Credit: Irasutoya, Michikazu Hara
Scientists at Tokyo Institute of Technology (Tokyo Tech) have developed an improved catalyst by taking the common dehydrating agent calcium hydride and adding fluoride to it. The catalyst facilitates the synthesis of ammonia at merely 50 °C, by using only half the energy that existing techniques require. This opens doors to ammonia production with low energy consumption and reduced greenhouse gas emission.
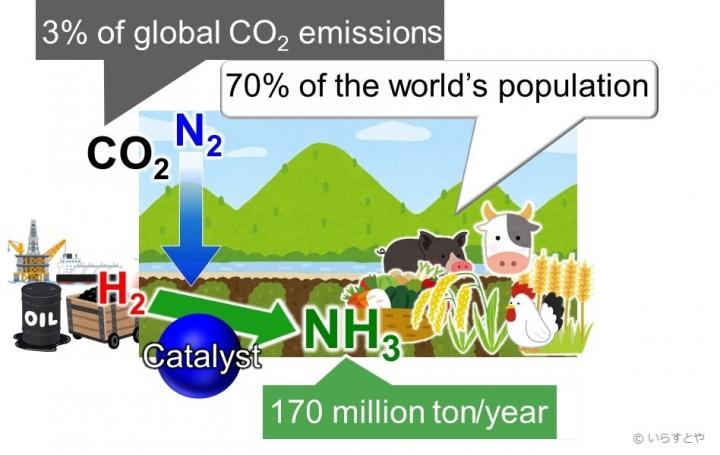
Ammonia is a critical for making plant fertilizer, which in turn feeds approximately 70% of the world’s population. In industries, ammonia is produced via the Haber-Bosch process, where methane is first reacted with steam to produce hydrogen, and hydrogen is then reacted with nitrogen to give ammonia. The problem with this process is that as the temperature increases, the yield decreases. To continue to get a good yield, the pressure applied in the reaction chamber needs to be increased. This requires much energy. Further, the iron-based catalysts used for the reaction are only effective above 350 °C. Maintaining such high temperatures also requires a significant amount of energy. To top it all, the yield is only 30-40%.
Fossil fuels are currently used to power the process, contributing large amounts of carbon dioxide to the atmosphere. Renewable resource alternatives, such as wind energy, have been applied, but those have not proven sustainable. To increase the yield while reducing harm to the environment, therefore, the reaction must take place at low temperatures. For this to happen, catalysts that enable the reaction at low temperatures are required.
So far, such catalysts have been elusive to scientists. “Conventional catalysts lose the catalytic activity for ammonia formation from N2 and H2 gases at 100-200 °C, even if they exhibit high catalytic performance at high temperatures,” remark a group of scientists from Tokyo Tech, Japan, who appear to have finally solved the catalyst problem. The scientists, led by Dr.Michikazu Hara, developed a catalyst that is effective even at 50 °C. “Our catalyst produces ammonia from N2 and H2 gases at 50 °C with an extremely small activation energy of 20 kJmol-1, which is less than half that reported for conventional catalysts,” Dr. Hara and colleagues report in their paper published in Nature Communications.
Their catalyst comprises a solid solution of CaFH, with ruthenium (Ru) nanoparticles deposited on its surface. The addition of fluoride (F–) to calcium hydride (CaH2), a common dehydrating agent, is what makes the catalyst effective at lower temperatures and pressures. After conducting spectroscopic and computational analyses, the scientists propose a possible mechanism by which the catalyst facilitates ammonia production.
The calcium-fluoride (Ca-F) bond is stronger than the calcium-hydrogen (Ca-H) bond. So, the presence of the Ca-F bond weakens the Ca-H bond and the Ru is able to extract H atoms from the catalyst crystal, leaving electrons in their place. The H atoms then desorb from the Ru nanoparticles as H2 gas. This occurs even at 50 °C. The resultant charge repulsion between the trapped electrons and F– ions in the crystal lower the energy barriers for these electrons to release, thereby giving the material high electron-donating capacity. These released electrons attack the bonds between the nitrogen atoms in the N2 gas, facilitating the production of ammonia.
This new method of ammonia production cuts energy demands, thereby reducing the carbon dioxide emissions from the use of large amounts of fossil fuels. The findings of this study illuminate the possibility of an environmentally sustainable Haber-Bosch process, opening the door to the next revolution in agricultural food production.
###
Video : A new catalyst to synthesize ammonia from H2 and N2 even at 50°C
The following videos, provided courtesy of team leader Michikazu Hara, describe the research in a visually and audibly appealing fashion.
[Trailer version]
[Full version]
Green catalysts with Earth-abundant metals accelerate production of bio-based plastic
Barium ruthenate: A high-yield, easy-to-handle perovskite catalyst for the oxidation of sulfides
A ruthenium-based catalyst with highly active, flat surfaces outperforms metal-based competitors
Highly efficient ammonia synthesis catalyst developed
Reusable ruthenium-based catalyst could be a game-changer for the biomass industry
Chemoselective acetalization by a bifuncional cerium phosphate catalyst
Hara & Kamata Laboratory
Media Contact
Emiko Kawaguch
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




