Seismologists of the GFZ observe processes in the upper mantle for the first time before the formation of an enormous underwater eruption
Credit: Image: Cesca et al. 2019, Nature Geoscience: DOI 10.1038/s41561-019-0505-5
A new submarine volcano was formed off the island of Mayotte in the Indian Ocean in 2018. This was shown by an oceanographic campaign in May 2019. Now an international team led by the scientist Simone Cesca from the German GeoForschungsZentrum GFZ is illuminating the processes deep inside the earth before and during the formation of the new volcano. It is as if the researchers had deciphered a new type of signal from the Earth’s interior that indicates a dramatic movement of molten rocks before the eruption. With their specially developed seismological methods, the researchers are reconstructing the partial emptying of one of the deepest and largest active magma reservoirs ever discovered in the upper mantle. The study is published in the journal Nature Geoscience.
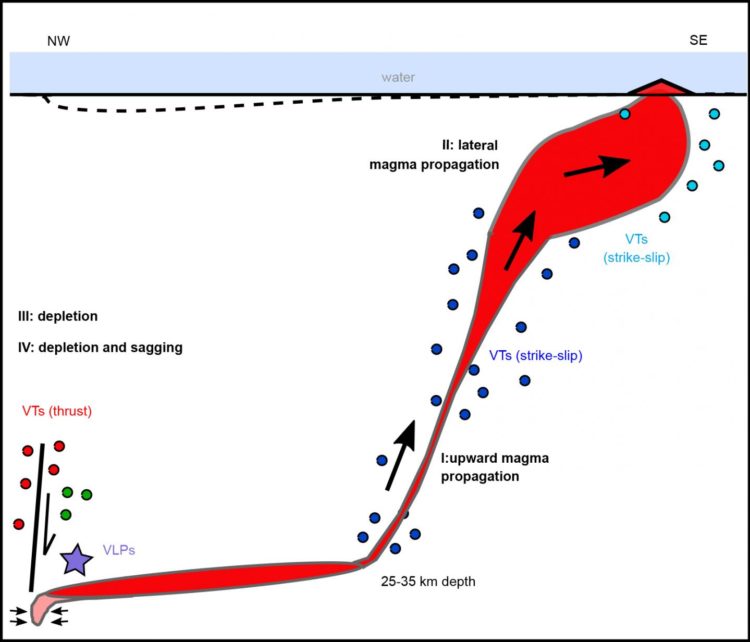
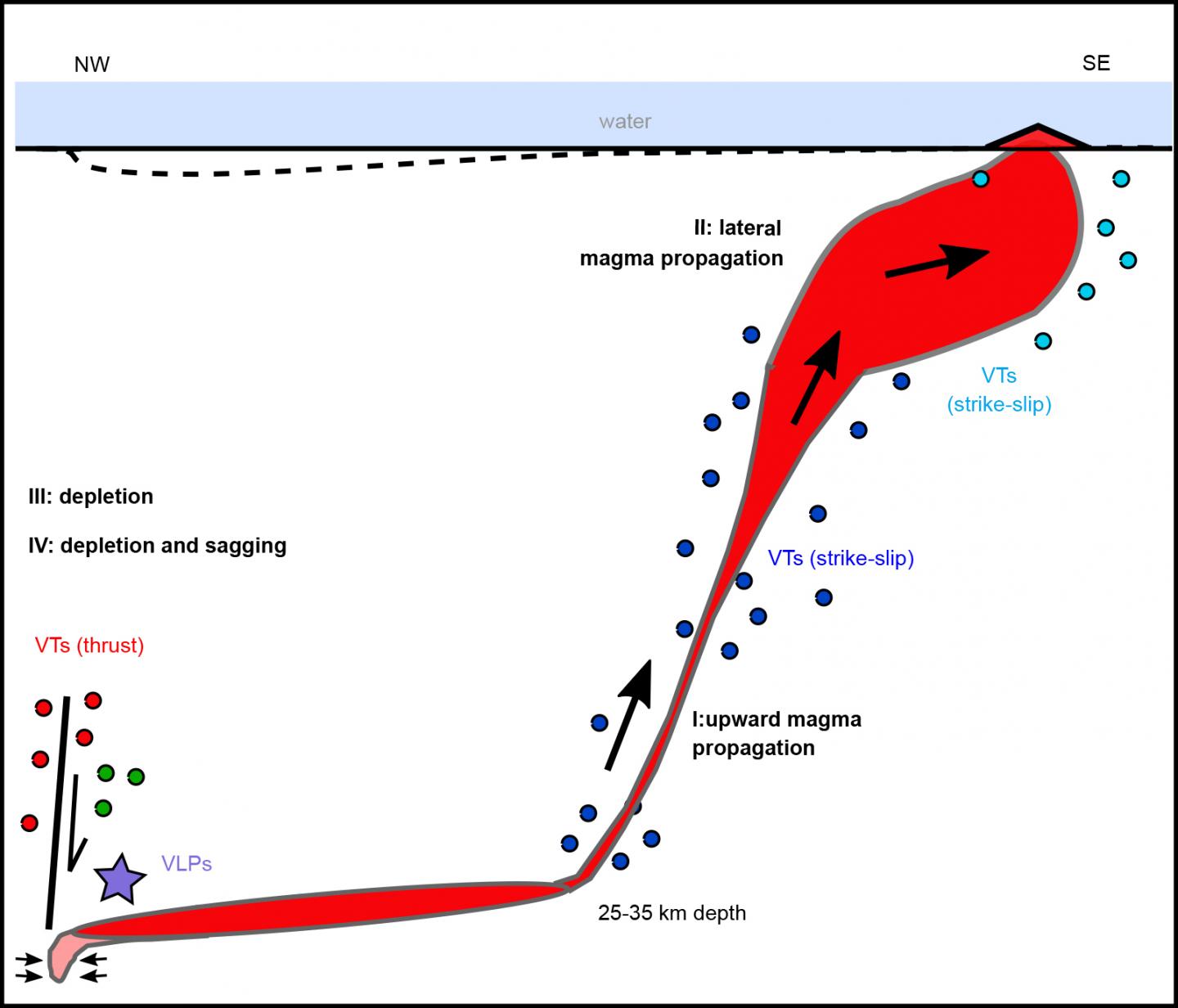
Since May 2018, an unusual sequence of earthquakes has been recorded off-coast the island of Mayotte in the Comoros archipelago between Africa and Madagascar. Seismic activity began with a swarm of thousands of “seemingly tectonic” earthquakes, culminating in an earthquake of magnitude 5.9 in May 2018. Mostly since June 2018, however, a completely new form of earthquake signal has emerged that was so strong that it could be recorded up to a thousand kilometers away. These 20 to 30 minute long signals are characterized by particularly harmonic, low frequencies, almost monochromatic, similar to a large bell or a double bass, and are called Very Long Period (VLP) signals. Although the centre of the seismic activity was located almost 35 kilometres offshore the east of the island, a continuous lowering and eastward motion of the earth’s surface at Mayotte had begun at the same time as the massive swarms of VLP events started, accumulating to almost 20 cm to date.
Although there was no evidence of earlier volcanic activity in the epicenter of the seismic activity, GFZ scientists had suspected magmatic processes from the beginning, as quake swarms in the upper earth crust often arise as a reaction to the rise of magma and VLPs in earlier years were associated with the collapse of large caldera volcanoes. The special frequency content of the VLP signals is caused by the resonance oscillation of the buried magma chamber. The deeper the vibrations, the larger the magma reservoir. However, the earthquake swarms under the ocean floor were much deeper than with other volcanoes and the resonance tones of the VLPs were unusually low and strong.
