New therapeutic approach points to potential treatment of liver cancer patients with Hepatitis B virus infection
Credit: Gastroenterology
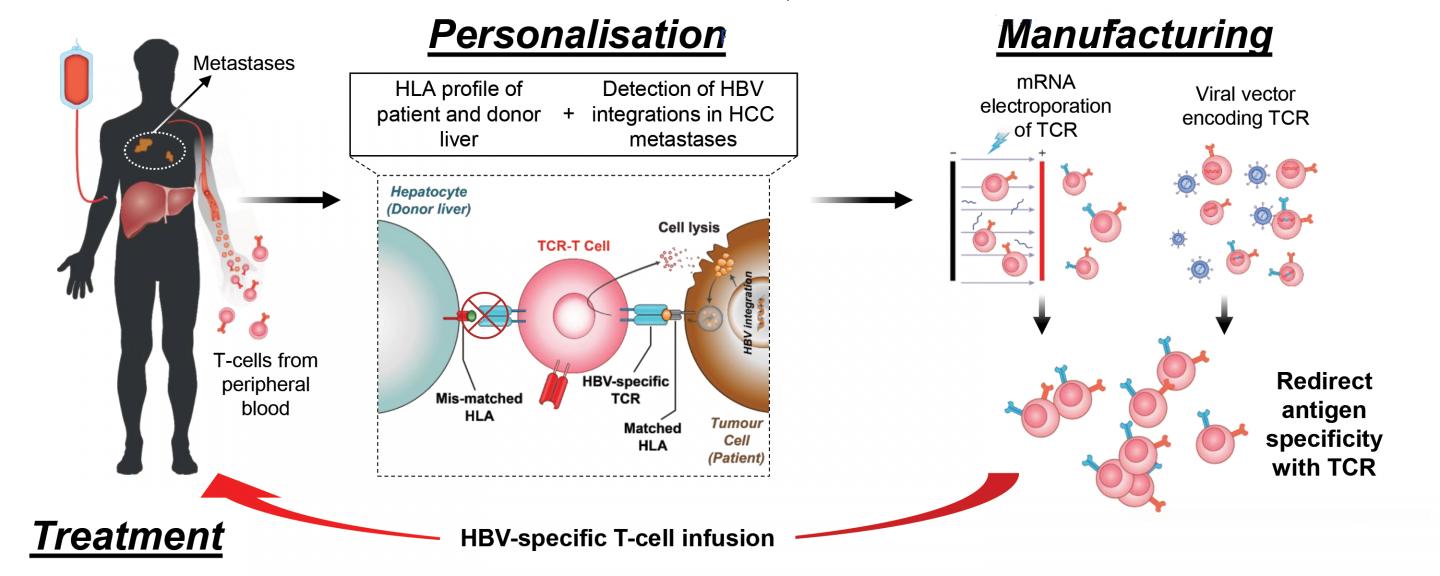
SINGAPORE, 27 March 2019 – Researchers from Duke-NUS Medical School, Singapore General Hospital (SGH) and Lion TCR have demonstrated that they were able to engineer HBV-specific T cells, a type of immune cells found in the body, to treat Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), a commonly occurring liver cancer. The treatment was also individualised, as T cells that were engineered were specific to the patients. The approach was successfully performed on two liver transplanted patients who had HBV associated liver cancer recurrence with one patient seeing a reduction in size of the tumour lesions.
Chronic hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is predominant in Asia and is highly associated with the development of Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the commonly occurring liver cancer. The currently effective treatments for small to moderate size HCC are restricted to surgery, liver transplantation and loco-regional treatment that kill cancer cells by interventional radiologic means, while treatment with drugs helps only in a modest increase in the overall survival in more extensive disease. In patients who have HCC recurrence after liver transplantation, the treatment options are even more limited.
“In this study we showed that the integrated HBV-DNA gene components in the HCC cells were able to activate functional HBV-specific T cells. Hence, by analyzing the specific HBV- DNA integration patterns in these HCC cells, we were able to select, design and engineer the individualised T cells for therapy. Our studies showed that these engineered T cells were able to destroy the tumor,” said Dr Antonio Bertoletti, Professor of the Emerging Infectious Diseases (EID) Programme at Duke-NUS, Founder of the Singapore biotech company Lion TCR and co- author of the study.
“There were over 20 T cell infusions that were successfully performed on the two liver- transplanted patients. None of the patients experienced adverse reactions related to the treatment and one of them had a reduction in the tumour size of distant metastases of the liver cancer. Given that 80 per cent of the HCC cases in Asia are currently HBV-related, this approach could lead to a major breakthrough in improving the survival and quality of life of patients suffering from this disease,” said Dr Thinesh Lee Krishnamoorthy, Consultant, Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, SGH, and co-author of this study.
The authors plan to further refine the technique and treatment strategy with further research study and trials to improve the efficacy of the therapy.
###
This translational research project won the SingHealth Duke-NUS Research Team Award last year and is the result of a collaboration between researchers and clinicians at Duke- NUS’ Emerging Infectious Diseases Programme, and SGH’s Department of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Department of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, and Department of Haematology, as well as Singapore biotechnology company, Lion TCR.
Media Contact
Lekshmy Sreekumar
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




