Credit: Hyung Joon Cha (POSTECH)
Antibody-based immunotherapy is one of treatment options for cancer immunotherapy by modulating our immune system with therapeutic antibodies. Among many strategies for cancer therapy, it has been considered as an advanced cancer treatment due to its favorable clinical benefits by effectively activating our immune cells to attack cancer cells in the body. The development of new cancer immunotherapy drugs has gained great attention as the next-generation research area with more than 1,600 clinical trials currently underway worldwide.
However, conventional cancer treatments that require intravenous administration throughout the whole body can cause side effects on normal cells or tissues by continuously supplying large amounts of antibodies. In particular, if large amounts of antibodies are released at once, there is a risk of excessive immune response that can lead to autoimmune diseases. The common localized treatment, such as local injection to tumor, still had a problem of rapidly spreading antibodies out of the target area by blood flow, leaving only a few, resulting in a significant reduction in treatment efficacy.
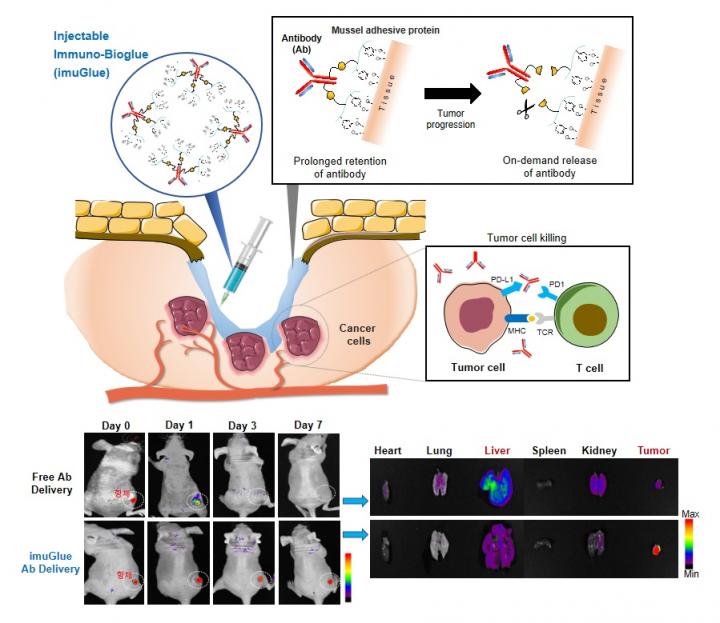
The POSTECH research team led by professors Hyung Joon Cha, Kye Il Joo, and Dr. Yeonsu Jung of the Department of Chemical Engineering along with Professor Sin-Hyeog Im and Dr. Sung-Min Hwang of the Department of Life Sciences have together developed a novel immunotherapy platform called imuGlue. This new platform can effectively connect mussel adhesive proteins (MPAs) – which has strong adhesion in even underwater conditions – to the antibodies used as immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) in order to deliver the antibodies to the target areas.
ImuGlue can significantly enhance the efficiency of cancer immunotherapy and reduce the side effects by allowing therapeutic antibodies to stay in the target area for long periods of time even in moisture-rich environment and release antibodies on-demand at cancer sites. It was also demonstrated that imuGlue could be utilized for combination therapy with other immunomodulatory drugs often used in cancer immunotherapy.
This new treatment platform for localized cancer immunotherapy has the advantage of not only being able to easily connect various therapeutic antibodies, but also does not mix or lose its property in body fluid- or blood-rich environments and at mucous surfaces. For this reason, it is anticipated to lead in the cancer immunotherapy market as it can be used not just through injections but also by spraying or other unique treatment methods.
“This study is the first immunotherapy that uses the mussel adhesion protein,” commented Professor Hyung Joon Cha who led the study. He added, “As an innovative antibody delivery platform, it should be useful in various forms of immunotherapy.”
###
The study was published in Biomaterials, an authoritative journal in biomaterial field, and was conducted with the support from the National Research Foundation of Korea funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT, Korea, the Basic Science Research Program funded by the Ministry of Education, Korea, and the Marine Biotechnology Program funded by the Ministry of Oceans and Fisheries, Korea.
Media Contact
Jinyoung Huh
[email protected]
Original Source
http://postech.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




