Toward the development of individual model of ischemic heart disease
Credit: ©2019 Okayama University
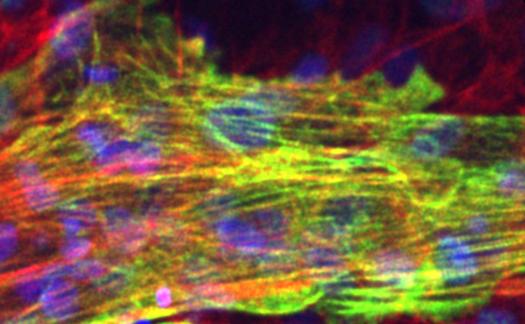
Researchers at Okayama University Graduate School of Medicine, Dentistry and Pharmaceutical Sciences developed a model of myocardial infarction using cardiomyocytes differentiated from human induced pluripotent stem cells.
The journal Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications published the study, with Ken Takahashi, Ph.D., as corresponding author, and Wei Heng, MSc., a graduate student in the Naruse Lab, as first author.
To date, laboratory animals such as mouse have been used to model diseases including myocardial infarction. However, there have been concerns about difference in characteristics of cardiomyocytes e.g. heart rate and action of drugs, based on the difference of gene expression between laboratory animals and human.
Using this model, researchers can evaluate the extent of myocardial tissue damage by microscope morphologically, and by measuring injury-marker proteins and analyzing contractility and its synchroneity from recorded movie quantitatively. Further analysis revealed that gene expression of interleukin-8, an inflammation marker known to increase in acute myocardial infarction, increased in this model.
“This myocardial infarction model will contribute to the development of preventive/therapeutic medicine more effective to human even without sacrificing animals,” said Ken Takahashi, Ph.D., assistant professor in the university and lead author of the study.
###
Okayama University
As one of the leading universities in Japan, Okayama University aims to create and establish a new paradigm for the sustainable development of the world. Okayama University offers a wide range of academic fields, which become the basis of the integrated graduate schools. This not only allows us to conduct the most advanced and up-to-date research, but also provides an enriching educational experience.
Media Contact
Takahashi Ken
[email protected]
Original Source
http://www.
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




