Credit: IPE
Using renewable energy to replace fossil energy is now considered the best solution for greenhouse gas emission and air pollution problems. As a result, the demand for new and better energy storage technology is strong.
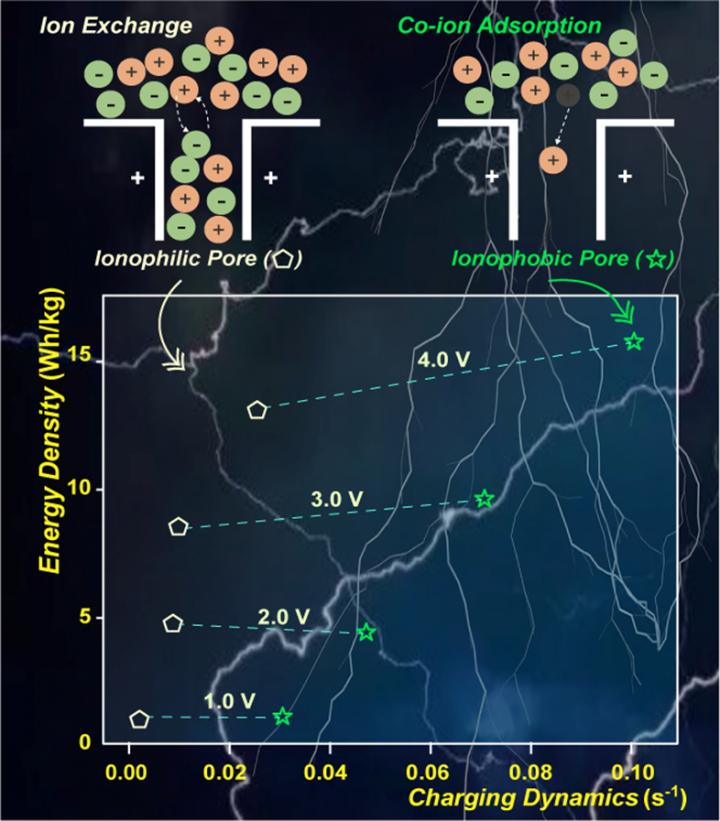
As part of the effort to improve this technology, a group led by Prof. ZHANG Suojiang from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) recently found that ionophobic electrodes can boost energy storage performance.
Their study was published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A on May 8.
Electric Double-Layer Capacitors (EDLCs) with ionic liquids (ILs)–as a new type of energy storage device–can fill the gap between the power density of batteries and the energy density of conventional capacitors. However, ILs in nanopores often exhibit sluggish diffusion dynamics, which hinder high power density.
In this study, the researchers proposed a new strategy to synergistically improve the energy density and power density of EDLCs with ILs based on massive molecular dynamics simulations.
They constructed a series of EDLCs with different wettability (from ionophilic to ionophobic), using the electrolyte 1-ethyl-3-methylimidazolium tetrafluoroborate.
When comparing EDLCs with an ionophilic electrode to EDLCs with an extremely ionophobic electrode, the researchers found that the charging time for the latter decreased by ~80% while the capacitance increased by nearly 100% (at U = 4V).
For EDLCs with an ionophobic electrode, ILs cannot spontaneously enter into the porous electrode without charging. With the increase in charging voltage, both the counter ion and co-ion will start to enter the nanopore when the voltage is beyond one critical value (~2 V). At the same time, the diffusion dynamics of ions are faster than the bulk ILs due to the sparsity of ions in the pore.
“Charging the ionophobic pore is like compressing a spring. Once the spring is released, much energy will be generated,” said Prof. HE Hongyan from IPE.
This study also identified the quantitative relationship between charging time/capacitance and ionophobic property/pore geometry/electric potential. It revealed how abnormal co-ion adsorption, which does not exist in the common ionophilic electrode, enhances the overall performance of EDLCs with ILs.
The idea of introducing ionophobicity may help the rational design of IL-based high-performance supercapacitors or other energy storage applications in the future.
###
Media Contact
LI Xiangyu
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




