Credit: DICP and SIBCB
Scientists from Dalian Institute of Chemical Physics (DICP) and Shanghai Institute of Biochemistry and Cell Biology (SIBCB) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences revealed that UDP-glucose accelerates SNAI1 mRNA decay and impairs lung cancer metastasis. Their findings were published in Nature.
Metastasis is the primary cause of cancer morbidity and mortality, and accounts for up to 95% of cancer-related deaths. UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase (UGDH) is a key enzyme in the uronic acid pathway that converts UDP-glucose to UDP-glucuronic acid; Hu antigen R (HuR) is a ubiquitously expressed RNA-binding protein that binds to the 3′-untranslated region (UTR) region of many short-lived mRNAs and increases their stability.
Dr. YANG Weiwei’s group from SIBCB has performed the experimental research. The results show that, upon EGFR activation, phosphorylated UGDH interacts with HuR and converts UDP-glucose to UDP-glucuronic acid. The resulting UDP-glucoronic acid attenuated the UDP-glucose-mediated inhibition of the association of HuR with SNAI1 mRNA, thus enhancing SNAI1 mRNA stability.
Increased SNAIL expression initiates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition, thereby promoting tumor cell migration and lung cancer metastasis. These findings reveal a tumor-suppressive role for UDP-glucose in lung cancer metastasis and uncover the mechanism by which UGDH promotes tumor metastasis by increasing SNAI1 mRNA stability.
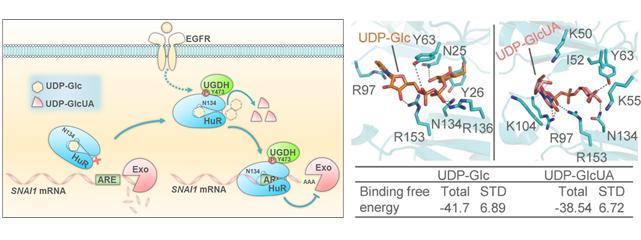
Dr. Li Guohui’s group from DICP has performed molecular dynamics (MD) simulations to elucidate the structural basis underlying the UDP-Glc- or UDP-GlcUA-regulated binding of HuR to mRNA. The MD results showed that both UDP-Glc and UDP-GlcUA bound to the same RNA-binding domain of HuR.
The binding affinity of UDP-Glc with HuR is stronger than UDP-GlcUA with HuR, which is consistent with experimental results. Essentially, two mutants of HuR(Y63F) and HuR(N134A) were generated and studied. It was found that HuR(N134A) had a much lower affinity for both metabolites than HuR(WT) and HuR(Y63F), but still bound to SNAI1 mRNA, and tumor cells rescued with rHuR(N134A) showed more migration.
###
This research was supported by the State Key Laboratory of Molecular Reaction Dynamics, the Strategic Priority Research Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Media Contact
WANG Yongjin
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