An international team led by GFZ scientist Simone Cesca analysed seismological and geodetic data from the region to study these observations and their evolution over time. However, the investigations were complicated by the fact that there was no seismic network on the ocean floor and therefore only measurements were available at great distances on Mayotte, Madagascar and in Africa. “We tried to improve the unfavourable initial situation by developing special new analytical methods such as cluster and directional beam methods,” says Cesca.
The team identified different activity phases within the sequence of events from May 2018 to today. The initial swarm phase indicated a rapid upward movement of magma from a deep mantle reservoir more than 30 kilometres below the Earth’s surface. Once an open channel had formed from the Earth’s mantle to the seabed, the magma began to flow unhindered and form a new underwater volcano. A French oceanographic campaign recently confirmed the birth of the submarine volcano, whose location coincides with the reconstructed magma rise.
In this phase, the apparent tectonic earthquake activity decreased again, while the lowering of the ground on the island of Mayotte began. Likewise, long-lasting monofreququent VLP signals started. “We interpret this as a sign of the collapse of the deep magma chamber off the coast of Mayotte,” explains Eleonora Rivalta, co-author of the scientific team. “It is the deepest (~30 km) and largest magma reservoir in the upper mantle (more than 3.4 cubic kilometres) to date, which is beginning to empty abruptly.
“Since the seabed lies 3 kilometers below the water surface, almost nobody noticed the enormous eruption. However, there are still possible hazards for the island of Mayotte today, as the Earth’s crust above the deep reservoir could continue to collapse, triggering stronger earthquakes,” says Torsten Dahm, Head of the section Physics of Earthquakes and Volcanoes at the GFZ.
###
Media Contact
Josef Zens
[email protected]
49-331-288-1040
Related Journal Article
http://dx.