KAIST team presents a novel pathways involving T immune cell exhaustion, providing evidence and rationale for designing optimal strategies for immune checkpoint blockades in cancer patients
Credit: KAIST
KAIST medical scientists have presented a novel pathways involving T immune cell exhaustion, providing evidence and rationale for designing optimal strategies for immune checkpoint blockades in cancer patients.
They succeeded in distinguishing the hepatocellular carcinoma group from the exhausted tumor infiltrating immune cell composition of liver cancer patients. The noble immune therapeutics study, conducted in collaboration with Asan Medical Center, confirmed the applicability for liver cancer patients, providing a new path for customized medicine as well as a new model for translational research.
When cancer occurs, the body activates an immune cell called a ‘T cell’ to remove cancer cells. The tumor constitutes an environment for inhibiting T-cell function. At this time, the infiltrating T cells are delivered to the cell surface as ‘PD-1’ protein, with its activity is decreasing and then exhausted.
Our immune system is able to destroy cancer cells in our body, however sometimes cancer cells can adapt and mutate, effectively hiding from our immune system. One of the mechanisms that has evolved to prevent destruction by the immune system is to functionally silence effector T cells, termed T-cell exhaustion that is mainly mediated by immune checkpoint molecules such as PD-1, TIM-3, and LAG-3.
Recent breakthroughs and encouraging clinical results with various immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) and anti-CTLA-4 mAbs, have demonstrated tremendous potential to control cancer by immune activation. Immune checkpoint inhibitors showed significant clinical benefit in several types of cancers, leading to their wide application in clinical practice.
Anti-PD1 blocking antibodies are one of the most representative agents in this class of drug. However, it has been challenging to precisely understand the biological and clinical significance of T-cell exhaustion in cancer. A KAIST research team led by Professor Su-Hyung Park reported the heterogeneity of T-cell exhaustion in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) and its potential clinical implication in Gastroenterology on December 4. The study was made available online in August 2018 ahead of final publication inprint this month.
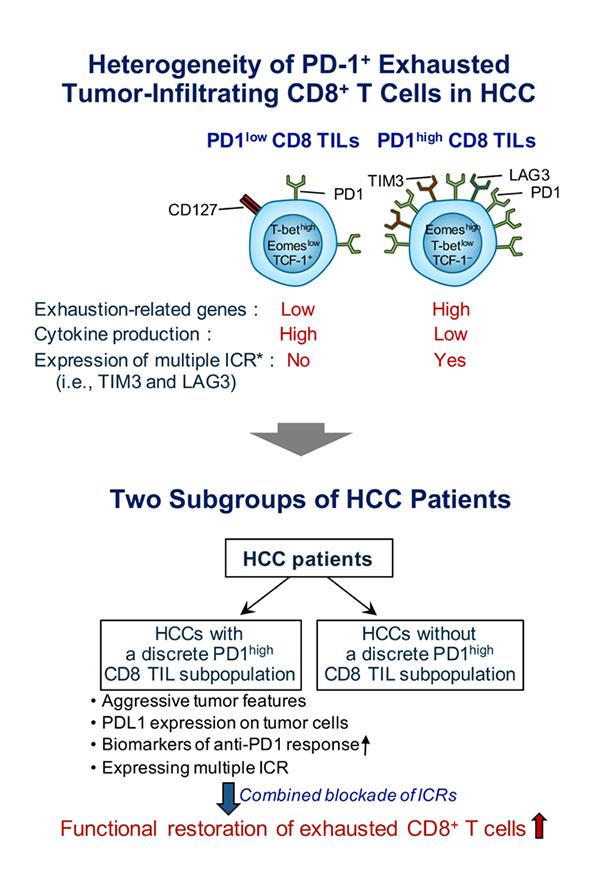
The team revealed heterogeneous T-cell exhaustion status determined by differential PD-1 expression levels in CD8+ T cells in HCC. The authors found that tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells with high PD-1 expression (PD-1high CD8+ TILs) from HCC patients are functionally impaired and deliver other immune checkpoint receptors such as TIM-3 and/or LAG3, compared to those with low PD-1 expression (PD-1low CD8+ TILs).
Moreover, based on these results, the authors defined two distinct subgroups of HCC patients according to the presence or absence of PD-1high CD8+ TILs. They found that HCC patients with PD-1high CD8+ TILs were associated with more aggressive biological tumor features and biomarkers predicting their response to anti-PD1 therapy. Also, the research team demonstrated that only HCC patients having PD-1high CD8+ TILs had tumor-infiltrating CD8+ T cells expressing multiple immune checkpoint receptors that could be further reinvigorated by combined immune checkpoint blockades.
Prof. Park said, “The new classification of HCC patients identified by this study can be utilized as a biomarker to predict the response of current cancer immunotherapy (anti-PD-1 therapy).” He also said they will continue to conduct research on T-cell exhaustion and activation in various types of cancer which could lead to better understanding of T-cell response against cancer, thereby providing evidence for future cancer immunotherapy to achieve the ultimate goal to prolong survival of cancer patients.
###
Media Contact
Younghye Cho
[email protected]
82-423-502-294
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




