High-resolution 3D microscopy shows how plants adapt flexibly to their surroundings
Credit: Daniel von Wangenheim
FRANKFURT. Plants use their roots to search for water. While the main root digs down-wards, a large number of fine lateral roots explore the soil on all sides. As researchers from Nottingham, Heidelberg and Goethe University of Frankfurt report in the current issue of “Nature Plants“, the lateral roots already “know” very early on where they can find water.
For his experiment, Daniel von Wangenheim, a former doctoral researcher in Professor Ernst Stelzer’s Laboratory for Physical Biology and most lately a postdoc at Malcolm Ben-nett’s, mounted thale cress roots along their length in a nutrient solution. They were, how-ever, not completely immersed and their upper side left exposed to the air. He then ob-served with the help of a high-resolution 3D microscope how the roots branched out.
To his surprise, he discovered that almost as many lateral roots formed on the air side as on the side in contact with the nutrient solution. As he continued to follow the growth of the roots with each cell division in the microscope, it became evident that the new cells drive the tip of the root in the direction of water from the very outset, meaning that if a lateral root had formed on the air side, it grew in the direction of the agar plate.
“It’s therefore clear that plants first of all spread their roots in all directions, but the root obvi-ously knows from the very first cell divisions on where it can find water and nutrients,” says Daniel von Wangenheim, summarizing the results. “In this way, plants can react flexibly to an environment with fluctuating resources.”
