Credit: Mount Sinai Health System
Mount Sinai researchers have found that myocardial injury (heart damage) is prevalent among patients hospitalized with COVID-19 and is associated with higher risk of mortality. More specifically, a serious myocardial injury can triple the risk of death. The results were published in the June 5 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
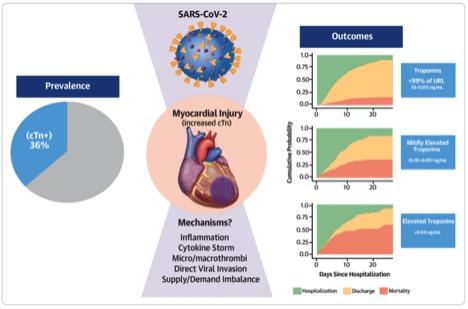
“There has been a lot of speculation about how COVID-19 affects the heart and blood vessels, and with what frequency. Our observational study may help to shed some light on this. We found that 36 percent of patients who were hospitalized with COVID-19 had elevated troponin levels–which represents heart injury–and were at higher risk of death,” says lead author Anu Lala, MD, Assistant Professor of Medicine (Cardiology) at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai. “These findings, which are consistent with reports from China and Europe, are important for clinicians. If COVID-19-positive patients arrive in the emergency room and their initial test results show troponin levels are elevated, doctors may be able to better triage these patients and watch over them more closely, but this remains a testable hypothesis.”
A team of investigators analyzed electronic health records of nearly 3,000 adult patients with confirmed positive COVID-19 admitted to five New York City hospitals within the Mount Sinai Health System between February 27 and April 12, 2020 (The Mount Sinai Hospital, Mount Sinai West, Mount Sinai Morningside, Mount Sinai Queens, and Mount Sinai Brooklyn). The median age for patients analyzed was 66, and roughly 60 percent were male. One-quarter of all patients self-identified as African American, and 27 percent self-identified as Hispanic or Latino. Roughly 25 percent of the patients had a history of heart disease (including coronary artery disease, atrial fibrillation and heart failure) and roughly 25 percent had cardiovascular disease risk factors (including diabetes or hypertension).
Mount Sinai researchers found that 36 percent of hospitalized COVID-19 patients had myocardial injury. For those with substantial injury, their risk of death was three times higher than COVID-19-positive patients without myocardial injury.
To get this information, researchers focused on the patients’ levels of troponin–proteins that are released when the heart muscle becomes damaged–and their outcomes. (Higher troponin levels mean greater heart damage.) All patients had a blood test for this within 24 hours of admission and were grouped into three categories: 64 percent were in the normal range (0.00-0.03 ng/mL); 17 percent had mild elevation (between one and three times the upper limit of normal, or >0.03-0.09 ng/mL), and 19 percent had higher elevation (more than three times the upper limit of normal, or >0.09 ng/mL). Higher troponin levels were more prevalent in patients who were over 70 years old and had previously known conditions including diabetes, high blood pressure, atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease and heart failure. Researchers made adjustments for these factors in the analysis.
Then, they analyzed the associated risk of death after adjusting for factors including age, sex, body mass index, history of cardiovascular disease, medication, and illness at hospital admission. They found patients with milder forms of myocardial injury were associated with lower likelihood of hospital discharge and a 75 percent higher risk of death compared to patients with normal levels. Patients with higher troponin concentrations were associated with a three times higher risk of death compared to those with normal levels. Additionally, when adjusting for relevant factors including heart disease, diabetes and high blood pressure, troponin was independently associated with risk of death. More specifically, heart injury seems to be a more important indicator in predicting risk of death than a history of heart disease.
“The study concludes that myocardial injury is common among patients hospitalized with COVID -19 but is more often mild and associated with low-level troponin elevation. Despite low levels, even small amounts of heart injury could be linked to a pronounced risk of death, and COVID-19 patients with a history of cardiovascular disease are more likely to have myocardial injury when compared to patients without heart disease,” explains Dr. Lala.
“Myocardial injury is frequent in COVID-19 patients, but the question is what is the main etiology? Is this by direct effect of the virus into the myocardium, or is it an indirect effect of the cytokine storm also into the myocardium, or a procoagulant causing coronary thrombotic ischemia? These are questions that need to be addressed in future studies,” says senior author Valentin Fuster, MD, PhD, Director of Mount Sinai Heart and Physician-in-Chief of The Mount Sinai Hospital. “Additionally, we now need to follow COVID-19 patients with myocardial injury to learn more about the consequences.”
###
About the Mount Sinai Health System
The Mount Sinai Health System is New York City’s largest academic medical system, encompassing eight hospitals, a leading medical school, and a vast network of ambulatory practices throughout the greater New York region. Mount Sinai is a national and international source of unrivaled education, translational research and discovery, and collaborative clinical leadership ensuring that we deliver the highest quality care–from prevention to treatment of the most serious and complex human diseases. The Health System includes more than 7,200 physicians and features a robust and continually expanding network of multispecialty services, including more than 400 ambulatory practice locations throughout the five boroughs of New York City, Westchester, and Long Island. The Mount Sinai Hospital is ranked No. 14 on U.S. News & World Report’s “Honor Roll” of the Top 20 Best Hospitals in the country and the Icahn School of Medicine as one of the Top 20 Best Medical Schools in country. Mount Sinai Health System hospitals are consistently ranked regionally by specialty by U.S. News & World Report.
For more information, visit https:/
Media Contact
ilana nikravesh
[email protected]




