Credit: Image by Chenggong Wang, Program in Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences, Princeton University
A recent analysis of the latest generation of climate models — known as a CMIP6 — provides a cautionary tale on interpreting climate simulations as scientists develop more sensitive and sophisticated projections of how the Earth will respond to increasing levels of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
Researchers at Princeton University and the University of Miami reported that newer models with a high “climate sensitivity” — meaning they predict much greater global warming from the same levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide as other models — do not provide a plausible scenario of Earth’s future climate.
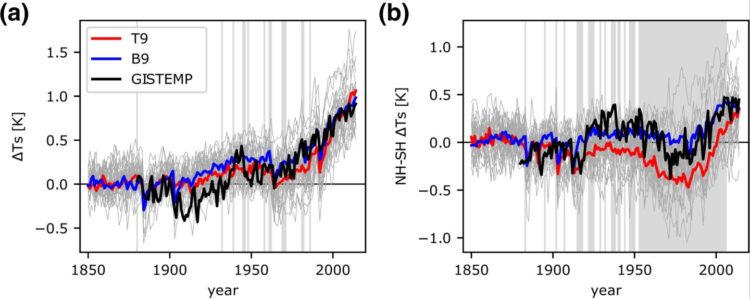
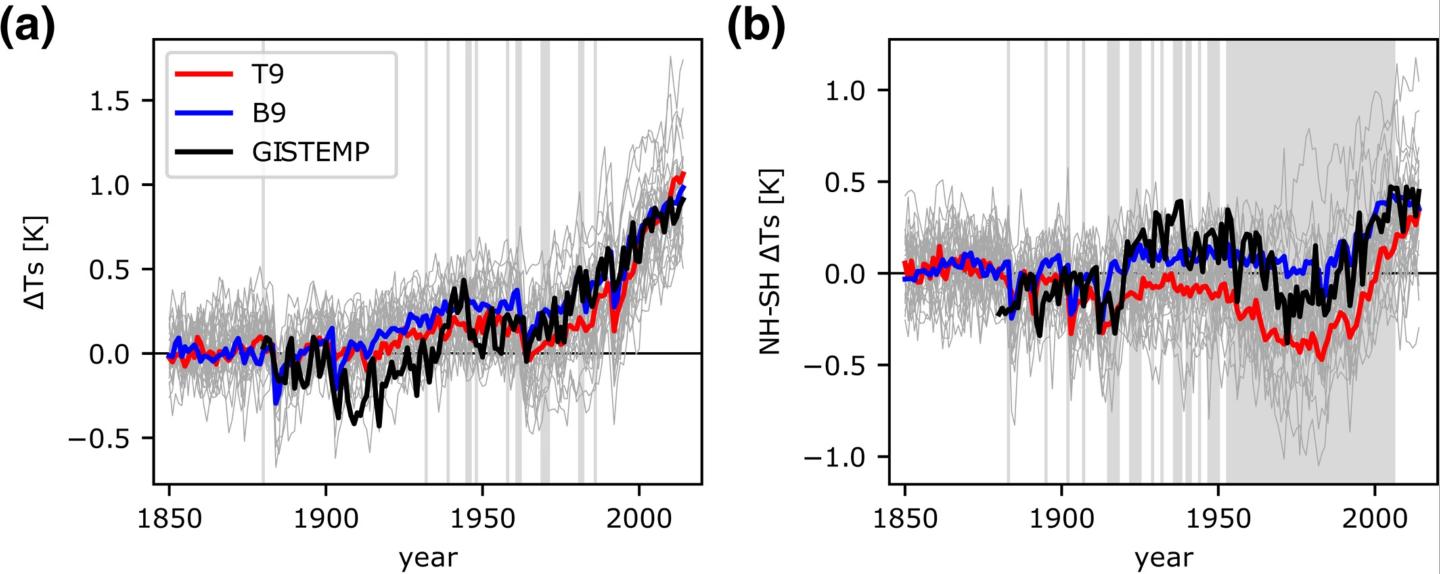
Those models overstate the global cooling effect that arises from interactions between clouds and aerosols and project that clouds will moderate greenhouse gas-induced warming — particularly in the northern hemisphere — much more than climate records show actually happens, the researchers reported in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
Instead, the researchers found that models with lower climate sensitivity are more consistent with observed differences in temperature between the northern and southern hemispheres, and, thus, are more accurate depictions of projected climate change than the newer models. The study was supported by the Carbon Mitigation Initiative (CMI) based in Princeton’s High Meadows Environmental Institute (HMEI).
These findings are potentially significant when it comes to climate-change policy, explained co-author Gabriel Vecchi, a Princeton professor of geosciences and the High Meadows Environmental Institute and principal investigator in CMI. Because models with higher climate sensitivity forecast greater warming from greenhouse gas emissions, they also project more dire — and imminent — consequences such as more extreme sea-level rise and heat waves.
The high climate-sensitivity models forecast an increase in global average temperature from 2 to 6 degrees Celsius under current carbon dioxide levels. The current scientific consensus is that the increase must be kept under 2 degrees to avoid catastrophic effects. The 2016 Paris Agreement sets the threshold to 1.5 degrees Celsius.
“A higher climate sensitivity would obviously necessitate much more aggressive carbon mitigation,” Vecchi said. “Society would need to reduce carbon emissions much more rapidly to meet the goals of the Paris Agreement and keep global warming below 2 degrees Celsius. Reducing the uncertainty in climate sensitivity helps us make a more reliable and accurate strategy to deal with climate change.”
The researchers found that both the high and low climate-sensitivity models match global temperatures observed during the 20th century. The higher-sensitivity models, however, include a stronger cooling effect from aerosol-cloud interaction that offsets the greater warming due to greenhouse gases. Moreover, the models have aerosol emissions occurring primarily in the northern hemisphere, which is not consistent with observations.
“Our results remind us that we should be cautious about a model result, even if the models accurately represent past global warming,” said first author Chenggong Wang, a Ph.D. candidate in Princeton’s Program in Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences. “We show that the global average hides important details about the patterns of temperature change.”
In addition to the main findings, the study helps shed light on how clouds can moderate warming both in models and the real world at large and small scales.
“Clouds can amplify global warming and may cause warming to accelerate rapidly during the next century,” said co-author Wenchang Yang, an associate research scholar in geosciences at Princeton. “In short, improving our understanding and ability to correctly simulate clouds is really the key to more reliable predictions of the future.”
Scientists at Princeton and other institutions have recently turned their focus to the effect that clouds have on climate change. Related research includes two papers by Amilcare Porporato, Princeton’s Thomas J. Wu ’94 Professor of Civil and Environmental Engineering and the High Meadows Environmental Institute and a member of the CMI leadership team, that reported on the future effect of heat-induced clouds on solar power and how climate models underestimate the cooling effect of the daily cloud cycle.
“Understanding how clouds modulate climate change is at the forefront of climate research,” said co-author Brian Soden, a professor of atmospheric sciences at the University of Miami. “It is encouraging that, as this study shows, there are still many treasures we can exploit from historical climate observations that help refine the interpretations we get from global mean-temperature change.”
###
The paper, “Compensation Between Cloud Feedback and Aerosol?Cloud Interaction in CMIP6 Models,” was published in the Feb. 28 edition of Geophysical Research Letters. The research was supported by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (grants NA20OAR4310393 and NA18OAR4310418) and the Carbon Mitigation Initiative based in Princeton University’s High Meadows Environmental Institute (HMEI).
Media Contact
Morgan Kelly, High Meadows Environmental Institute
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.