Credit: Credit: NASA/NRL
A low-pressure area strengthened quickly and became Tropical Storm Cristina in the Eastern Pacific Ocean and infrared imagery from NASA revealed the powerful thunderstorms fueling that intensification.
Cristina developed by 5 p.m. EDT on Monday, July 6, according to the National Hurricane Center in Miami, Fla. Six hours later it strengthened into a tropical storm and was renamed Cristina.
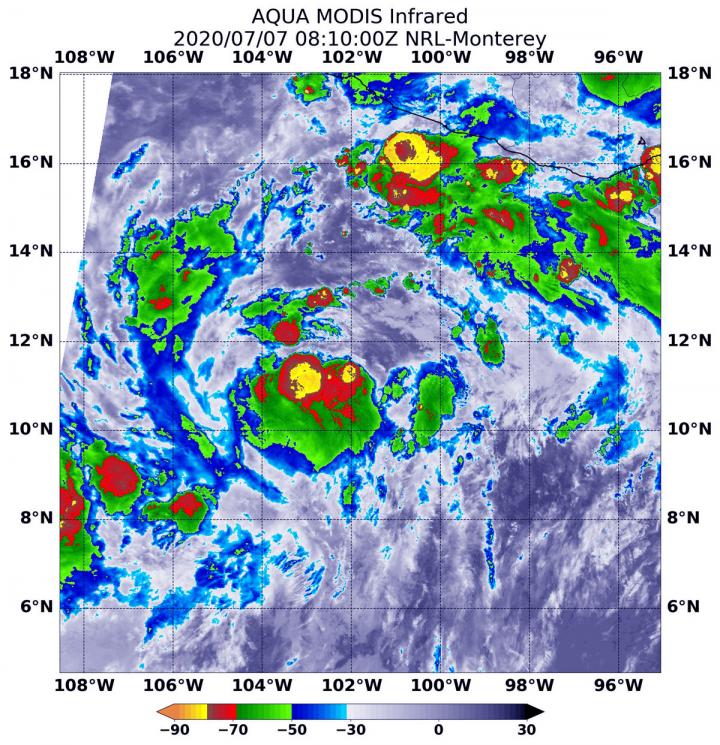
On July 7 at 4:10 a.m. EDT (0810 UTC), the Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer or MODIS instrument that flies aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite used infrared light to analyze the strength of storms within Cristina. NASA researches these storms to determine how they rapidly intensify, develop and behave.
Tropical cyclones are made of up hundreds of thunderstorms, and infrared data can show where the strongest storms are located. That is because infrared data provides temperature information, and the strongest thunderstorms that reach highest into the atmosphere have the coldest cloud top temperatures.
MODIS found those strongest storms in two areas around Cristina’s center of circulation where cloud top temperatures were as cold as minus 80 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 62.2 Celsius). NASA research has found that cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms with the potential to generate heavy rainfall.
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC) on July 7, the National Hurricane Center (NHC) said the center of Tropical Storm Cristina was located near latitude 12.2 degrees north and longitude 102.8 degrees west. Cristina is centered about 480 miles (770 km) south-southeast of Manzanillo, Mexico. The estimated minimum central pressure is 1005 millibars. Maximum sustained winds are near 40 mph (65 kph) with higher gusts.
Cristina was moving toward the west-northwest near 13 mph (20 kph), and the NHC expects that general motion to continue for the next few days, keeping the cyclone well away from the coast of Mexico.
NHC forecaster David Zelinsky noted in the July 7 Discussion, “The [vertical wind] shear and some nearby dry air that appear to have inhibited Cristina’s organization so far are not expected to persist as negative factors for much longer. All of the models still forecast strengthening, and given the very favorable environment that the cyclone will encounter in a day or two, a period of rapid intensification at some point would not be surprising.”
Strengthening is anticipated and Cristina is forecast to become a hurricane in a day or two.
Typhoons/hurricanes are the most powerful weather events on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
For updated forecasts, visit: http://www.
By Rob Gutro
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
###
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




