Credit: WMG, University of Warwick
- By 2030 only EV’s will be in production, meaning manufacturers are racing to create a high-energy battery that’s affordable and charges efficiently, but conventional battery cathodes cannot reach the targets of 500Wh/Kg
- Lithium-excess cathodes offer the ability to reach 500Wh/Kg but unlocking their full capacity means understanding how they can store charge at high voltages.
- A new X-ray study lead by WMG, University of Warwick has resolved how the metals and oxygen facilitate the charge storage at high voltages.
High energy storage batteries for EVs need high capacity battery cathodes. New lithium-excess magnesium-rich cathodes are expected to replace existing nickel-rich cathodes but understanding how the magnesium and oxygen accommodate charge storage at high voltages is critical for their successful adaption. Research led by WMG, University of Warwick in collaboration with U.S. researchers employed a range of X-ray studies to determine that the oxygen ions are facilitating the charge storage rather than the magnesium ions.
Electric vehicles will one day dominate UK roads and are critical for eliminating CO2 emissions, but a major issue car manufacturers face is how to make an affordable long-lasting energy-dense battery that can be charged quickly and efficiently. There is therefore a race to make EV batteries with an energy storage target of 500 Wh/Kg, but these targets are not possible without changing to new cathode materials.
Although progress has continued over the last 10 years to push the performance of state-of-the-art nickel-rich cathodes for EV, the material is unable to provide the energy density needed. To increase the capacity more lithium needs to be used, which means going beyond the ability of nickel to store electron charge.
Lithium-excess magnesium-rich cathodes offer sufficient energy density but to reach ultimately reach energy storage targets of 500Wh/Kg we need to understand how the electron charge is stored in the material. Simply put, is the electron charge stored on the magnesium or oxygen sites.
In the paper, ‘Whither Mn Oxidation in Mn-Rich Alkali-Excess Cathodes?’, published in the Journal ACS Energy Letters today the 17th of February, researchers from WMG, University of Warwick have overcome a significant milestone in understanding of charge storage in lithium-excess magnesium-rich cathodes.
Li-excess compounds that involve conventional and non-conventional redox, conventional refers to metal ions changing their electron density. Reversibly changing the electron density on the oxygen (or oxygen redox) without it forming O2 gas is unconventional redox. Various computational models exist in the literature describing different mechanisms involving both, but careful x-ray studies performed while the battery is cycling (operando) are ultimately required to validate these models.
Researchers between the UK and US, led by WMG at the University of Warwick, performed operando x-ray studies to precisely quantify magnesium and oxygen species at high voltages. They demonstrated how x-ray beams could irreversibly drive highly oxidized magnesium (Mn7+) to trapped O2 gas irreversibly in other materials.
However, by performing careful operando x-ray studies that circumvented beam damage and observe only trace amounts of Mn7+ forming upon charging in Li-excess cathodes during battery cycling.
Professor Louis Piper, from WMG, University of Warwick explains:
“We have ultimately resolved that oxygen rather than metal redox is driving the higher capacity, which means we can now design better strategies to improve cycling and performance for this class of materials.”
###
17 FEBRUARY 2021
NOTES TO EDITORS
High-res images available at:
https:/
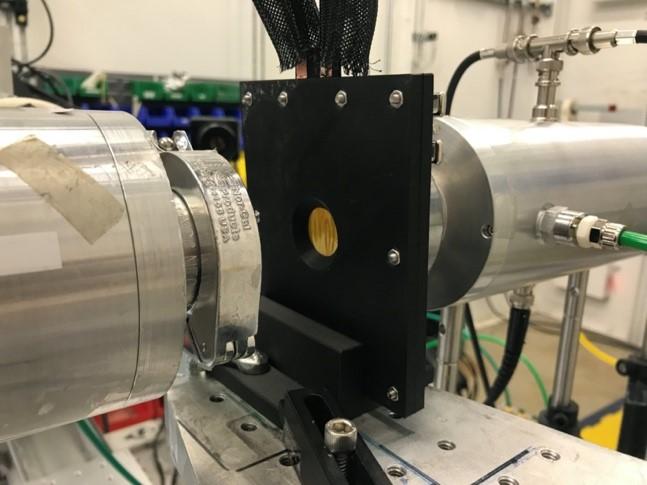
Caption: Photo of the operando x-ray studies being performed at a Synchrotron facility.
Credit: WMG, University of Warwick
Paper available to view at: https:/
For further information please contact:
Alice Scott
Media Relations Manager – Science
University of Warwick
Tel: +44 (0) 7920 531 221
E-mail: [email protected]
Media Contact
Alice Scott
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




