Credit: Image courtesy of the Iliev lab.
Common fungi, often present in the gut, teach the immune system how to respond to their more dangerous relatives, according to new research from scientists at Weill Cornell Medicine. Breakdowns in this process can leave people susceptible to deadly fungal infections.
The study, published Feb. 5 in Cell, reveals a new twist in the complex relationship between humans and their associated microbes, and points the way toward novel therapies that could help combat a rising tide of drug-resistant pathogens.
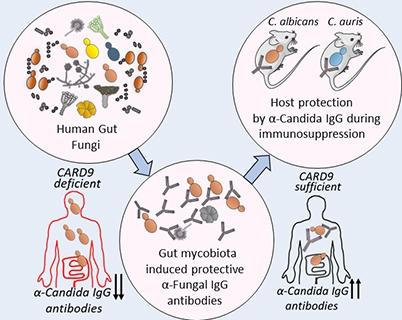
The new discovery stemmed from work on inflammatory bowel disease, which often causes patients to carry larger than normal populations of fungi in their guts. These patients often develop strong antibody responses against mannan, a molecule common to a wide range of fungal species. However, Dr. Iliyan Iliev, associate professor of immunology in medicine in the Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology at Weill Cornell Medicine, noticed that healthy controls in these studies also had some level of anti-fungal antibodies. “There was no actual evidence for fungal infections in the healthy individuals that we examined, so we started thinking about the possible function of those antibodies,” said Dr. Iliev, who is senior author on the study and a member of the Jill Roberts Institute for Research in Inflammatory Bowel Disease.
The team developed a platform that allowed them to determine which gut fungi are targeted by antibodies in the blood of individual patients. They detected a strong response against the yeast Candida albicans. Turning to experiments in mice, Dr. Iliev and Itai Doron, a Weill Cornell Medicine Graduate School of Medical Sciences doctoral candidate in the lab and lead author on the study, found that colonizing the animals’ guts with Candida albicans caused them to develop antibodies against the fungus in their bloodstreams, even though they didn’t develop blood-borne fungal infections. Instead, the animals’ immune cells appeared to transport fungal antigens to the spleen, stimulating the production of circulating antibodies in the bloodstream. “Those fungi just educate that immune response,” Dr. Iliev said.
In patients with suppressed immune systems, such as organ transplant recipients and some cancer patients, fungi in the gut can invade the bloodstream and cause life-threatening infections. Dr. Iliev and his colleagues mimicked this process by treating mice with immunosuppressive drugs. When a Candida species colonizes the gut of these mice, the fungus moves into the bloodstream, causing a fatal infection. Treating the mice with purified anti-fungal antibodies from donor animals protected the immunosuppressed mice from these infections. The same strategy worked against infection with either Candida albicans or the emerging pathogenic yeast Candida auris, which has become a major cause of fungal disease in immunosuppressed patients and the elderly in recent years.
Collaborating with researchers at INSERM in Paris, France, the Weill Cornell Medicine team also looked at serum from patients with mutations in a gene called CARD9. This mutation affects a critical adapter protein in the immune system, leaving the affected individuals susceptible to severe fungal infections. Dr. Iliev’s team found that the serum of these patients lacked the anti-fungal antibodies normally seen in serum of patients without this mutation. Experiments in mice confirmed an essential and specific role for CARD9 in priming the production of anti-fungal antibodies.
Graphic depicting relationship between fungi in gut, antibody levels and CARD gene
Relationship between gut fungi, anti-fungal antibodies, CARD9 gene, and fungal immunity. Image courtesy of the Iliev lab.
The results suggest that normal intestinal fungi such as Candida albicans may function as a kind of intestinal vaccine against fungal infection in healthy people, by inducing the production of bloodborne antibodies that can target multiple species of potentially pathogenic fungi. When those fungi do enter the bloodstream, the antibodies bind them and target them for destruction by cells of the immune system. In patients with suppressed immunity, the anti-fungal antibodies may decline, leaving them vulnerable to fungal infection. New therapies that involve either stimulating the production of anti-fungal antibodies, or injecting such purified antibodies directly into patients’ bloodstreams, could potentially help combat these increasingly common infections.
If that approach works, it would be a welcome development. “Many fungal infections in immunosuppressed patients and elderly patients are happening by translocation of pathogenic Candida species from the gastrointestinal tract, and the survival rates upon systemic spreading are alarmingly low,” said Dr. Iliev.
###
Media Contact
Krystle Lopez
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/




