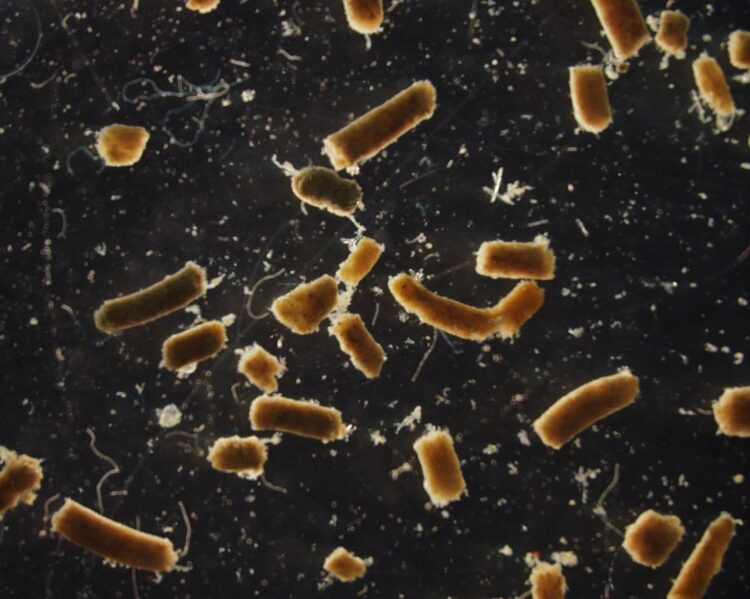
Study estimates fishes contribute about 16 percent of the sinking carbon in upper ocean waters
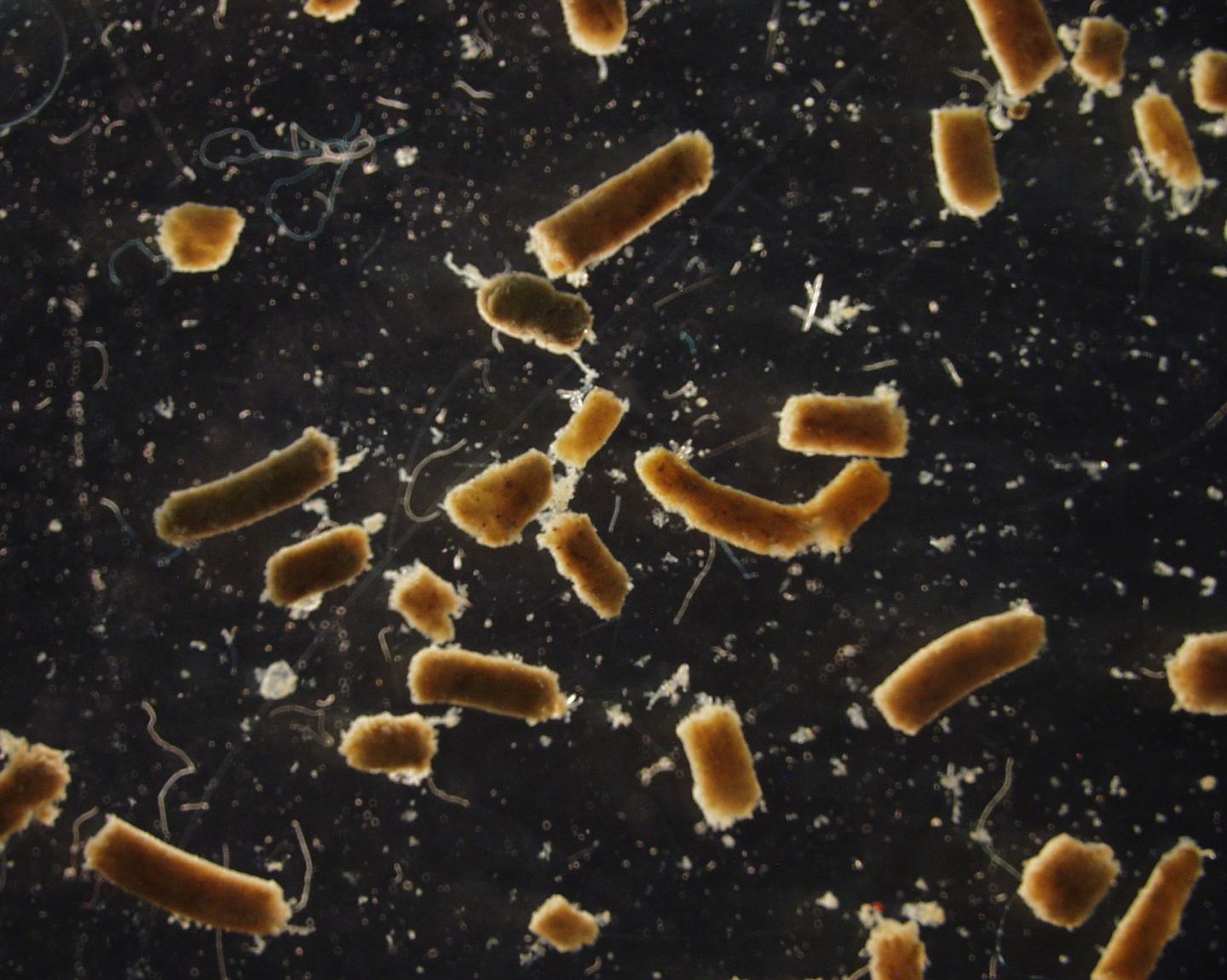
Credit: Grace Saba
Scientists have little understanding of the role fishes play in the global carbon cycle linked to climate change, but a Rutgers-led study found that carbon in feces, respiration and other excretions from fishes – roughly 1.65 billion tons annually – make up about 16 percent of the total carbon that sinks below the ocean’s upper layers.
Better data on this key part of the Earth’s biological pump will help scientists understand the impact of climate change and seafood harvesting on the role of fishes in carbon flux, according to the study – the first of its kind – in the journal Limnology and Oceanography. Carbon flux means the movement of carbon in the ocean, including from the surface to the deep sea – the focus of this study.
“Our study is the first to review the impact that fishes have on carbon flux,” said lead author Grace K. Saba, an assistant professor in the Center for Ocean Observing Leadership in the Department of Marine and Coastal Sciences in the School of Environmental and Biological Sciences at Rutgers University-New Brunswick. “Our estimate of the contribution by fish – about 16 percent – includes a large uncertainty, and scientists can improve it with future research. Forms of carbon from fish in ocean waters where sunlight penetrates – up to about 650 feet deep – include sinking fecal pellets, inorganic carbon particles (calcium carbonate minerals), dissolved organic carbon and respired carbon dioxide.”
The ocean plays a vital role in the Earth’s carbon cycle by exchanging carbon dioxide, a key greenhouse gas linked to global warming and climate change, with the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide absorbed by the ocean is taken up by phytoplankton (algae), small single-celled plants at the ocean’s surface. Through an important process called the biological pump, this organic carbon can go from the surface to ocean depths when algal material or fecal pellets from fishes and other organisms sink. The daily migration of fishes to and from the depths also contributes organic carbon particles, along with excreted and respired material. Another factor is mixing of ocean waters.
“Carbon that makes its way below the sunlit layer becomes sequestered, or stored, in the ocean for hundreds of years or more, depending on the depth and location where organic carbon is exported,” Saba said. “This natural process results in a sink that acts to balance the sources of carbon dioxide.”
###
Scientists at many institutions contributed to the study, which is a product of the Fish Carbon Working Group led by Saba since 2018 and funded by the Ocean Carbon and Biogeochemistry program, which is supported by the National Science Foundation and National Aeronautics and Space Administration.
Media Contact
Todd Bates
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.