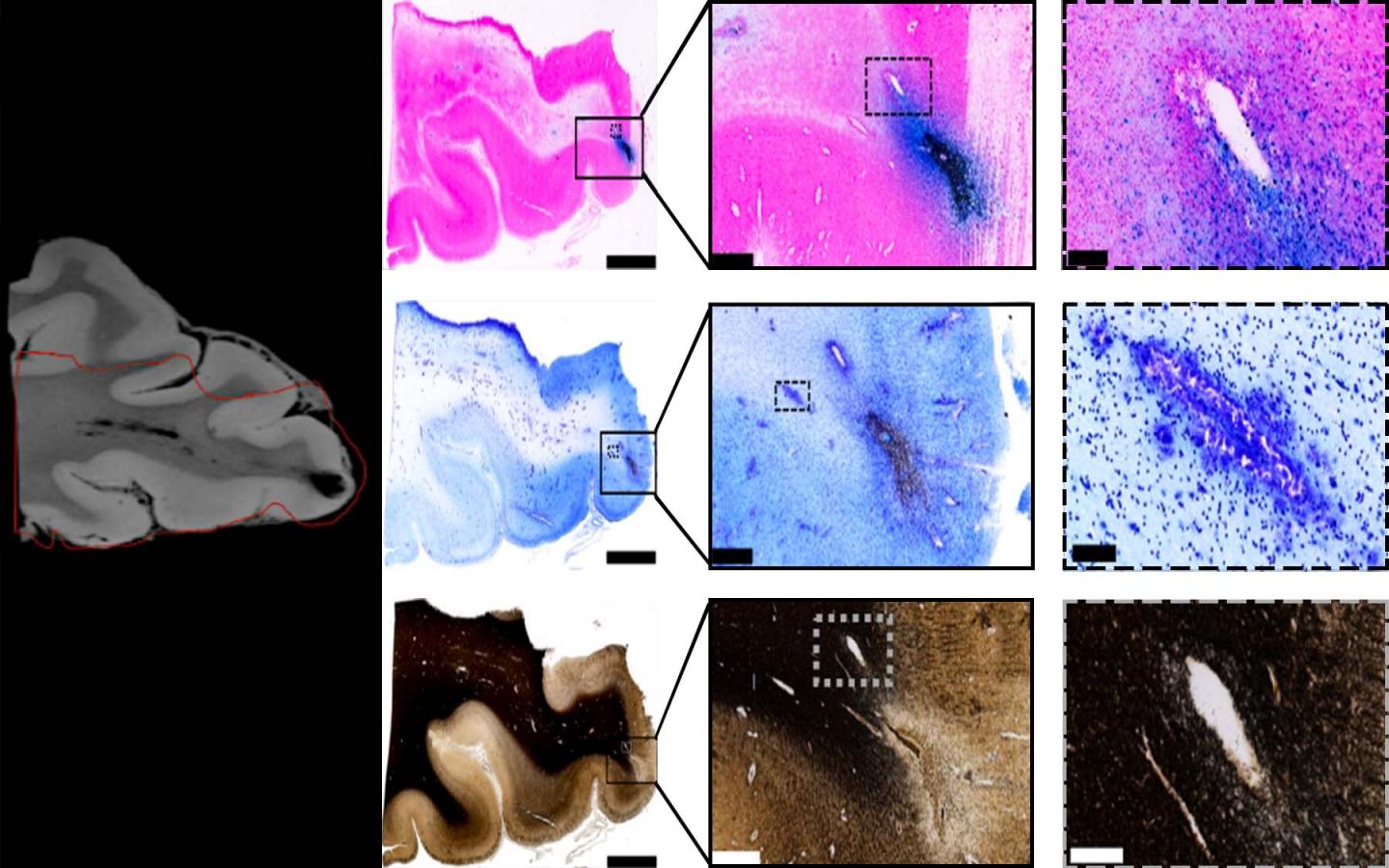
Mitra’s lab worked on the research with colleagues at the National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Neurological Disease and Stroke, University of Maryland, Center for Neuroscience and Regenerative Medicine, and Uniformed Services University of the Health Sciences who had been studying human brains of deceased patients using MRI. The CSHL team performed closer analysis on the postmortem brain tissue using a high-throughput neurohistological pipeline (an assemblage of techniques for labeling and visualizing brain slices) Mitra developed to study the wiring of mouse brains.
With MRI, the resolution is limited to several hundred microns, which makes it hard to discern whether nerve fiber (axonal) or blood vessel (vascular) injuries had occurred, Mitra said. Digitally analyzing the postmortem tissue at micron resolution, correlated with the MRI scan, allowed the team to see the vascular injury more clearly.
Mitra focused on areas surrounding lesions, or where the trauma left a physical imprint on the brain. They appeared on MRI scans as “black blobs.” The team used an iron stain (which shows up in blue) for presence of blood and a myelin stain for presence of nerve fiber fragments on the brain samples. They saw a significant amount of iron-marked blood cells across the area where the lesion was located in the brain sample, indicating traumatic microbleeds caused by ruptures along the blood vessels across the brain. The researchers did not observe any significant nerve damage from the myelin stains.
While the researchers could not completely rule out that patients with TMBs also suffered axonal injury, they concluded that traumatic vascular injury is a distinct characteristic of traumatic microbleeds and could be a target for new therapies.
The team also found that traumatic microbleeds often predict future health problems and disabilities for people with TBI, but could not determine the direction of the relationship between TMBs and acute injuries. TMBs could simply be a signature of more severe injury, or they could cause a worse outcome.
Because of this, the team thinks that follow-up experiments are needed to identify the underlying causes and effects of TBI for better diagnosis, prognosis, identifying therapeutic targets and improving patient outcomes.
###
Media Contact
Sara Roncero-Menendez
[email protected]
516-367-6866
Related Journal Article
http://dx.