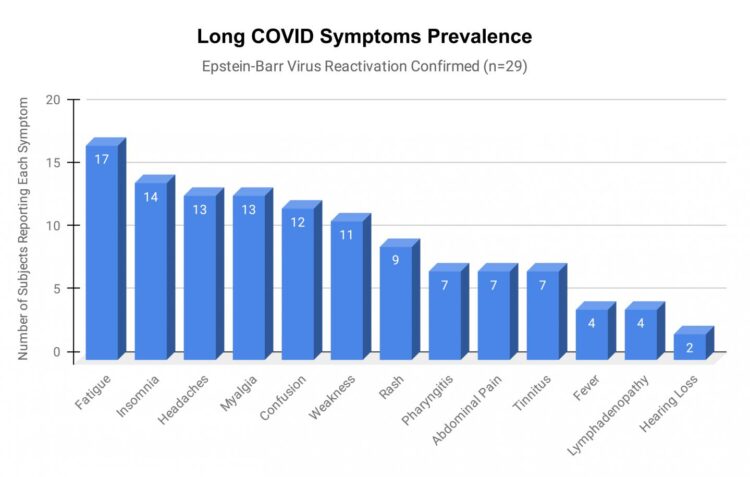
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) reactivation resulting from the inflammatory response to coronavirus infection may be the cause of previously unexplained long COVID symptoms — such as fatigue, brain fog, and rashes — that occur in approximately 30% of patients after recovery from initial COVID-19 infection. The first evidence linking EBV reactivation to long COVID, as well as an analysis of long COVID prevalence, is outlined in a new long COVID study published in the journal Pathogens.
“We ran EBV antibody tests on recovered COVID-19 patients, comparing EBV reactivation rates of those with long COVID symptoms to those without long COVID symptoms,” said lead study author Jeffrey E. Gold of World Organization. “The majority of those with long COVID symptoms were positive for EBV reactivation, yet only 10% of controls indicated reactivation.”
The researchers began by surveying 185 randomly selected patients recovered from COVID-19 and found that 30.3% had long term symptoms consistent with long COVID after initial recovery from SARS-CoV-2 infection. This included several patients with initially asymptomatic COVID-19 cases who later went on to develop long COVID symptoms.
The researchers then found, in a subset of 68 COVID-19 patients randomly selected from those surveyed, that 66.7% of long COVID subjects versus 10% of controls were positive for EBV reactivation based on positive EBV early antigen-diffuse (EA-D) IgG or EBV viral capsid antigen (VCA) IgM titers. The difference was significant (p
“We found similar rates of EBV reactivation in those who had long COVID symptoms for months, as in those with long COVID symptoms that began just weeks after testing positive for COVID-19,” said coauthor David J. Hurley, PhD, a professor and molecular microbiologist at the University of Georgia. “This indicated to us that EBV reactivation likely occurs simultaneously or soon after COVID-19 infection.”
The relationship between SARS-CoV-2 and EBV reactivation described in this study opens up new possibilities for long COVID diagnosis and treatment. The researchers indicated that it may be prudent to test patients newly positive for COVID-19 for evidence of EBV reactivation indicated by positive EBV EA-D IgG, EBV VCA IgM, or serum EBV DNA tests. If patients show signs of EBV reactivation, they can be treated early to reduce the intensity and duration of EBV replication, which may help inhibit the development of long COVID.
“As evidence mounts supporting a role for EBV reactivation in the clinical manifestation of acute COVID-19, this study further implicates EBV in the development of long COVID,” said Lawrence S. Young, PhD, a virologist at the University of Warwick, and Editor-in-Chief of Pathogens. “If a direct role for EBV reactivation in long COVID is supported by further studies, this would provide opportunities to improve the rational diagnosis of this condition and to consider the therapeutic value of anti-herpesvirus agents such as ganciclovir.”
###
For more information about this and other COVID-19 studies conducted by World Organization, go to https:/
Original publication: Gold, J.E.; Okyay, R.A.; Licht, W.E.; Hurley, D.J. Investigation of Long COVID Prevalence and Its Relationship to Epstein-Barr Virus Reactivation. Pathogens 2021, 10, 763. https:/
Media Contacts:
Jeffrey E. Gold
World Organization
[email protected]
202-642-4445
David J. Hurley, PhD
Professor and Molecular Microbiologist
University of Georgia
[email protected]
Lawrence S. Young, PhD
Virologist and Professor of Molecular Oncology
Warwick Medical School, University of Warwick
Editor-in-Chief, Pathogens
[email protected]
Media Contact
Jeffrey E. Gold
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.