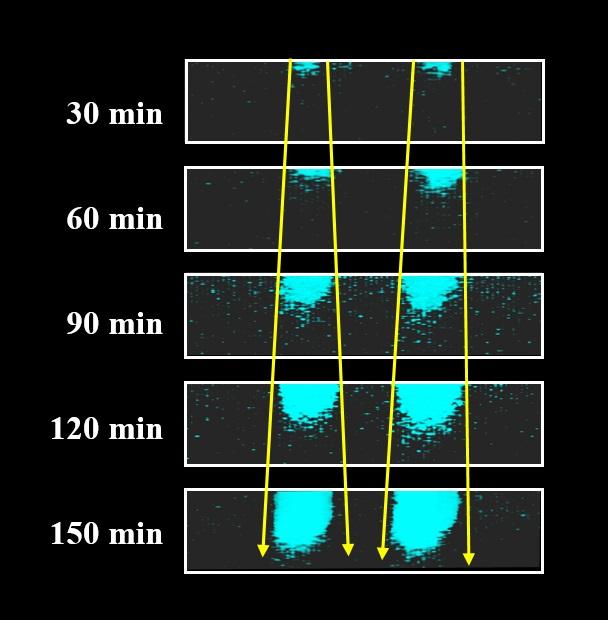
Credit: Adapted from ACS Central Science 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acscentsci.0c00133
Modern society relies on polymers, such as polypropylene or polyethylene plastic, for a wide range of applications, from food containers to automobile parts to medical devices. However, like people, polymers age, and when they do, the materials become prone to cracking or breaking. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have developed a method to visualize variations in polymers that arise with age.
Heat, sunlight, oxygen and humidity can all cause polymers to degrade over time. At early stages, polymer chains break, producing functional groups, such as hydroxyl groups, and generating free radicals that speed up the aging process. Scientists have developed methods to study more advanced signs of polymer aging, but these techniques don’t provide a microscopic 3D picture, and most aren’t sensitive enough to detect early aging. Rui Tian, Chao Lu and colleagues wanted to find a way to visualize the aging process of polypropylene and polyethylene polymers in 3D. Such a technique could be used to detect aged polymers so they can be repaired or replaced with new parts before they fail.
The researchers based their method on a commercially available fluorescent dye, called DBPA, that can specifically attach to hydroxyl groups in polymers as the chains break. The team heated a thin sheet of polypropylene or polyethylene at 140 F and then soaked the plastic in a DPBA solution to dye the aged sites with hydroxyl groups. When the researchers observed the sheets under a confocal microscope, they found that the aged sites in the polymers — as revealed by the fluorescently tagged hydroxyl groups — grew deeper, wider and more frequent with time. The method detected faster polymer aging when the sheets were exposed to higher temperatures. To the researchers’ knowledge, the fluorescent technique is the first that can sensitively monitor polymer aging in 3D, which will assist in identifying deteriorating polymers at the earliest stages.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
The paper’s abstract will be available on May 6 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]




