Credit: Credit: NASA/NRL
Tropical Cyclone Diane formed late on January 24 and by the next day it was reduced to a remnant low-pressure system in the Southern Indian Ocean. NASA’s Aqua satellite provided a look at its remnants on Jan. 27.
On Jan. 24 by 4 p.m. EST (2100 UTC), Diane formed just 38 nautical miles northwest of Port Louis, Mauritius. On Jan. 25, Diane reached maximum sustained winds near 45 knots (52 mph/83 kph) and that strength was maintained until early on Jan. 26.
At 4 p.m. EST (2100 UTC) on Jan. 26, the Joint Typhoon Warning Center issued the final warning on Diane. At that time, Diane was located near latitude 23.8 degrees south and longitude 70.1 degrees east, about 746 nautical miles east-southeast of Port Louis, Mauritius. Maximum sustained winds dropped to 40 knots (46 mph/74 kph) and were weakening because of vertical wind shear.
In general, wind shear is a measure of how the speed and direction of winds change with altitude. Tropical cyclones are like rotating cylinders of winds. Each level needs to be stacked on top each other vertically in order for the storm to maintain strength or intensify. Wind shear occurs when winds at different levels of the atmosphere push against the rotating cylinder of winds, weakening the rotation by pushing it apart at different levels. Wind shear from the northeast was pushing against Diane, sending the bulk of clouds southwest of the center.
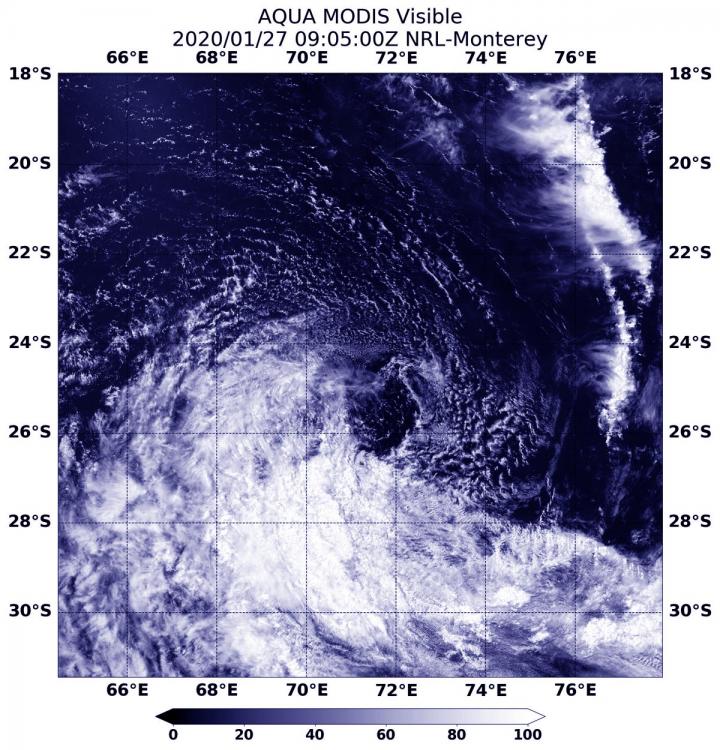
On Jan. 27 at 4 a.m. EST (0900 UTC) the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite provided a visible image of Diane that showed wind shear had taken a final toll on the storm. The MODIS image revealed that the bulk of clouds associated with the former tropical storm had been blown to the southeast of the weak center of circulation and Diane was dissipating.
NASA’s Aqua satellite is one in a fleet of NASA satellites that provide data for hurricane research.
Tropical cyclones/hurricanes are the most powerful weather events on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
###
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




