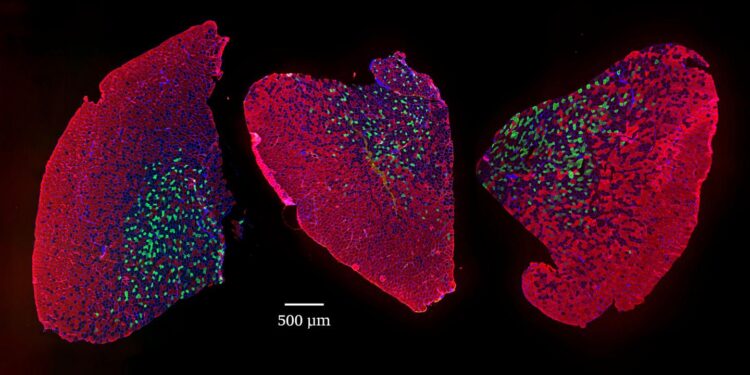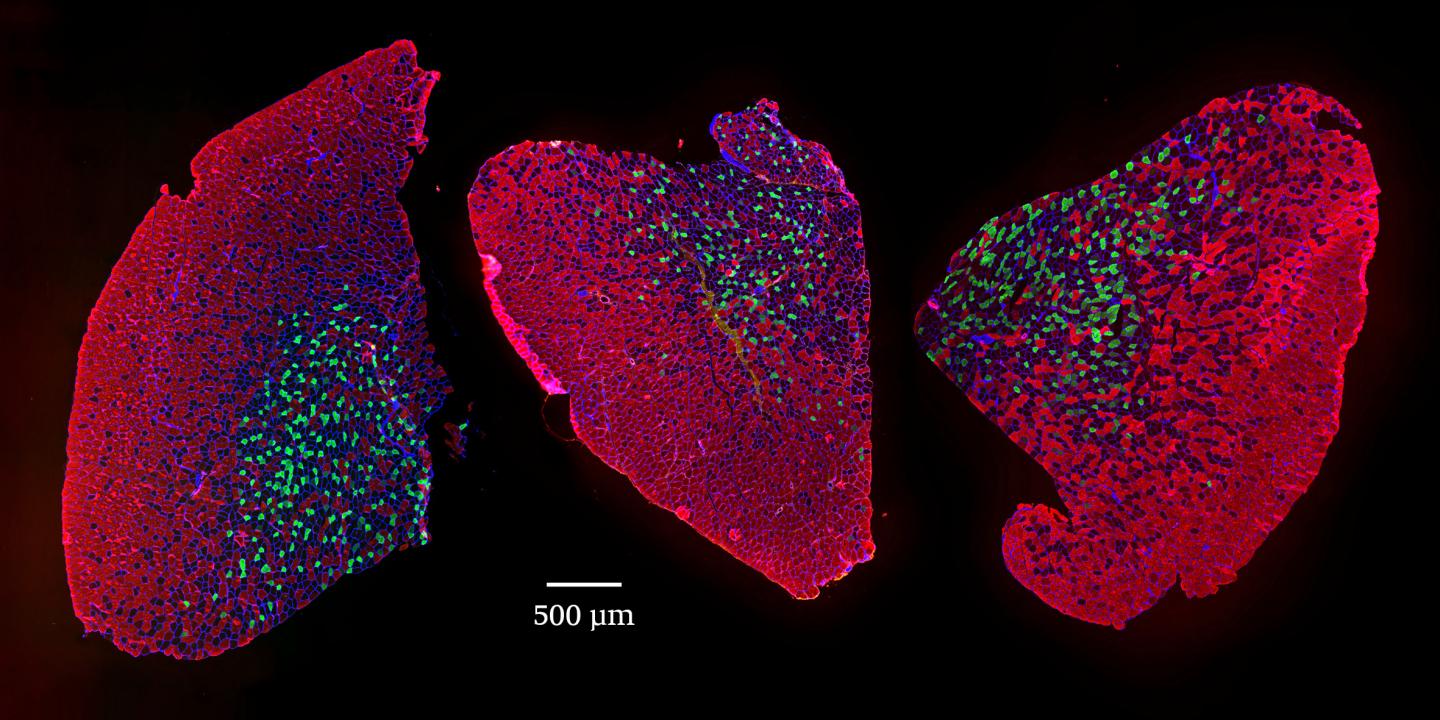
Credit: Image: University of Basel, Biozentrum
With life expectancy increasing, age-related diseases are also on the rise, including sarcopenia, the loss of muscle mass due to aging. Researchers from the University of Basel’s Biozentrum have demonstrated that a well-known drug can delay the progression of age-related muscle weakness.
Already in our best years, our muscles begin to shrink and their strength dwindles. Unfortunately, this is a natural part of aging. For some people, the decline in muscle mass and function is excessive. This condition, called sarcopenia, affects every second or third person over 80, reducing mobility, autonomy and quality of life.
The causes of sarcopenia are diverse, ranging from altered muscle metabolism to changes in the nerves supplying muscles. Researchers led by Professor Markus Rüegg have now discovered that mTORC1 also contributes to sarcopenia and its suppression with the well-known drug rapamycin slows age-related muscle wasting.
Rapamycin preserves muscle function
“Contrary to our expectations, the long-term mTORC1 suppression with rapamycin is overwhelmingly beneficial for skeletal muscle aging in mice, preserving muscle size and strength,” says Daniel Ham, first author of the study. “Neuromuscular junctions, the sites where neurons contact muscle fibers to control their contraction, deteriorate during aging. Stable neuromuscular junctions are paramount to maintaining healthy muscles during aging and rapamycin effectively stabilizes them.” The researchers also demonstrate that permanently activating mTORC1 in skeletal muscle accelerates muscle aging.
Molecular signature of sarcopenia
In collaboration with Professor Mihaela Zavolan’s team, the scientists identified a molecular ?signature? of sarcopenia, with mTORC1 as the key player. To help the scientific community further investigate how gene expression in skeletal muscle changes during aging or in response to rapamycin treatment, they developed the user-friendly web application, SarcoAtlas, which is supported by sciCORE, the Center for Scientific Computing at the University of Basel.
There is currently no effective pharmacological therapy to treat sarcopenia. This study provides hope that it may be possible to slow down age-related muscle wasting with treatments that suppress mTORC1 and thereby extend the autonomy and life quality of elderly people.
###
Media Contact
Reto Caluori
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.