Automated approach transformative for computational materials science
Credit: Los Alamos National Laboratory
LOS ALAMOS, N.M., February 23, 2021–A revolutionary machine-learning (ML) approach to simulate the motions of atoms in materials such as aluminum is described in this week’s Nature Communications journal. This automated approach to “interatomic potential development” could transform the field of computational materials discovery.
“This approach promises to be an important building block for the study of materials damage and aging from first principles,” said project lead Justin Smith of Los Alamos National Laboratory. “Simulating the dynamics of interacting atoms is a cornerstone of understanding and developing new materials. Machine learning methods are providing computational scientists new tools to accurately and efficiently conduct these atomistic simulations. Machine learning models like this are designed to emulate the results of highly accurate quantum simulations, at a small fraction of the computational cost.”
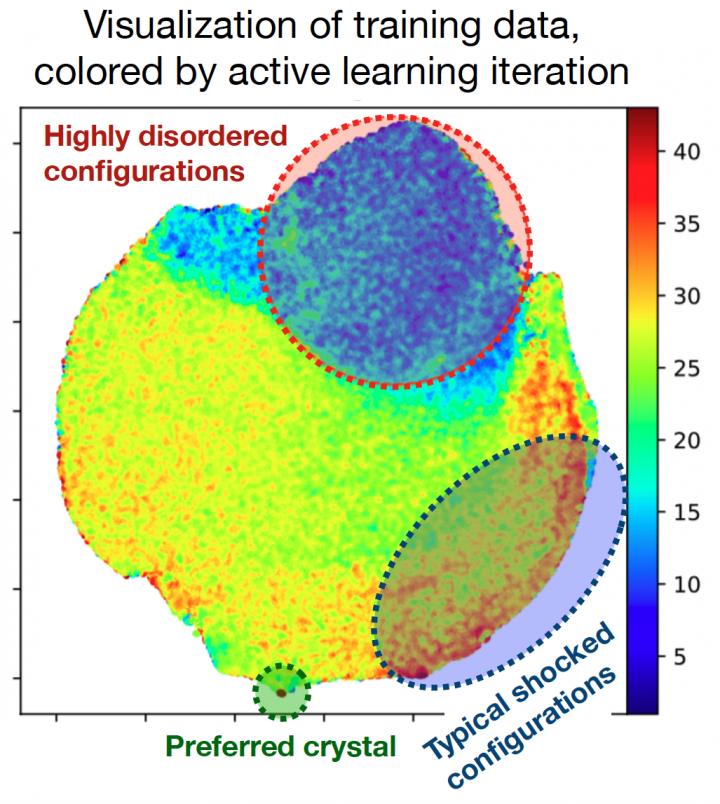
To maximize the general accuracy of these machine learning models, he said, it is essential to design a highly diverse dataset from which to train the model. A challenge is that it is not obvious, a priori, what training data will be most needed by the ML model. The team’s recent work presents an automated “active learning” methodology for iteratively building a training dataset.
At each iteration, the method uses the current-best machine learning model to perform atomistic simulations; when new physical situations are encountered that are beyond the ML model’s knowledge, new reference data is collected via expensive quantum simulations, and the ML model is retrained. Through this process, the active learning procedure collects data regarding many different types of atomic configurations, including a variety of crystal structures, and a variety of defect patterns appearing within crystals.
###
The paper: Automated discovery of a robust interatomic potential for aluminum, Nature Communications, DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-21376-0
The funding: This work was funded in part by the Los Alamos National Laboratory Advanced Simulation and Computing (ASC) program and computer time was provided by the Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory Sierra Supercomputer during its open access period.
About Los Alamos National Laboratory
Los Alamos National Laboratory, a multidisciplinary research institution engaged in strategic science on behalf of national security, is managed by Triad, a public service oriented, national security science organization equally owned by its three founding members: Battelle Memorial Institute (Battelle), the Texas A&M University System (TAMUS), and the Regents of the University of California (UC) for the Department of Energy’s National Nuclear Security Administration.
Los Alamos enhances national security by ensuring the safety and reliability of the U.S. nuclear stockpile, developing technologies to reduce threats from weapons of mass destruction, and solving problems related to energy, environment, infrastructure, health, and global security concerns.
LA-UR-21-21717
Media Contact
Nancy Ambrosiano
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




