Credit: Adapted from ACS Nano 2020, DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.9b09880
Flexible temporary electronic displays may one day make it possible to sport a glowing tattoo or check a reading, like that of a stopwatch, directly on the skin. In its current form, however, this technology generally depends on plastic. New research in ACS Nano describes a way to make these displays, which would likely be discarded after a single use, more environmentally friendly using a plentiful and biodegradable resource: fish scales.
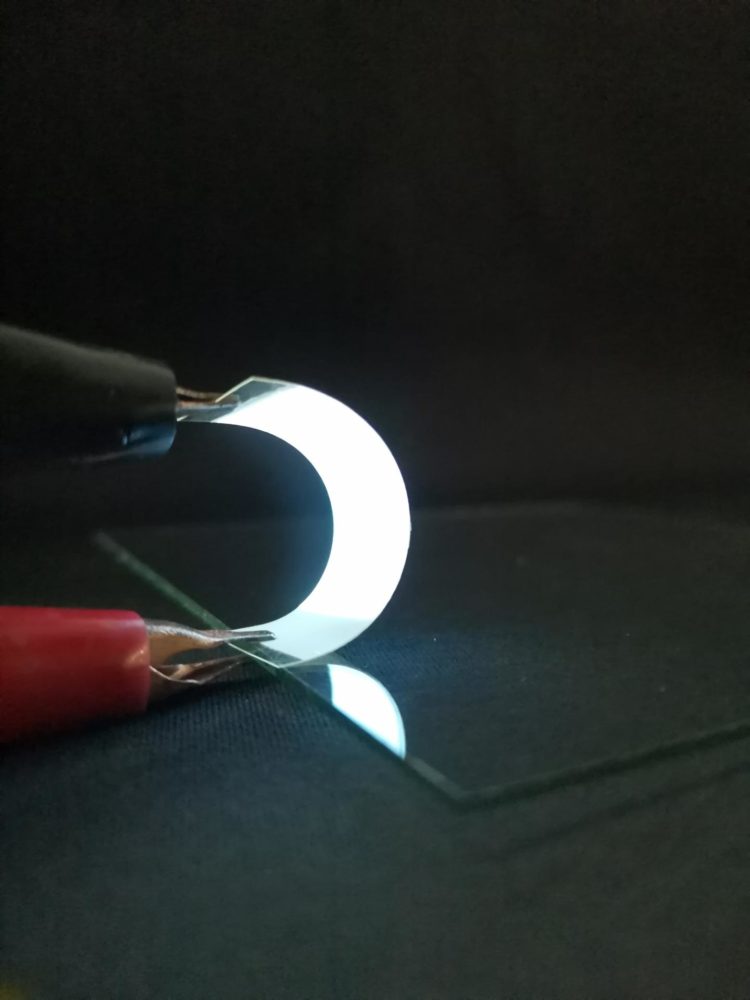
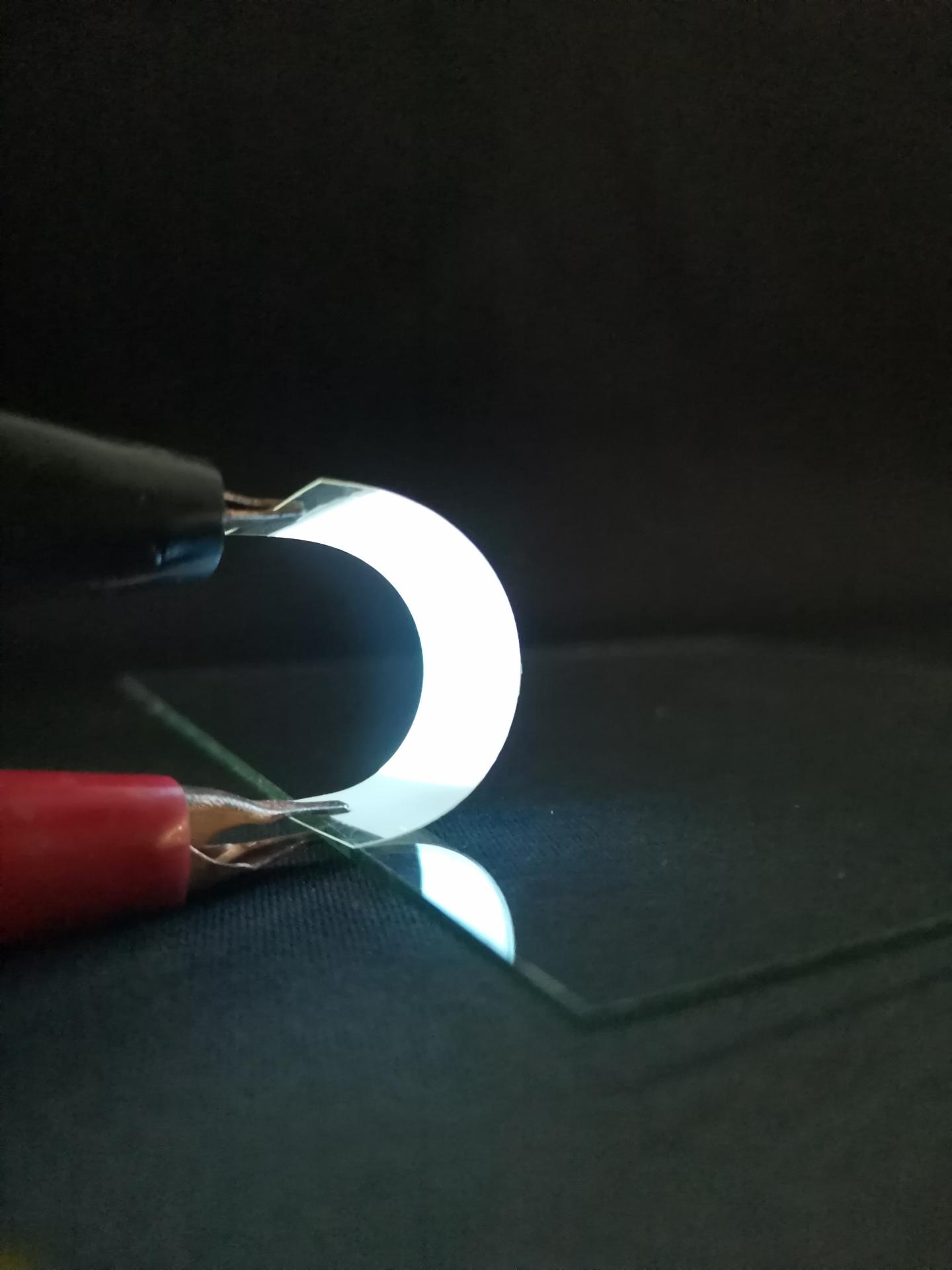
Within such displays, electricity-conducting and light-emitting components are layered onto a transparent film. To make them flexible enough to withstand the bending required to stay on skin or other soft surfaces, researchers have so far relied on films made of plastic — a substance derived from fossil fuels, a limited resource and a source of pollution. Hai-Dong Yu, Juqing Liu, Wei Huang and colleagues wanted to find a more sustainable and environmentally friendly material for the film. They settled on gelatin derived from collagen in fish scales, which are usually thrown away.
After preparing a gelatin solution from the fish scales, they poured it into a petri dish that acted as a mold for the film as it dried. In tests, they found the film had the attributes, including flexibility and transparency, needed for use in wearable devices. The film also appeared unlikely to linger in landfills: It dissolved within seconds in hot water and could then be recycled into a new film. When buried in soil, it degraded within 24 days. The team used the film to build a working alternating current electroluminescent device that continued to glow even after being bent and relaxed 1,000 times. Films derived from fish scales are a promising alternative for more sustainable flexible electronics, including wearables and folding displays, the researchers conclude.
###
The authors acknowledge funding from the National Key R&D Program of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the China-Sweden Joint Mobility Project, the Ministry of Science and Technology of the People’s Republic of China funding for Fundamental Studies of Perovskite Solar Cells, the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province for Distinguished Young Scholars.
The paper’s abstract will be available on March 18 at 8 a.m. Eastern time here: http://pubs.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and its people. The Society is a global leader in providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a specialist in scientific information solutions (including SciFinder® and STN®), its CAS division powers global research, discovery and innovation. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact [email protected].
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook
Media Contact
Katie Cottingham
[email protected]
301-775-8455