Since patients with ballistic embedded fragments are frequently denied MRI, due to indeterminate bullet composition sans shell casings, radiography and CT can be used to identify nonferromagnetic projectiles that are safe for MRI
Credit: American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS), American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR)
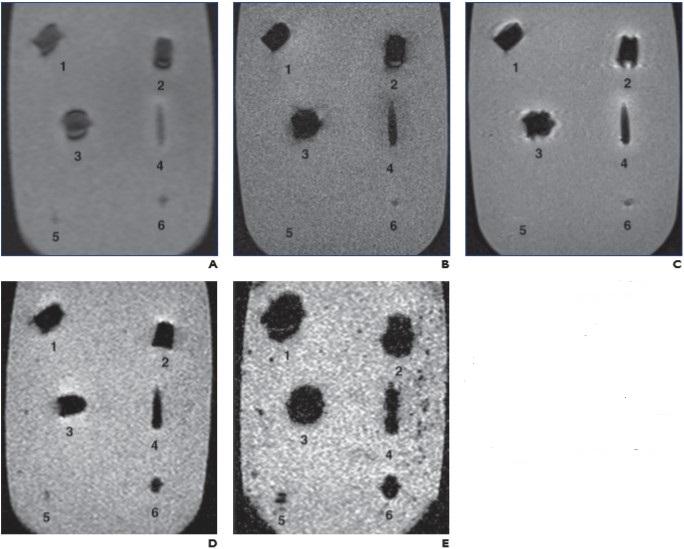
Leesburg, VA, December 29, 2020–According to an article in ARRS’ American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), because patients with ballistic embedded fragments are frequently denied MRI (due to indeterminate bullet composition sans shell casings), radiography and CT can be used to identify nonferromagnetic projectiles that are safe for MRI.
“Commercially available handgun and shotgun ammunition representing projectiles commonly encountered in a clinical setting was fired into ballistic gelatin as a surrogate for human tissue,” explained first author Arthur J. Fountain from the department of radiology and imaging sciences at Emory University.
After obtaining radiographs and CT images of these gelatin blocks, Fountain and colleagues then obtained MR images of unfired bullets suspended in gelatin blocks using T1- and T2-weighted sequences. Magnetic attractive force, rotational torque, and heating effects of unfired bullets were assessed at 1.5 T.
Based upon debris trail and primary projectile deformation, the team separated the fired bullets into two groups: ferromagnetic and nonferromagnetic. Although ferromagnetic bullets showed mild torque forces and marked imaging artifacts at 1.5 T, nonferromagnetic bullets did not exhibit these effects.
Importantly, heating above the Food and Drug Administration limit of 2°C was not observed in any of the projectiles tested.
Additionally, the authors of this AJR article presented a triage algorithm for patients with retained ballistic fragments. “In particular,” Fountain et al. described, “a projectile that leaves a metallic debris trail from entry to final position or has been appreciably deformed is of copper, copper-alloy, or lead composition with a partial jacketed configuration or represents lead shotgun shot and does not pose a significant risk for imaging at 1.5 T or less, regardless of when the injury occurred.”
“Nonferromagnetic ballistic projectiles do not undergo movement or heating during MRI, and the imaging modality can be performed when medically necessary without undue risk and with limited artifact susceptibility on the resulting images, even when the projectile is in or near a vital structure,” the authors concluded.
###
Founded in 1900, the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is the first and oldest radiological society in North America, dedicated to the advancement of medicine through the profession of radiology and its allied sciences. An international forum for progress in medical imaging since the discovery of the x-ray, ARRS maintains its mission of improving health through a community committed to advancing knowledge and skills with an annual scientific meeting, monthly publication of the peer-reviewed American Journal of Roentgenology (AJR), quarterly issues of InPractice magazine, AJR Live Webinars and Podcasts, topical symposia, print and online educational materials, as well as awarding scholarships via The Roentgen Fund®.
Media Contact
Logan K. Young
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




