Ancient spillway Cambodia reveals structure built for water storage failed and forced Cambodian Kings to relocate capital
Credit: Dr Ian Moffat, Flinders University
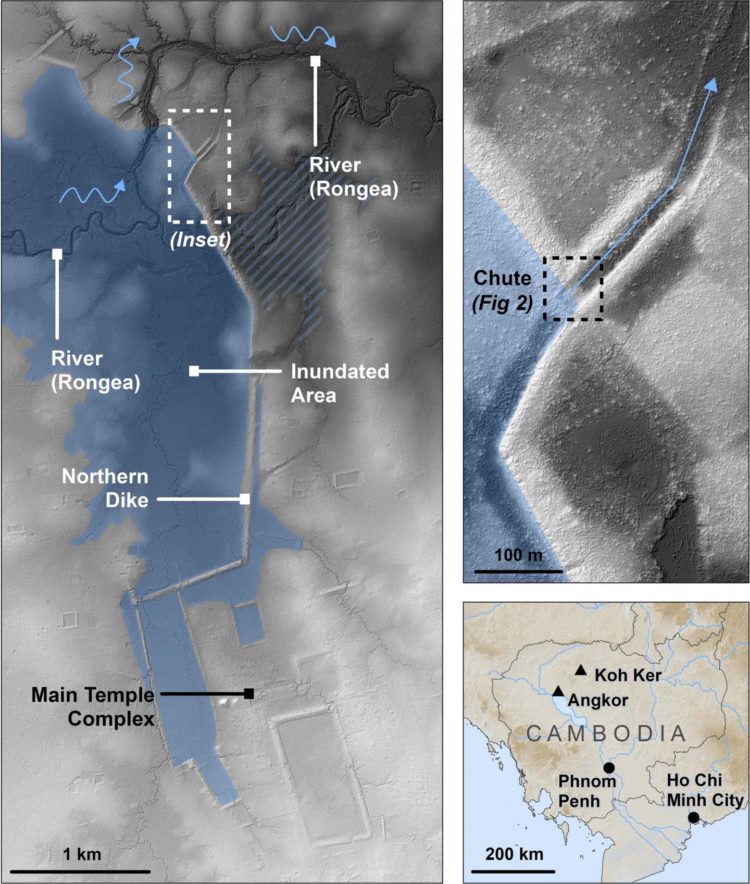
The largest water management feature in Khmer history was built in the 10th century as part of a short-lived ancient capital in northern Cambodia to store water but the system failed in its first year of operation, possibly leading to the return of the capital to Angkor.
An international team of researchers led by Dr Ian Moffat from Flinders University in Australia used ground penetrating radar to map the surface of a buried spillway in Koh Ker to better understand why the reservoir failed during its first year of use.
In a study published in Geoarchaeology, archaeologists explain that the 7km long embankment was designed to capture water from the Stung Rongea river but modelling indicates it was inadequate to contain the average water flow in the catchment, putting into question the legitimacy of Khmer kings, and forcing them to re-establish their capital in Angkor.
“At that time, embarking on projects of civil engineering such as temple building, urban renewal, and the development of water infrastructure was central to establishing the legitimacy of Khmer kings,” says Dr Moffat
“It’s not difficult to envisage that the failure of the embankment at Koh Ker–the largest and most ambitious infrastructure project of the era–may have had a significant impact on the prestige of the sovereign capital, and contributed to the decision to re-establish Angkor as the capital of the Khmer Empire.”
“Our study shows that this ambitious engineering feat was always doomed to rapid failure.”
The monumental complex of Koh Ker, located 90 km northeast of Angkor, remains relatively poorly understood even though it was briefly the capital in the middle of the 10th century CE under King Jayavarman IV, the only capital throughout six centuries to be established outside of the Angkor region.
The site is located in an area of gently sloping hills and stone outcrops, far removed from the low-lying floodplains that define the Khmer heartland.
###
Researchers from Flinders, University of British Columbia and Ecole francaise d’Extreme-Orient in Paris contributed to the study.
Media Contact
Ian Moffat
[email protected]
61-403-050-935
Related Journal Article
http://dx.