These results will help researchers to identify at an early stage the people most at risk of developing the disease, well before the first cognitive symptoms appear
Credit: ©ULiège/CRC In Vivo Imaging
Study conducted by researchers from the GIGA CRC In vivo Imaging laboratory at ULiège demonstrates, for the first time in humans, how the first deposits of tau proteins in the brainstem are associated with neurophysiological processes specific to the early stages of Alzheimer’s disease development.
During the pre-clinical stages of Alzheimer’s disease, i.e. when subtle changes are taking place in the brain but no cognitive symptoms can be observed, the cortex presents a state of transient hyperexcitability. To date, several studies conducted in animals have shown that tau and beta-amyloid proteins – central to the development of Alzheimer’s disease – were associated with increased cortical excitability and dysfunction of brain networks. However, the relationship between the accumulation of Alzheimer’s disease-related proteins and cortical hyperexcitability during the earliest stages of the disease remains poorly understood in humans, in particular due to technological limitations in the precise quantification of early protein deposition.
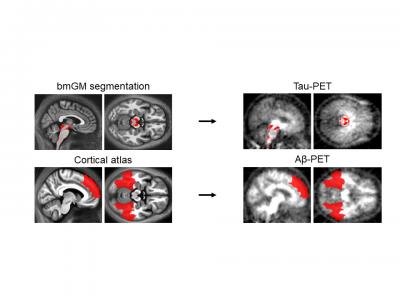
A study, conducted by researchers from the Cyclotron Research Centre (CRC In vivo Imaging / GIGA) of ULiège studied whether the first deposits of tau and beta-amyloid proteins in the brains of healthy individuals aged between 50 and 70 years old could be linked to a higher level of cortical excitability. To do this, we combined different neuroimaging methodologies (magnetic resonance imaging, positron emission tomography) in order to characterise the quantity of tau and beta-amyloid proteins in their first agglomeration regions,” explains Gilles Vandewalle, head of the laboratory. That is to say, respectively, in the brainstem and in a series of upper cortical areas. “In addition, the researchers also measured the excitability of the participants’ cortex in a non-invasive manner, using transcranial magnetic stimulation techniques in conjunction with the acquisition of electroencephalographic recordings.
The results of this study show that an increased amount of tau protein in the brainstem – its primary site of agglomeration – is specifically associated with a higher level of cortical excitability, while the researchers did not observe a significant relationship for the amount of beta-amyloid protein in the upper cortical areas. These results constitute a first in vivo observation in humans of the early link between proteins linked to Alzheimer’s disease and their impact on brain function,” says Maxime Van Egroo, scientific collaborator at the CRC In Vivo Imaging and first author of the scientific article. Furthermore, they suggest that measuring the hyperexcitability of the cortex could be a useful marker to provide information on the progress of certain cerebral pathological processes linked to Alzheimer’s disease, and thus contribute to the early identification of people most at risk of developing the disease, well before the first cognitive symptoms appear. »
###
Media Contact
Gilles Vandewalle
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.




