Credit: NASA JPL/Heidar Thrastarson
NASA’s Aqua satellite passed over the Gulf of Mexico and took the temperature of Potential Tropical Cyclone 2 as it moved westward through the Gulf of Mexico. NASA found the very cold cloud tops indicating the storm had potential for dropping heavy rain.
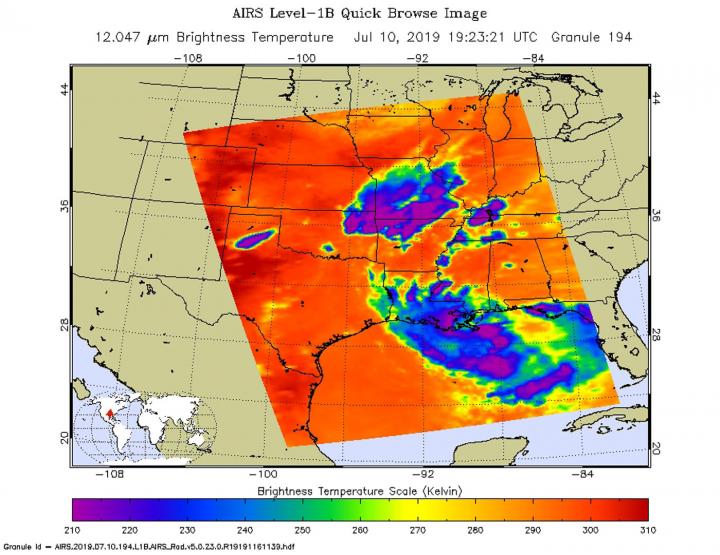
Infrared light enables NASA to take the temperatures of clouds and thunderstorms that make up tropical cyclones. The stronger the storms are indicate that they extend high into the troposphere and have cold cloud top temperatures.
An infrared look by NASA’s Aqua satellite on July 10, 2019 at 3:23 p.m. EDT (1923 UTC) revealed where the strongest storms were located within Potential Tropical Cyclone 2. The Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite analyzed cloud top temperatures and found cloud top temperatures of strongest thunderstorms as cold as or colder than minus 63 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 53 degrees Celsius) circling the center (which is still not well-defined) and in thunderstorms northwest of the center, extending over southern Louisiana. Cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms that have the capability to create heavy rain.
On July 10, the National Weather Service Office in New Orleans reported the official rainfall in New Orleans at more than 7 inches, which fell over six hours on the morning of July 10.
On July 11 at 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC) NOAA’s National Hurricane Center (NHC) continued to post warnings and watches for the Gulf coast states. A Storm Surge Watch is in effect from the mouth of the Pearl River to Intracoastal City, Louisiana. A Hurricane Watch is in effect from the mouth of the Mississippi River to Cameron, and a Tropical Storm Watch is in effect from the mouth of the Mississippi River northward to the mouth of the Pearl River.
At 8 a.m. EDT (1200 UTC), the NHC said the disturbance was centered near latitude
27.6 degrees north and longitude 88.5 degrees west. That puts the center of circulation about 115 miles (185 km) south-southeast of the mouth of the Mississippi River. Reports from a NOAA Hurricane Hunter aircraft indicate that maximum sustained winds are near 35 mph (55 km/h) with higher gusts. Strengthening is forecast during the next couple of days, and the disturbance is forecast to become a tropical depression or a tropical storm later today, and could become a hurricane by late Friday.
NHC noted that the associated thunderstorm activity is gradually becoming better organized, and the disturbance is expected to become a tropical depression or a tropical storm later today or Friday. The chance that the system will become a tropical storm through 48 hours is high at 100 percent.
The system is moving toward the west near 5 mph (7 kph), but the NHC forecasters said a west-northwest motion is expected on Friday, July 12, followed by a northwestward track by early Saturday. On the forecast track, the system is expected to approach the Louisiana coast this weekend.
###
For updated forecasts, visit: http://www.
By Rob Gutro
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/