###
The result is based on many hours of film material recorded using Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy (LSFM), a technique developed by Ernst Stelzer. In a vivid video clip, Daniel von Wangenheim shows the root-branching process in slow motion. His tweet has already attracted considerable attention from his colleagues in the field.
https:/
Publication: Daniel von Wangenheim, Jason Banda, Alexander Schmitz, Jens Boland, An-thony Bishopp, Alexis Maizel, Ernst H. K. Stelzer and Malcolm Bennett: Early developmental plasticity of lateral roots in response to asymmetric water availability, in Nature Plants (3 February 2020), https:/
A picture can be downloaded under: http://www.
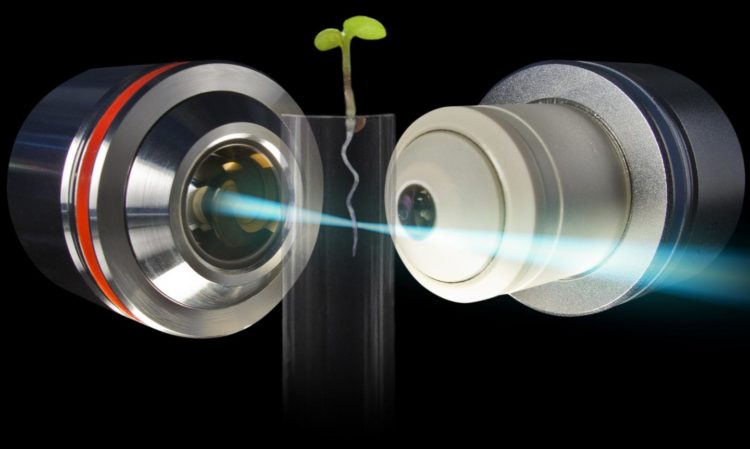
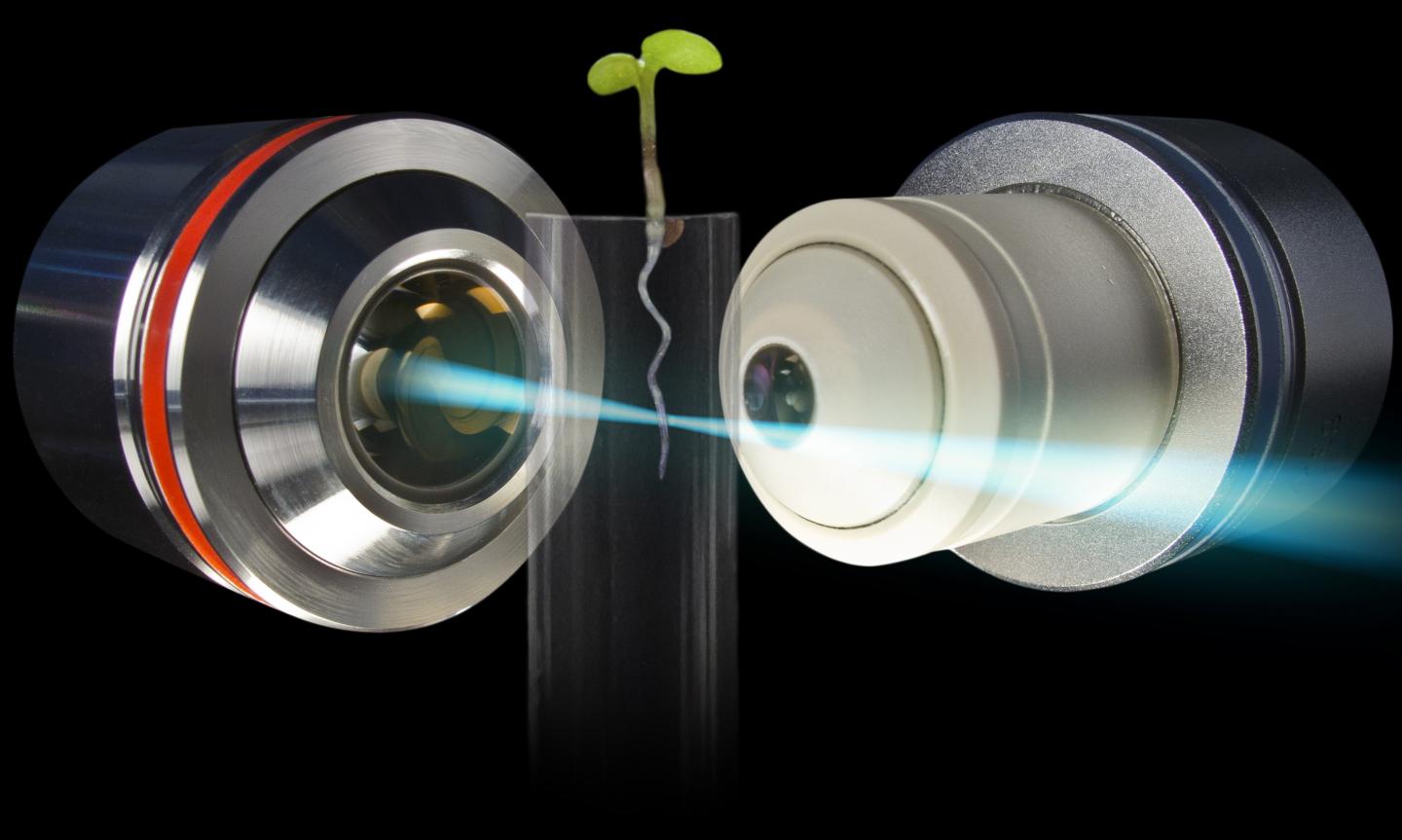
Caption: Light Sheet Fluorescence Microscopy is based on two processes: 1) lateral illumination of the specimen with laser light along a plane and 2) detection of fluorescent light emitted from a thin volume centred around the illumination plane. The plant (Arabidopsis thaliana) is mounted in a three-dimensional assembly, stands upright in a plant-derived gel appropriate for the species and supplied with medium and light.
Image rights: Daniel von Wangenheim.
Further information: Dr Daniel von Wangenheim, Plant and Crop Sciences, School of Biosci-ences, University of Nottingham, UK, Email: [email protected]
Professor Ernst Stelzer, Institute for Cell Biology and Neuroscience and Buchmann Institute for Molecular Life Sciences, Riedberg Campus, Tel.: +49(0)69-798-42547, Email: [email protected]
Media Contact
Dr. Daniel von Wangenheim
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.