Credit: Credit: NASA Worldview, Earth Observing System Data and Information System (EOSDIS)
As Tropical Storm Lorena was nearing landfall in northwestern Mexico, NASA-NOAA’s Suomi NPP satellite provided forecasters with an image of the storm. By Monday, Sept. 23, Lorena’s remnants were affecting the southern U.S. and bringing heavy rainfall to Arizona.
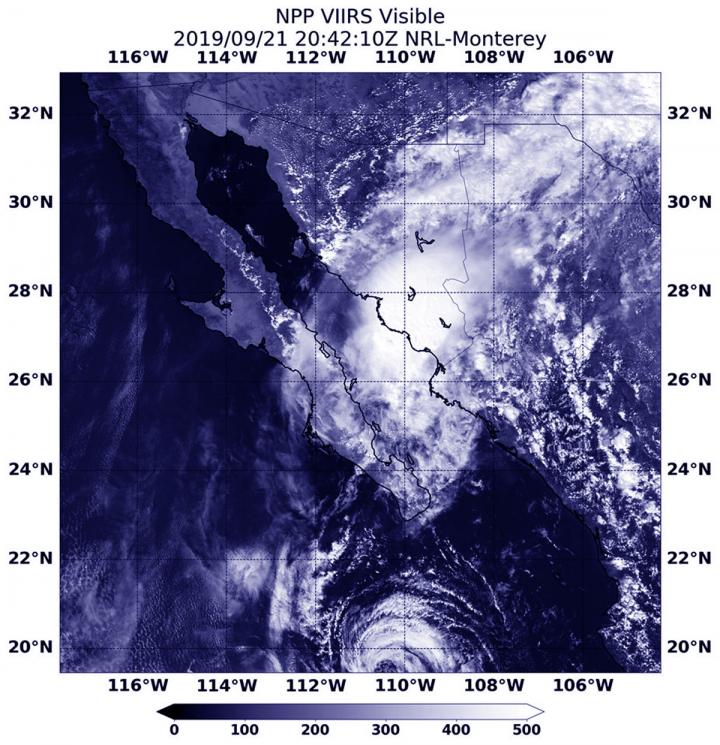
Visible imagery from NASA satellites help forecasters understand if a storm is organizing or weakening. The Visible Infrared Imaging Radiometer Suite (VIIRS) instrument aboard Suomi NPP provided a visible image of Lorena on Sept. 21 at 4:42 p.m. EDT (2042 UTC).
The shape of a tropical cyclone provides forecasters with an idea of its organization and strength, and NASA-NOAA’s Suomi NPP satellite provided a visible image of the storm to forecasters as its center was approaching landfall. The storm already appeared elongated from south to north after its northeastern side had begun moving over the high terrain of northwestern Mexico. Lorena made a slow track to the coast and made landfall about 12 hours later.
Lorena’s Final Advisory
At 11 am EDT on Sunday, Sept. 22, NOAA’s National Hurricane Center issued the final advisory on the system. By that time, Post-Tropical Cyclone Lorena crossed the coast of northwestern Mexico in the morning. The center of the disturbance was estimated near latitude 28.8 degrees north and longitude 111.5 degrees west. The post-tropical cyclone was moving toward the north near 9 mph (15 kph). Maximum sustained winds associated with this system are near 30 mph (45 kph) with higher gusts.
After landfall, Lorena’s remnant clouds and rain moved north into Arizona.
Lorena’s Remnants in Arizona on Sept. 23
NOAA’s Weather Prediction Center College Park, Md. reported, “Moisture from the remnants of Lorena will contribute to heavy rain, strong to severe thunderstorms and possible flooding across the Southwest through Tuesday. There should be enough moisture in place to support a significant rainfall event with widespread 1 to 2 inch rainfall totals with much higher amounts locally, with the greatest amounts in central and southern Arizona. This degree of rainfall warrants flash flood concerns, and a Moderate Risk of excessive rainfall is in effect for that region. Some strong to severe thunderstorms will also be possible.”
Hurricanes are the most powerful weather event on Earth. NASA’s expertise in space and scientific exploration contributes to essential services provided to the American people by other federal agencies, such as hurricane weather forecasting.
For updated forecasts. visit: http://www.
###
Media Contact
Rob Gutro
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




