Credit: SUTD
Malaria is the most prevalent blood-borne infectious disease caused by parasites of the species Plasmodium. In 2016, more than 216 million malaria infections were reported resulting in 445,000 deaths across the developing world.
During the blood stage development, Plasmodium (P.) falciparum, the most common causative agent of malaria-associated pathology in humans, exports a number of parasitic proteins to the surface of infected red blood cells facilitating its cyto-adhesion to endothelial receptors. This adhesive behavior prevents splenic clearance and induces microvasculature obstruction, forming critical contributors towards the disease outcome.
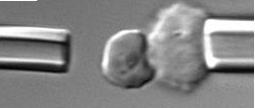
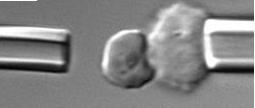
In a recent study, a research team from Singapore demonstrated how the adhesion of plasmodium-infected blood cells is elevated at febrile temperatures. Through dual-micropipette step-pressure technique between P. falciparum-infected RBCs (iRBCs) and Chinese Hamster Ovary cells expressing Chondroitin sulfate A (CHO-CSA), they determined that adhesion is elevated at febrile temperatures. The team also noticed that exposures to febrile temperature significantly increased both the adhesion force and adhesion percentage between iRBCs and CSA-CHO cells.
Using flow cytometry analysis, the team documented an increase in phosphatidylserine expression on the iRBC surface following exposure to febrile temperature. They demonstrate that elevated levels of phosphatidylserine is linked to increased cyto-adhesion, since the trend was reversed by introducing soluble Annexin V. "These results suggest that elevated PS recruitment on iRBC under thermally stressed conditions contributes to the increased adhesive behavior of iRBCs, which might be relevant to clinical manifestations associated with malaria fever," said Dr Rajesh Chandramohanadas from the Singapore University of Technology & Design (SUTD).
###
First author of this study, published in the science journal Scientific Reports, is Dr Rou Zhang from the Infectious Disease IRG, Singapore-MIT Alliance for Research and Technology (SMART) Centre. Other investigators involved in this project are Professor Ming Dao (SMART and Massachusetts Institute of Technology), Professor Chwee Teck Lim (SMART & National University of Singapore) and Dr Rajesh Chandramohanadas (SMART and Singapore University of Technology & Design).
Media Contact
Melissa Koh
[email protected]
65-649-98742
http://www.sutd.edu.sg
Related Journal Article
http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33358-2