New research from scientists at the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California (USC) shows that the body’s immune system may be able to clear the brain of toxic plaque build-up that is the hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease, reversing memory loss and brain cell damage.
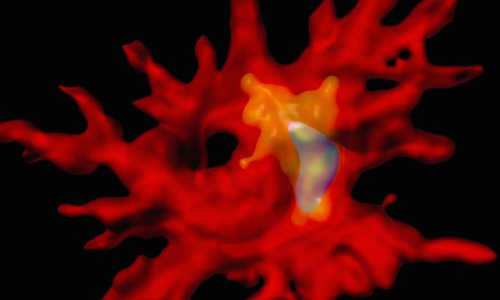
A 3D reconstruction of an immune cell (red) containing β-amyloid (blue) within an intracellular degradation compartment (yellow). Deletion of the anti-inflammatory cytokine, Il10, activates innate immune cells to clear the brain of toxic β-amyloid plaques. Photo Credit: Marie-Victoire Guillot-Sestier, Ph.D
The study, which appears in the Feb. 4 edition of the peer-reviewed scientific journal Neuron, identifies a promising avenue for treating a disease that the Alzheimer’s Association projects will affect 16 million Americans over age 65 by 2050.
“Alzheimer’s disease is the public health crisis of our time, and effective treatment does not yet exist,” said Terrence Town, PhD, professor of physiology and biophysics at the Keck School of Medicine of USC and the study’s senior author. “Our study shows that ‘rebalancing’ the immune response to wipe away toxic plaques from the brain may bring new hope for a safe and effective treatment for this devastating illness of the mind.”
Alzheimer’s disease is an irreversible, progressive brain disease that causes problems with memory, thinking and behavior. Affecting more than 5 million Americans today, Alzheimer’s is the most common type of dementia, a general term for loss of memory and other mental abilities. Brains with Alzheimer’s disease show build-up of a sticky plaque — made of a protein called beta-amyloid — that induces memory loss. When afflicted with Alzheimer’s, the immune system, which typically rids the body of toxic substances, becomes imbalanced and inefficient at clearing those plaques.
In the Neuron study, Town and his team used genetically modified mice to show that blocking a substance called interleukin-10 activates an immune response to clear the brain of the beta-amyloid plaques to restore memory loss and brain cell damage. Alzheimer’s-afflicted mice in which the immune cells were activated behaved more like mice without the disease in various learning and memory tests. Future studies will test the effectiveness of drugs that target interleukin-10 in rats that the scientists have genetically modified to develop Alzheimer’s disease.
Story Source:
The above story is based on materials provided by University of Southern California – Health Sciences.