Findings of researchers at Mainz University could lead to the creation of new drugs
Credit: ill./©: Walter Stöcker
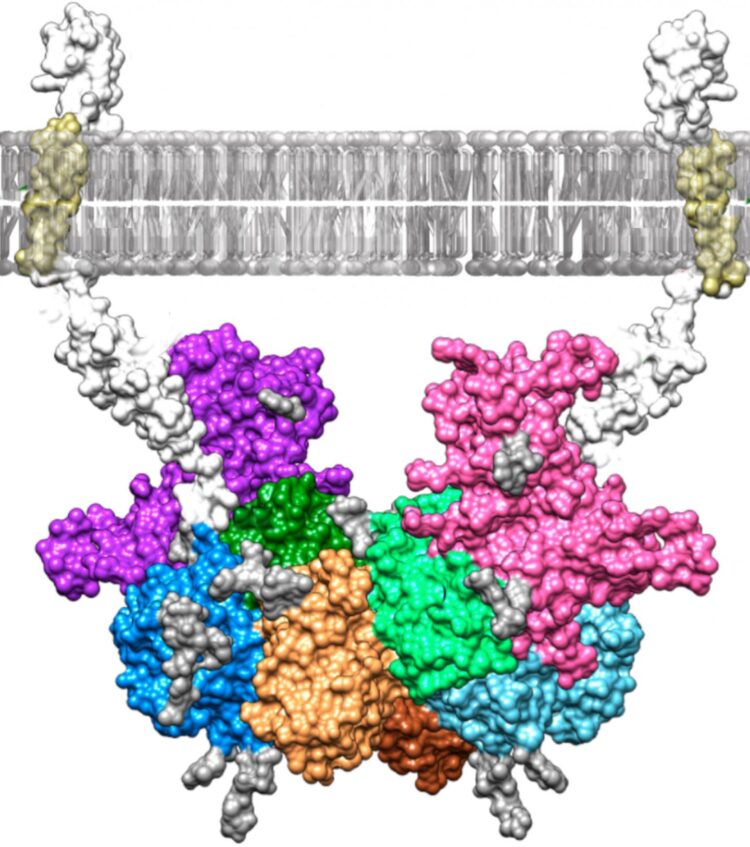
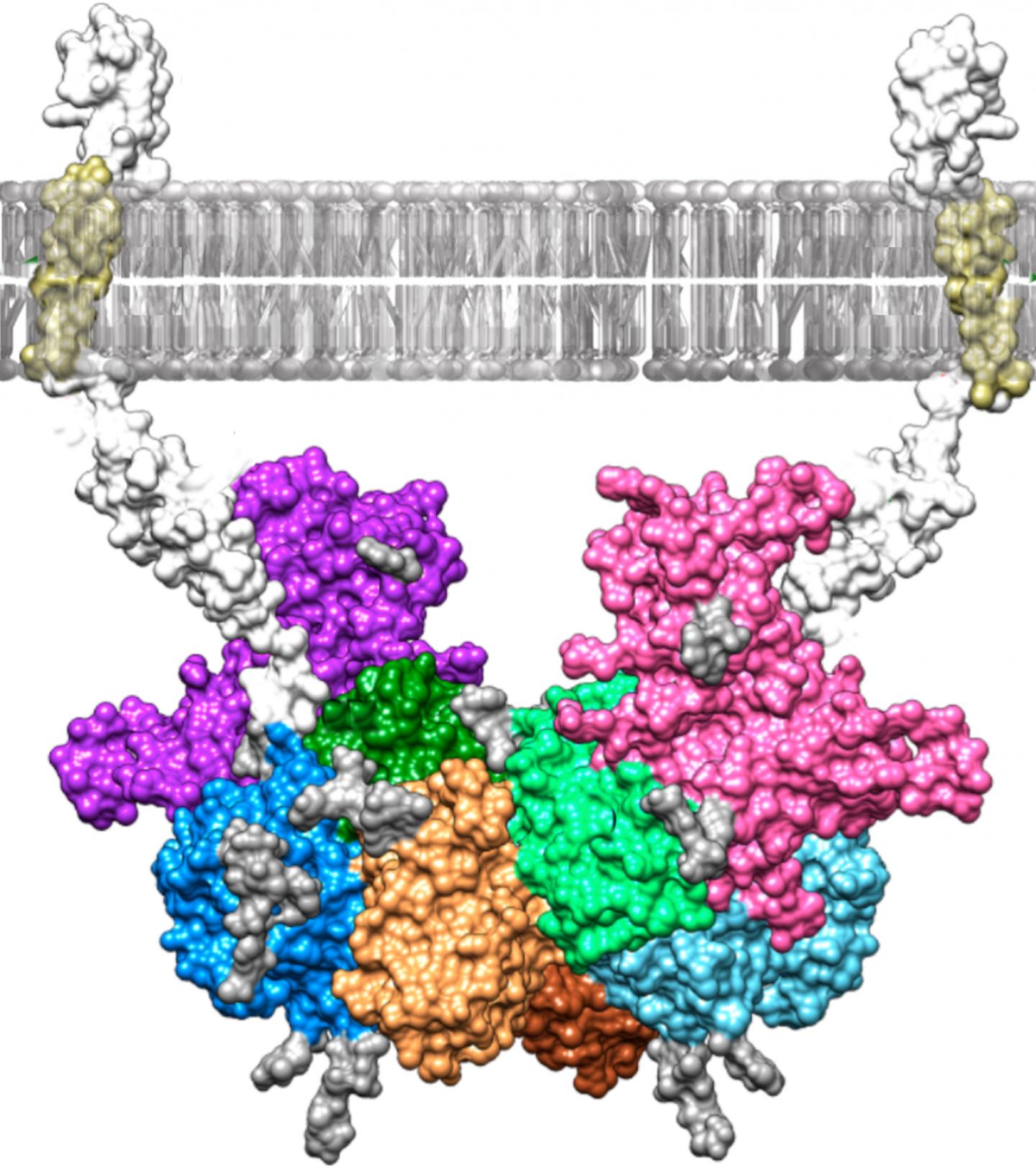
Researchers at Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz (JGU) in Germany and the Institute of Molecular Biology of Barcelona in Spain have discovered how the blood plasma protein fetuin-B binds to the enzyme meprin β and used a computer model to visualize their findings. These results could lead to the development of new drugs to treat serious diseases such as Alzheimer’s and cancer. Meprin β releases proteins from cell membranes, thus controlling important physiological functions in the human body. However, a dysregulation of this process can trigger the development of Alzheimer’s and cancer. Meprin β is regulated by fetuin-B binding to the enzyme when required, thereby preventing the release of other proteins. Presenting their findings in the journal “Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences“, the researchers are now the first to describe this binding in detail.
The team at Mainz University produced both meprin β and fetuin-B in insect cells and then allowed them to react with one other in a test tube. By means of measurement of enzyme kinetics and biophysical analyses, the researchers determined that this reaction resulted in an exceptionally stable, high-molecular-mass complex. Their colleagues in Barcelona subsequently managed to crystallize the complex and determine its three-dimensional structure using X-ray crystallography. This involved X-rays being fired at the protein crystals, which allowed the atomic structure of the crystals to be calculated from the diffraction of the X-rays. A computer model of the structure was then generated. “Thanks to the model, we can now see exactly how meprin β and fetuin-B bind together,” said Professor Walter Stöcker, who conducted the research at JGU together with Dr. Hagen Körschgen and Nele von Wiegen. “This research represents an excellent starting point for gaining a better understanding of diseases such as Alzheimer’s and for developing the drugs to combat them.” Meprin β is already known to be involved in the formation of so-called beta-amyloid plaques, which are a characteristic feature of the condition. Moreover, people with Alzheimer’s disease have relatively little fetuin-B in their blood, which in turn may lead to a lack of regulation of meprin β. “If it is possible to develop a drug that binds to the enzyme and inhibits it in a similar way to fetuin-B, this could be a new way of treating Alzheimer’s,” concluded Stöcker.
###
Media Contact
Professor Dr. Walter Stöcker
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.