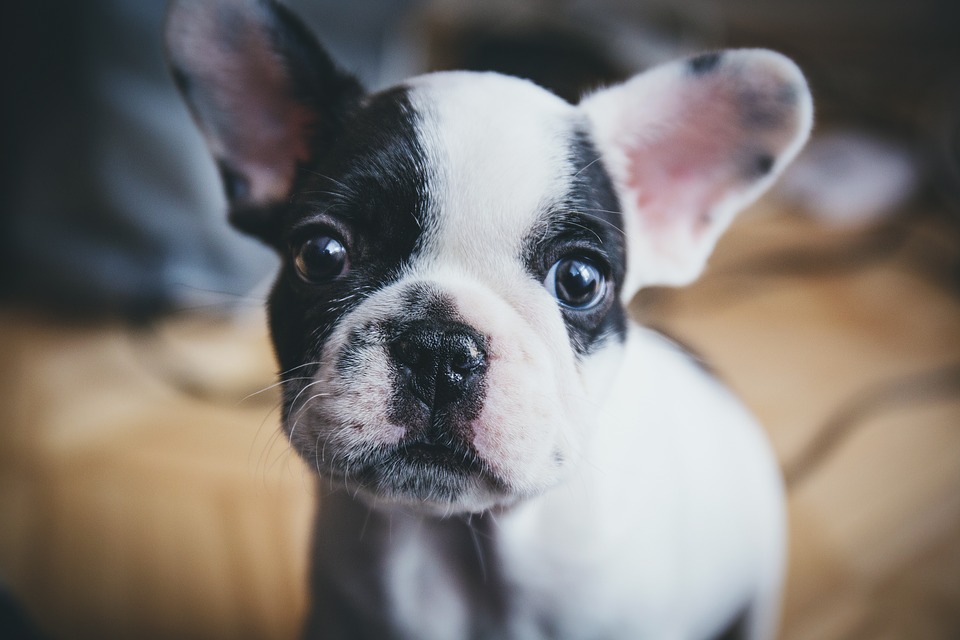
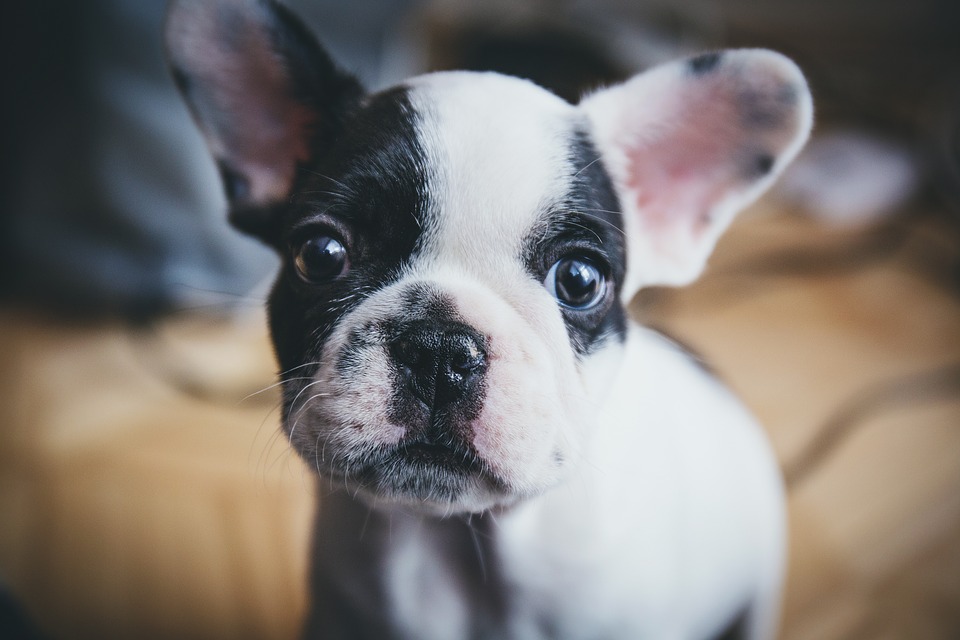
The social ability of dogs is affected by genes that also seems to influence human behaviour, according to a new study from Linköping University in Sweden. The scientists have found a relationship between five different genes and the ability of dogs to interact with humans. Four of them also show similarities to certain conditions in humans.

“Our findings are the first to reveal genes that can have caused the extreme change in social behaviour, which has occurred in dogs since they were domesticated,” says Per Jensen, professor of ethology, who is the leader of the research group.
The dog is the oldest domesticated animal and during thousands of years it has adapted to a life among humans. During this period dogs have developed unique abilities to communicate and cooperate with humans. In this respect, they are widely superior to their wild ancestors, the wolves. Facing a difficult task, most dogs seek contact with a human, apparently to solicit help. In similar situations, wolves generally attempt to solve the problem themselves.
In the new study, published in the scientific journal Scientific Reports, the researchers wanted to study the behaviour of the dogs by presenting them with an unsolvable problem. The task was to open a tight lid to obtain a treat. Almost 500 beagles with similar earlier experiences of human interactions were part of the behavioural studies. The scientists used video recordings to quantify the willingness of the dogs to seek physical contact with a person in the room when the problem turned out to be too difficult.
For more than 200 of the dogs also the DNA was studied. By using a method called GWAS (genome-wide association study), the researchers examined a large number of genetic variants throughout the genome. GWAS can be used to find out if a particular genetic variant is more common among individuals with a particular trait, such as contact seeking behaviour in this case. It turned out that the contact seeking dogs more often carried certain genetic variants.
“We found a clear association with DNA-regions containing five different interesting genes,” says Mia Persson, PhD-student and main author of the paper.
“If the associations we have found can be confirmed in other dog breeds it is possible that dog behaviour also can help us to better understand social disorders in humans,” says Per Jensen.
Web Source: Linköping University.
The post Genes underlying dogs’ social ability revealed appeared first on Scienmag.