Credit: S. Doijad, L. La Pietra
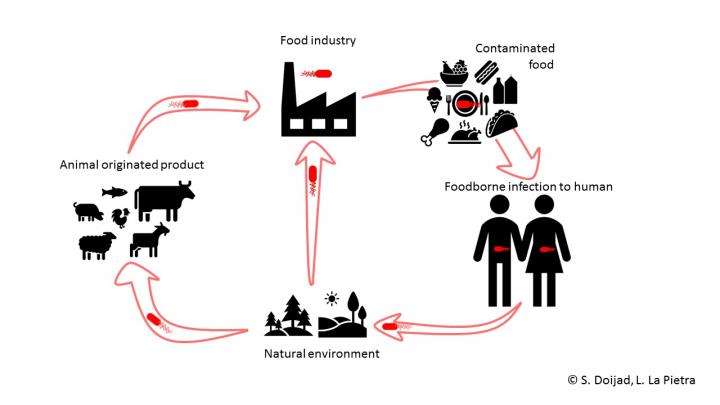
The bacterium Listeria monocytogenes can cause listeriosis, a life-threatening infection in animals and humans. Contaminated food is a frequent source of infection. Elderly people, people with a weakened immune system and pregnant women are particularly at risk with a mortality rate of up to 30 per cent. An international research group led by the Institute of Medical Microbiology at the Justus Liebig University Giessen (JLU) has now discovered the most virulent representatives of this bacterial species to date. They were identified as the cause of serious diseases in sheep in a remote area of the Chinese province Jiangsu.
‘The detection of a completely new form of pathogenic Listeria monocytogenes in China highlights the need for international collaboration’, emphasises Prof. Dr Trinad Chakraborty, Director of the Institute of Medical Microbiology at the JLU and research scientist at the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF). ‘Only by combining resources and expertise can we rapidly identify newly emerging threats to food safety from highly virulent strains worldwide.’
After decoding the genome sequence of these bacteria, the scientists were able to determine the genetic basis for their hypervirulence. They identified the factors that enhance the ability of this Listeria strain to cause severe septic diseases. ‘These isolates are unique in the sense that they combine the virulence characteristics of various highly pathogenic Listeria species that infect animals or humans into a single strain’, says Prof. Chakraborty. ‘Since listeriosis is a food-borne infection, measures to identify such highly virulent strains are extremely urgent.’
Clinical symptoms of listeriosis include fever, blood poisoning (sepsis) and infections of the central nervous system, which can lead to lifelong sequelae. Infections during pregnancy can lead to premature birth, miscarriage or stillbirth. Both raw and processed foods can be contaminated by listeria, especially dairy products, meat, seafood and ready-to-eat products such as pre-packaged salads. Due to the extremely hazardous nature of listeriosis in humans, many countries have set up monitoring systems to quickly identify and recall contaminated food products. Since it can take up to 70 days for a listeria infection to manifest itself with severe symptoms, it can be very difficult to identify the source of contamination and initiate the food recall.
Currently, there are reported listeriosis outbreaks in Germany (Hesse), the Netherlands, Lithuania, Spain, Great Britain, Canada and the United States, posing a particular threat to vulnerable populations. Therefore, considerable efforts are now underway to identify the origin of these pathogens and prevent further outbreaks of listeriosis.
###
Research scientists from the State Key Laboratory of Zoonosis of the University of Yangzhou in Jiangsu (China), the Laboratory of Food Microbiology of the Swiss Federal Institute of Technology (ETH) Zurich (Switzerland) and the Institute of Medical Microbiology of the Justus Liebig University Giessen (JLU, Germany) were involved in the study on the highly virulent listeria strain isolated in China, which was published in the journal ‘Nature Communications‘. The work done at the JLU was funded by the EU ERA-NET PROANTILIS programme. The study was also supported by the German Center for Infection Research (DZIF).
Media Contact
Dr Trinad Chakraborty
[email protected]
49-641-994-1250
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




