Credit: Credit: NASA JPL/Heidar Thrastarson
The Northern Indian Ocean has generated a new tropical cyclone. NASA provided an infrared look a recently formed Tropical Storm Hikaa, moving through the Arabian Sea.
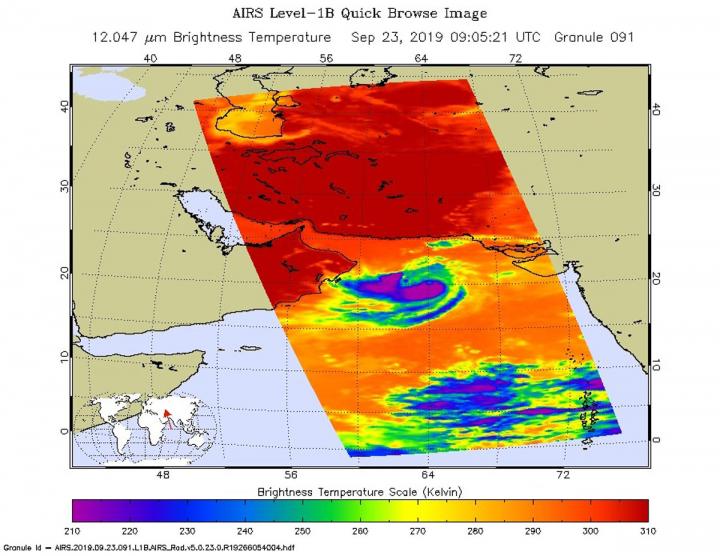
One of the ways NASA researches tropical cyclones is by using infrared data that provides temperature information. The AIRS instrument aboard NASA’s Aqua satellite captured a look at those temperatures in Hikaa and gave insight into the storm’s rainfall potential. Cloud top temperatures provide information to forecasters about where the strongest storms are located within a tropical cyclone. Tropical cyclones do not always have uniform strength, and some sides have stronger sides than others. The stronger the storms, the higher they extend into the troposphere, and the colder the cloud temperatures are.
NASA provides data to forecasters around the world so they can incorporate that data into their forecasting.
On Sept. 23 at 4:05 a.m. EDT (0905 UTC) NASA’s Aqua satellite analyzed the storm using the Atmospheric Infrared Sounder or AIRS instrument. AIRS found coldest cloud top temperatures as cold as or colder than minus 63 degrees Fahrenheit (minus 53 degrees Celsius) from west to south around Hikaa’s center. NASA research has shown that cloud top temperatures that cold indicate strong storms that have the capability to create heavy rain.
At 11 a.m. EDT (1500 UTC), The Joint Typhoon Warning Center said the center of Tropical Hikaa was located near latitude 20.2 degrees north and longitude 65.5 degrees east. It is located about 265 miles east of Masirah Island, Oman. The tropical storm was moving toward the west. Maximum sustained winds are near 60 knots (69 mph/111 kph) with higher gusts.
Hikaa will strengthen slightly before making landfall in Oman after a day or so.
The AIRS instrument is one of six instruments flying onboard NASA’s Aqua satellite, launched on May 4, 2002.
Hurricanes are the most powerful weather event on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
###
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




