Credit: Frank Ortmann
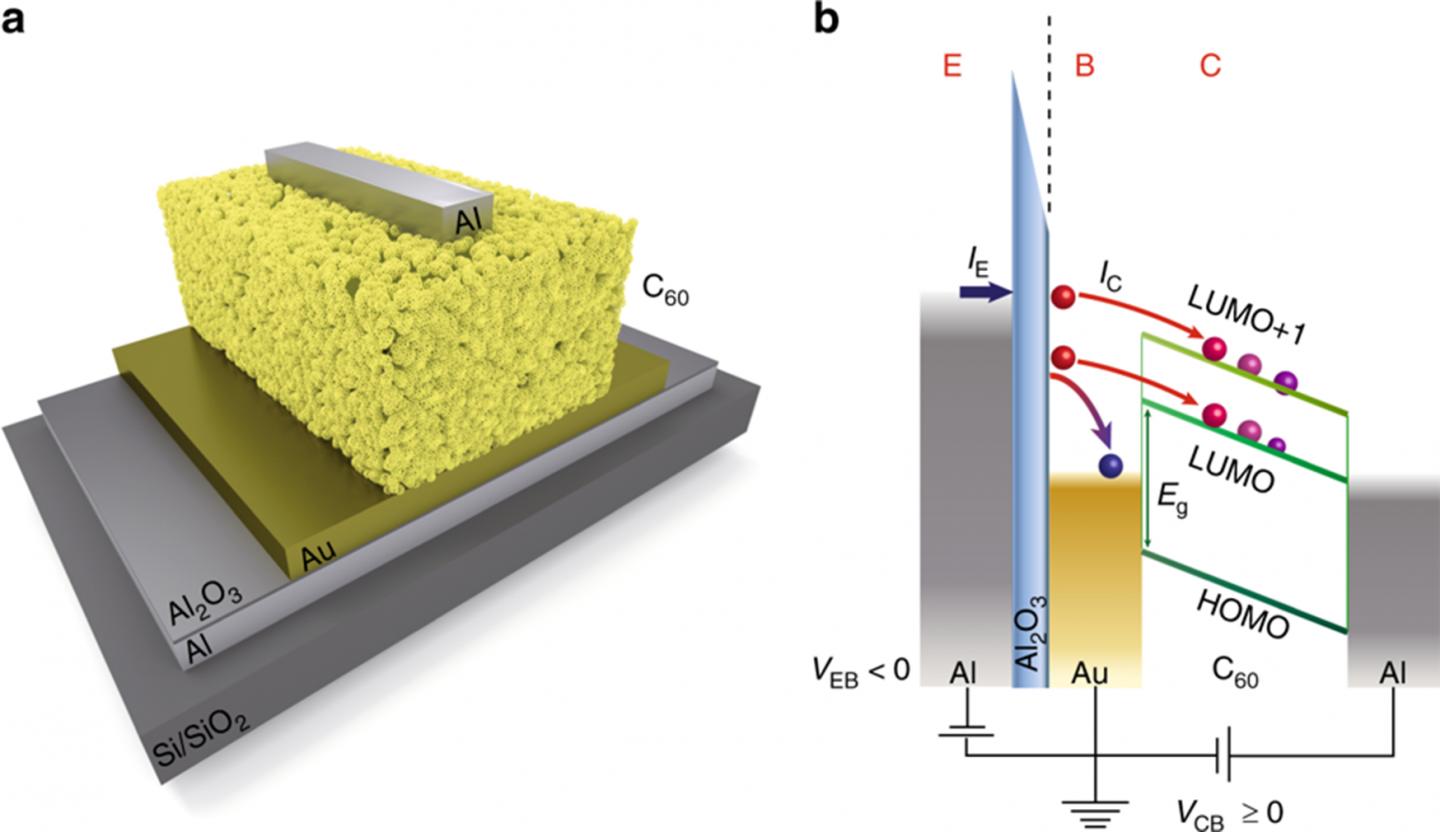
Charge transfer processes play a fundamental role in all electronic and optoelectronic devices. For devices based on organic thin-film technology, these include the injection of the charge carriers via the metallic contacts and the charge transport in the organic film itself. Injection processes at the contacts are of particular interest here because the contact resistances at the interfaces must be minimized for optimum device efficiency. However, such internal interfaces are difficult to access and therefore not yet understood very well.
The team of cfaed research group leader Frank Ortmann (Computational Nanoelectronics Group), together with researchers from Spain, Belgium and Germany, has now shown in a study that the electronic transport mechanism when injected into an organic film can be described by the so-called Marcus hopping model known from physical chemistry. The model was developed by the American chemist Rudolph Arthur Marcus. Comparative theoretical and experimental investigations unequivocally identified the transport regimes predicted in the Marcus theory. “The predictions derived by R.A. Marcus in the context of chemical synthesis in the 1950s, in particular the so-called ‘inverted Marcus regime’, could only be confirmed many decades later by systematic experiments on chemical reactions. For his important theoretical contributions, R.A. Marcus received the Nobel Prize for Chemistry in 1992 “, says Ortmann.
“Now, the observation of the ‘Inverted Marcus Region’, in which a higher voltage generates a lower current, succeeded for the first time in an organic transistor, in which the injection voltage can be actively controlled”, Ortmann continues. This leads to a better understanding of electronic and optoelectronic organic devices in general. The publication has been published on 7th May, 2019 in the journal “Nature Communications“.
###
About the Computational Nanoelectronics Group
The research group at the Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden (cfaed) headed by Dr. Frank Ortmann investigates electronic properties and charge transport properties of novel semiconductor materials. Here, organic semiconductors are currently an important focus of the work, which is funded by the German Research Foundation under the Emmy Noether Program. The group has been based at the cfaed since 2017. Info: https:/
Media inquiries:
Matthias Hahndorf
Center for Advancing Electronics Dresden, TU Dresden
Head of Communications
Tel.: +49 351 463-42847
Email: [email protected]
Media Contact
Dr. Frank Ortmann
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




