Micro-CT scanning of ‘Little Foot’ skull reveals new aspects of the life of this more than 3-million year-old-human ancestor
Credit: Amélie Beaudet/Wits University
High-resolution micro-CT scanning of the skull of the fossil specimen known as “Little Foot” has revealed some aspects of how this Australopithecus species used to live more than 3 million years ago.
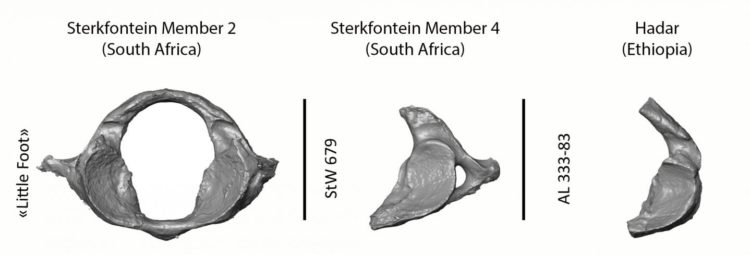
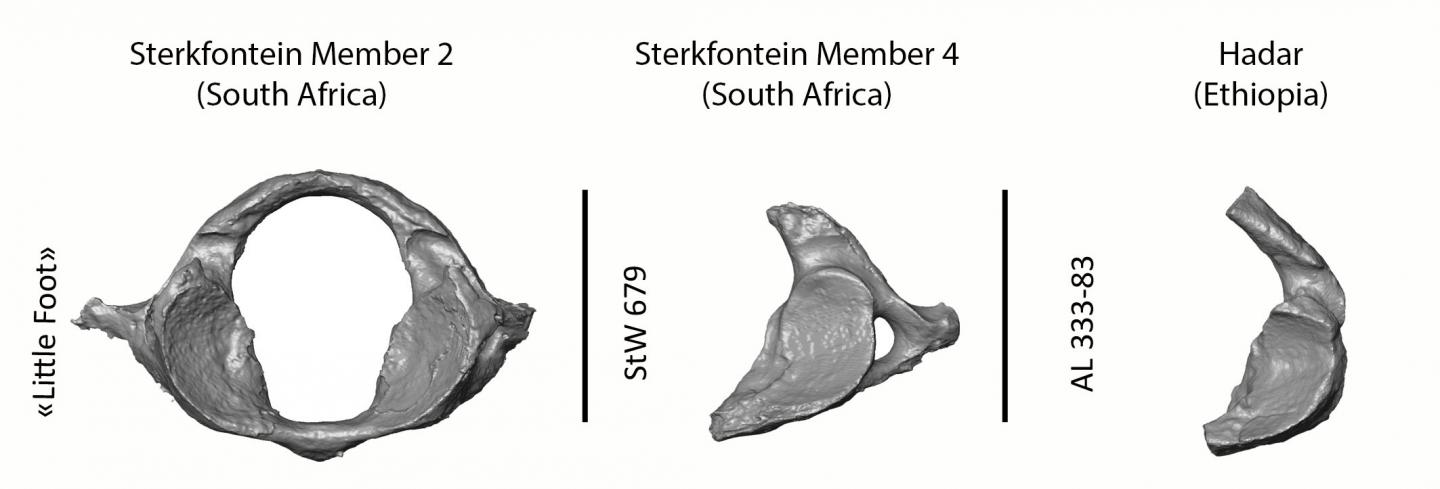
The meticulous excavation, cleaning and scanning of the skull of the ~3.67 million-year-old fossil specimen has revealed the most complete Australopithecus adult first cervical vertebra yet found. A description of the vertebra by Wits University researchers Dr Amélie Beaudet and the Sterkfontein team was published in the Scientific Reports. This research program is supported by the the Centre of Excellence in Palaeosciences, Scientific Palaeontological Trust, National Research Foundation, University of the Witwatersrand and the French National Centre for Scientific Research through the French Institute of South Africa.
The first cervical vertebra (or atlas) plays a crucial role in vertebrate biology. Besides acting as the connection between the head and the neck, the atlas also plays a role in how blood is supplied to the brain via the vertebral arteries.
By comparing the atlas of “Little Foot” with other fossils from South and East Africa as well as living humans and chimpanzees, the Wits University team shows that Australopithecus was capable of head movements that differ from modern humans.
“The morphology of the first cervical vertebra, or atlas, reflects multiple aspects of an organism’s life,” says Beaudet, the lead author of the study. “In particular, the nearly complete atlas of ‘Little Foot’ has the potential to provide new insights into the evolution of head mobility and the arterial supply to the brain in the human lineage.”
The shape of the atlas determines the range of head motions while the size of the arteries passing through the vertebrae to the skull is useful for estimating blood flow supplying the brain.
“Our study shows that Australopithecus was capable of head movements that differ from us. This could be explained by the greater ability of Australopithecus to climb and move in the trees. However, a southern African Australopithecus specimen younger than ‘Little Foot’ (probably younger by about 1 million years) may have partially lost this capacity and spent more time on the ground, like us today.”
The overall dimensions and shape of the atlas of “Little Foot” are similar to living chimpanzees. More specifically, the ligament insertions (that could be inferred from the presence and configuration of bony tubercles) and the morphology of the facet joints linking the head and the neck all suggest that “Little Foot” was moving regularly in trees.
Because “Little Foot” is so well-preserved, blood flow supply to the brain could also be estimated for the first time, using evidence from the skull and vertebrae. These estimations demonstrate that blood flow, and thus the utilisation of glucose by the brain, was about three times lower than in living humans, and closer to the those of living chimpanzees.
“The low investment of energy into the brain of Australopithecus could be tentatively explained by a relatively small brain of the specimen (around 408cm3), a low quality diet (low proportion of animal products) or high costs of other aspects of the biology of Australopithecus (such as upright walking). In any case, this might suggest that the human brain’s vascular system emerged much later in our history.”
###
Media Contact
Schalk Mouton
[email protected]
27-827-399-637
Original Source
http://www.