McMaster and Harvard researchers create ‘intelligent’ interaction between light and material, establishing a promising new platform for computing
Credit: McMaster University
HAMILTON, Feb. 3, 2020 – A collaboration between McMaster and Harvard researchers has generated a new platform in which light beams communicate with one another through solid matter, establishing the foundation to explore a new form of computing.
Their work is described in a paper published today in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
Kalaichelvi Saravanamuttu, an associate professor of Chemistry and Chemical Biology at McMaster, explains that the technology brings together a form of hyrdrogel developed by the Harvard team with light manipulation and measurement techniques performed in her lab, which specializes in the chemistry of materials that respond to light.
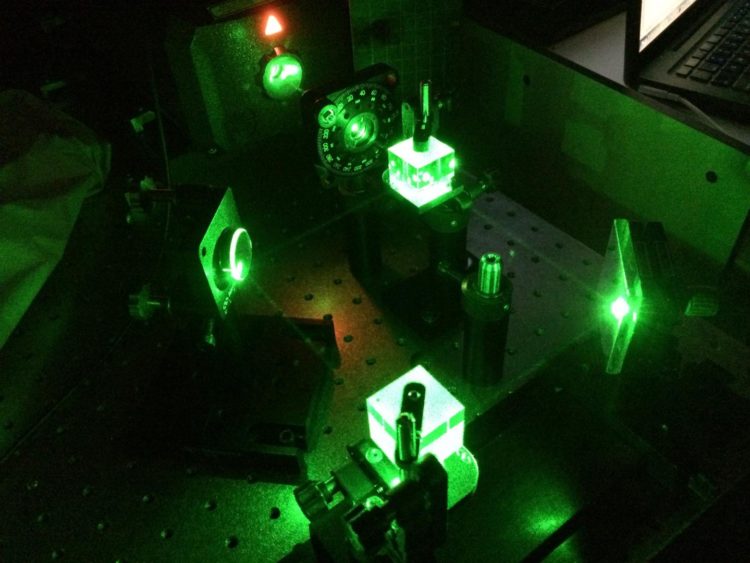
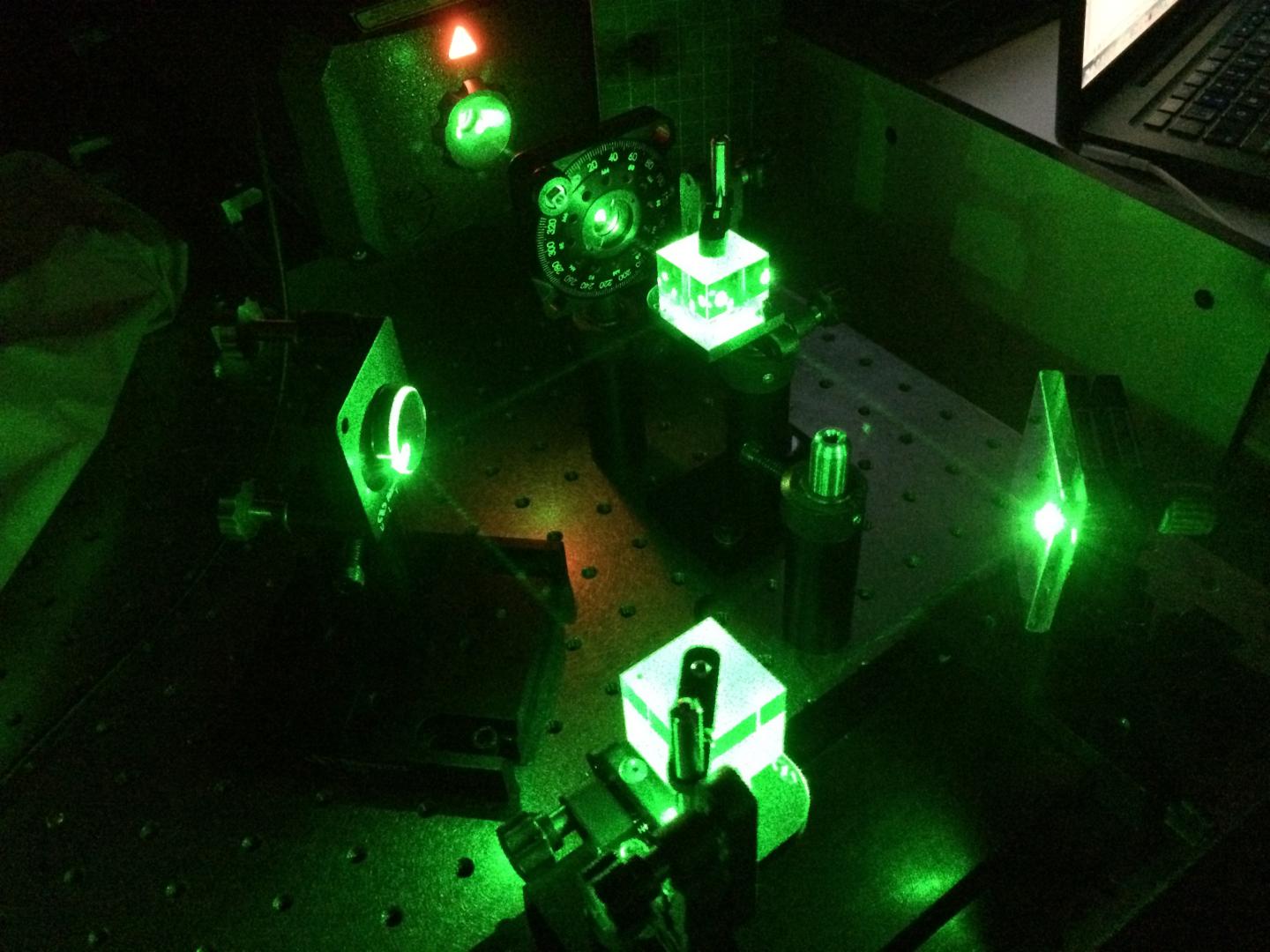
The translucent material, which resembles raspberry Jell-O in appearance, incorporates light-responsive molecules whose structure changes in the presence of light, giving the gel special properties both to contain light beams and to transmit information between them.
Typically, beams of light broaden as they travel, but the gel is able to contain filaments of laser light along their pathway through the material, as though the light were being channeled through a pipe.
When multiple laser beams, each about half the diameter of a human hair, are shone through the same material, the researchers have established that they affect one another’s intensity, even without their optical fields overlapping at all – a fact that proves the gel is “intelligent.”
