Credit: [Credit: Dr. Danika Hill]
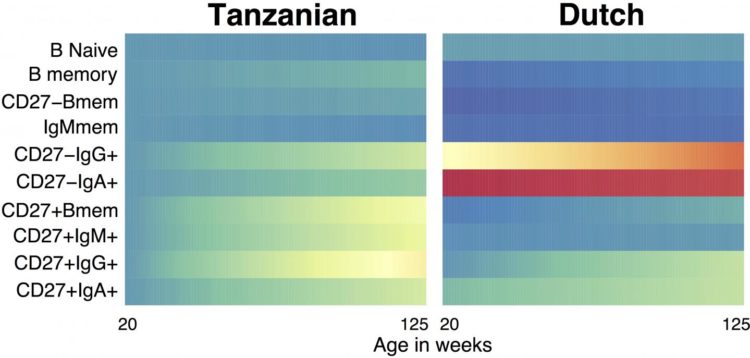
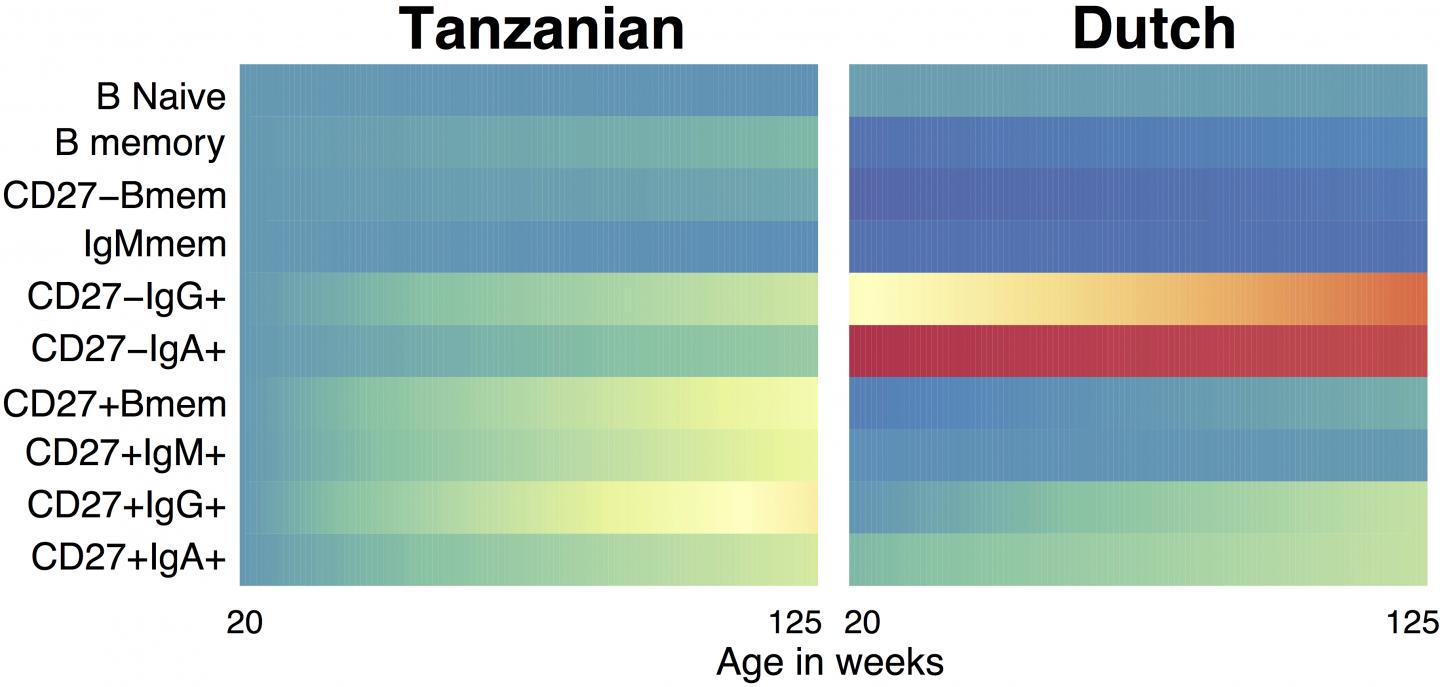
Vaccine responses in the developing immune systems of children may depend on factors such as age, location and anemia status, according to a study comparing samples from 1,119 Dutch children to 171 children in sub-Saharan Africa who took part in a malaria vaccine trial. By casting light on how geography shapes immune responses in children, the findings could help health authorities conduct more effective vaccination campaigns in developing countries. Children in low-income countries are highly susceptible to both vaccine-preventable diseases and infections such as malaria that have historically lacked a vaccine. However, some immunizations do not work as well in children as in adults, partly because scientists don’t fully understand how age, nutrition and genetics influence the developing immune system. Danika Hill and colleagues examined blood samples from 55 children in Tanzania and 116 children in Mozambique under the age of five who had taken part in a phase 3 trial for RTS,S (MosquirixTM) – one of the first vaccines for malaria licensed in Europe. They found that the composition of immune cells in the children evolved over the 32-month trial, and in some cases matured more quickly when compared with samples from Dutch children collected during a previous study. Furthermore, children in Mozambique showed a stronger antibody response to the malaria vaccine compared with Tanzanian children, hinting that geography within continents also influences immune dynamics. One key finding was that children in Tanzania and Mozambique with anemia showed weaker immune responses to the vaccine and lower frequencies of B cells, which, through follow-up studies in the lab, the authors tied to a lack of bioavailable iron. They say their results could explain the poor vaccination outcomes observed in anemic children and iron-deficient adults, but add that further studies should dissect the influence of iron deficiency.
###
Media Contact
Press Package Team
[email protected]
202-326-6440
Related Journal Article
http://dx.