Credit: Jonathan Wilker/Purdue University
WEST LAFAYETTE, Ind. – Make them tougher by making them weaker.
That’s the proposed solution from a Purdue University research team – well-known for its adhesive technology.
“We have been using inspiration from sea creatures to develop several new adhesives,” said Jonathan Wilker, a Purdue professor of chemistry and materials engineering, who helps lead the research team. “Recently we have been seeking strategies for making adhesives tougher. One way to get there can be viewed as making the materials tougher by, first, making them weaker.”
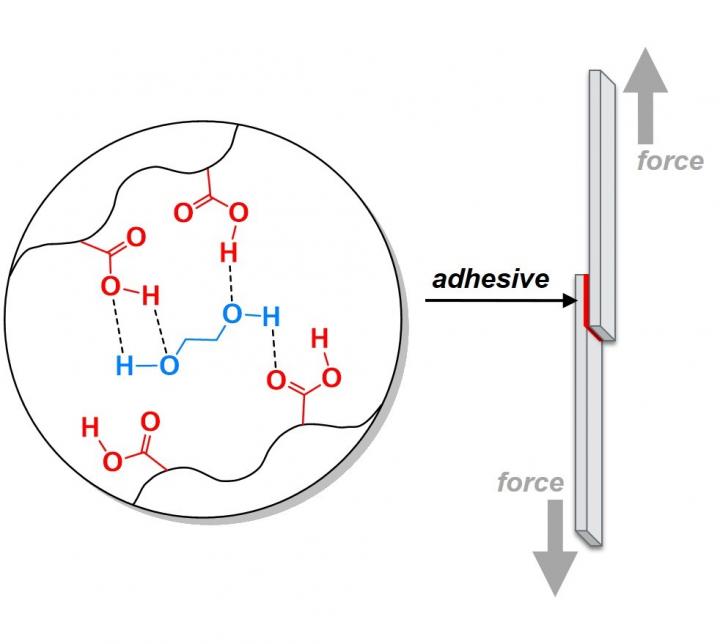
The Purdue team added bonds that are broken easily throughout the material. When pressure or stress is applied to the glue, these sacrificial bonds are designed to absorb energy and break apart. Meanwhile, the rest of the larger adhesive system remains intact.
The Purdue team’s work is published in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
“The idea is somewhat similar to how a brick wall is made of bricks that are offset from each other,” Wilker said. “You stagger the bricks and cement so that a crack does not shoot right down through the cement lines. A crack hits the middle of a brick and the forces get spread out toward both sides, eventually decreasing to the point that the wall stays intact.
“We added weak bonds within the adhesive so that mechanical forces and growing cracks lose energy by breaking these bonds instead of having the whole, larger material fracture. The idea is to manage how energy moves through the material. The overall adhesive system can become tougher and less likely to break apart when placed under mechanical stress.”
Wilker’s team tested this idea with several types of bonds. The ones that worked best were neither too weak nor too strong. He said that this technique for managing energy in adhesives might be a general phenomenon that could be applied to adhesives in industries ranging from consumer electronics to construction to manufacturing airplanes and automobiles.
The team has hundreds of mussels and oysters growing in its laboratory for studying proteins used by the sea creatures attaching to rocks. After working to understand the nature of these natural adhesives, the researchers then generate several synthetic versions with different properties.
They have worked to patent several of their toxin-free adhesive systems with the Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization, which recently moved into the Convergence Center for Innovation and Collaboration in Discovery Park District.
The researchers are looking for partners to continue developing their technology. For more information on licensing and other opportunities, contact Joseph Kasper of OTC at [email protected].
###
About Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization
The Purdue Research Foundation Office of Technology Commercialization operates one of the most comprehensive technology transfer programs among leading research universities in the U.S. Services provided by this office support the economic development initiatives of Purdue University and benefit the university’s academic activities through commercializing, licensing and protecting Purdue intellectual property. The office is managed by the Purdue Research Foundation, which received the 2019 Innovation and Economic Prosperity Universities Award for Place from the Association of Public and Land-grant Universities. The Purdue Research Foundation is a private, nonprofit foundation created to advance the mission of Purdue University. Contact [email protected] for more information.
Writer: Chris Adam, 765-588-3341, [email protected]
Source: Jonathan Wilker, [email protected]
Media Contact
Chris Adam
[email protected]
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




