Credit: Osaka University
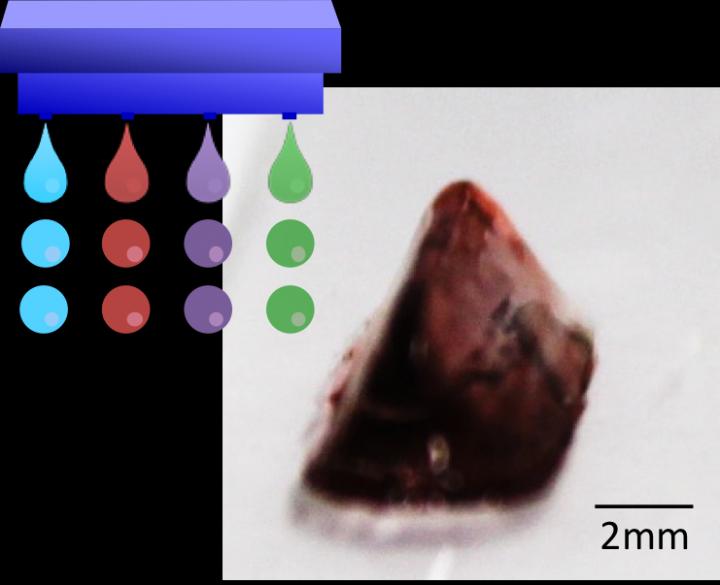
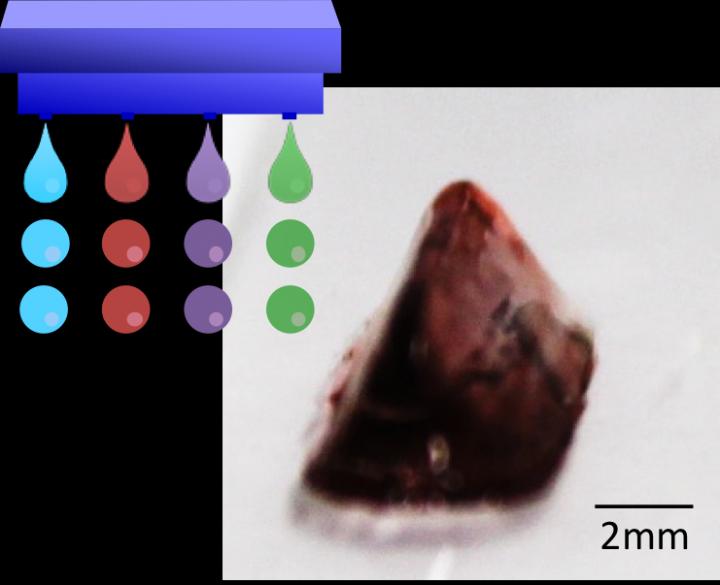
Osaka – Printed replacement human body parts might seem like science fiction, but this technology is rapidly becoming a reality with the potential to greatly contribute to regenerative medicine. Before any real applications, "bioprinting" still faces many technical challenges. Processing the bio-ink and making it stick to itself and hold the desired printed gel structure have been proving particularly difficult especially in inkjet printing. Few methods currently exist for gluing bio-ink droplets together and these do not work for every kind of cell, motivating new alternative approaches.
Building on their previous work, researchers at Osaka University have now refined an enzyme-driven approach to sticking biological ink droplets together, enabling complex biological structures to be printed. They recently published their findings in Macromolecular Rapid Communications.
Lead author, Shinji Sakai says, "Printing any kind of tissue structure is a complex process. The bio-ink must have low enough viscosity to flow through the inkjet printer, but also needs to rapidly form a highly viscose gel-like structure when printed. Our new approach meets these requirements while avoiding sodium alginate. In fact, the polymer we used offers excellent potential for tailoring the scaffold material for specific purposes."
Currently, sodium alginate is the main gelling agent used for inkjet bioprinting, but has some compatibility problems with certain cell types. The researchers' new approach is based on hydrogelation mediated by an enzyme, horseradish peroxidase, which can create cross-links between phenyl groups of an added polymer in the presence of the oxidant hydrogen peroxide.
Although hydrogen peroxide itself can also damage cells, the researchers carefully tuned the delivery of cells and hydrogen peroxide in separate droplets to limit their contact and keep the cells alive. More than 90% of the cells were viable in biological test gels prepared in this way. A number of complex test structures could also be grown from different types of cells.
"Advances in induced pluripotent stem cell technologies have made it possible for us to induce stem cells to differentiate in many different ways," co-author Makoto Nakamura says. "Now we need new scaffolds so we can print and support these cells to move closer to achieving full 3D printing of functional tissues. Our new approach is highly versatile and should help all groups working to this goal."
###
Media Contact
Saori Obayashi
[email protected]
81-661-055-886
@osaka_univ_e
http://www.osaka-u.ac.jp/en
Original Source
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29226501 http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/marc.201700534