The interaction between those filaments of light can be stopped, started, managed and read, producing a predictable, high-speed output: a form of information that could be developed into a circuit-free form of computing, Saravanamuttu explains.
“Though they are separated, the beams still see each other and change as a result,” she says. “We can imagine, in the long term, designing computing operations using this intelligent responsiveness.”
While the broader concept of computing with light is a separate and developing field unto itself, this new technology introduces a promising platform, says Derek Morim, a graduate student in Saravanamuttu’s lab who is co-first author on the paper.
“Not only can we design photoresponsive materials that reversibly switch their optical, chemical and physical properties in the presence of light, but we can use those changes to create channels of light, or self-trapped beams, that can guide and manipulate light,” he says. “Further study may allow us to design even more complex materials to manipulate both light and material in specific ways.”
Amos Meeks, a graduate student at Harvard’s John A. Paulson School of Engineering and Applied Sciences, said the technology helps to advance the idea of all-optical computing, or computations done solely with beams of light.
“Most computation right now uses hard materials such as metal wires, semiconductors and photodiodes, to couple electronics to light,” said Meeks, who is also co-first author of the research. “The idea behind all optical computing is to remove those rigid components and control light with light. Imagine, for example, an entirely soft, circuitry-free robot driven by light from the sun.”
###
Media Contact
Wade Hemsworth
[email protected]
289-925-8382