Credit: NASA/GSFC/ASU
In October 2015, a spectacular rockfall occurred in the Swiss Alps: in the late morning hours, a large, snow-covered block with a volume of more than 1500 cubic meters suddenly detached from the summit of Mel de la Niva. It fell apart on its way downslope, but a number of boulders continued their journey into the valley. One of the large boulders came to a halt at the foot of the summit next to a mountain hut, after travelling more than 1.4 kilometers and cutting through woods and meadows.
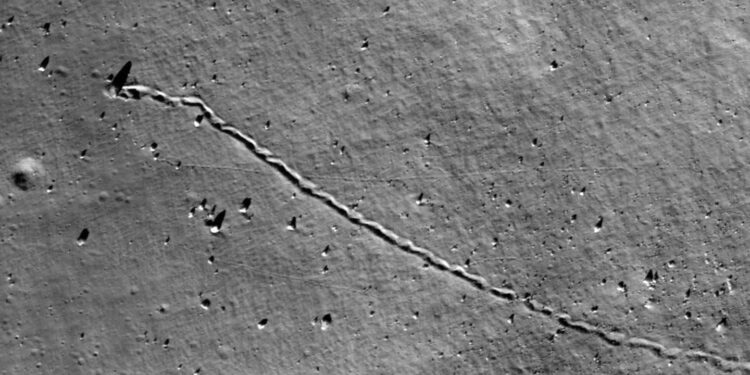
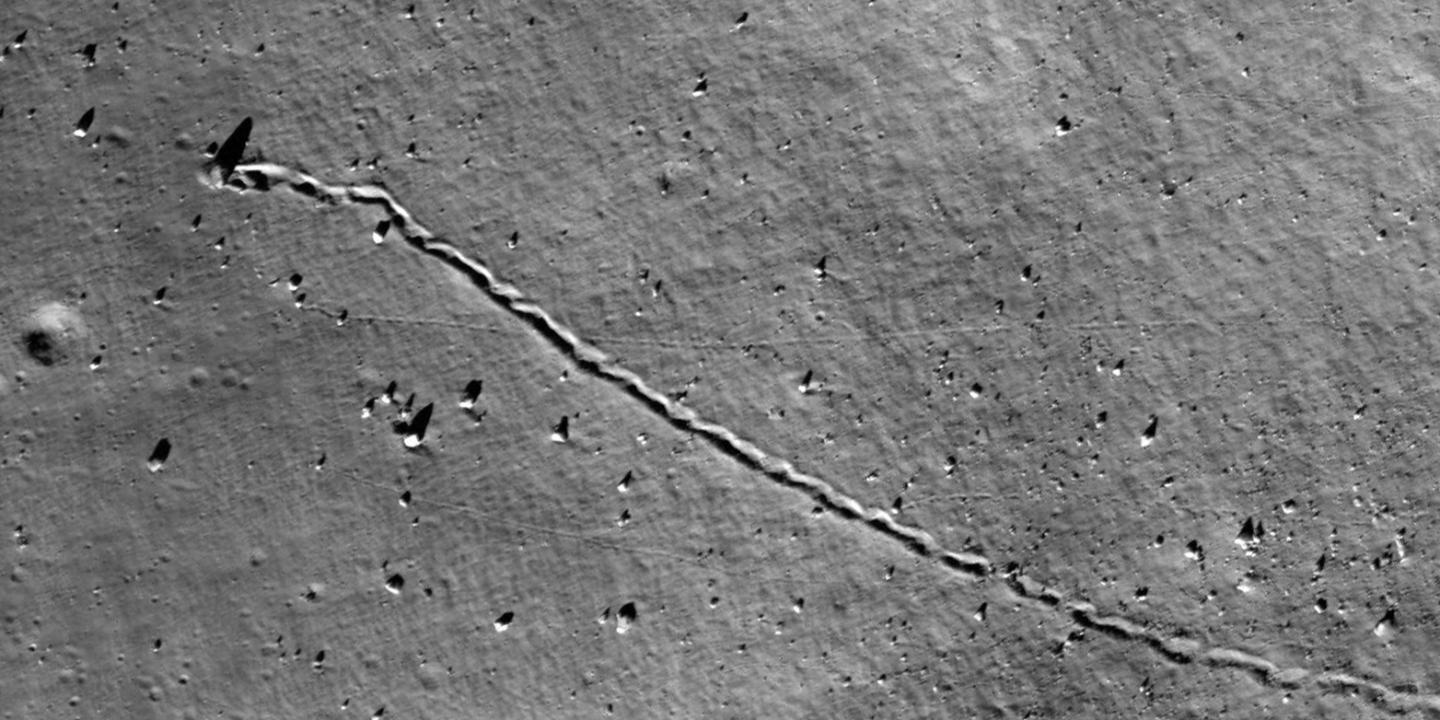
On the Moon, time and again boulders and blocks of rock travel downslope, leaving behind impressive tracks, a phenomenon that has been observed since the first unmanned flights to the Moon in the 1960s. During the Apollo missions, astronauts examined a few such tracks on site and returned displaced rock block samples to Earth. However, until a few years ago, it remained difficult to gain an overview of how widespread such rock movements are and where exactly they occur.
Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Solar System Research (MPS) in Germany and ETH Zurich have analyzed an archive of more than two million images of the lunar surface and present the first global map of rockfalls on the Moon in today’s edition of Nature Communications.
“The vast majority of displaced boulders on the Moon have a diameter of between seven and ten meters,” explains Valentin Bickel of MPS and ETH Zurich, first author of the new study. “Earlier space probes that have studied the Moon were unable to detect such small features on a global scale,” he adds. It was not until 2010, with the launch of NASA’s Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter, that imagery of the entire lunar surface, with the necessary spatial resolution and coverage, has been available.
The result is a map of the lunar surface between 80 degrees northern and southern latitude that shows 136,610 rockfalls with diameters of more than two and a half meters. “For the first time, this map enables us to systematically analyze the occurrence and causes of rockfalls on another celestial body”, says Dr. Urs Mall from MPS.
Previously, scientists had assumed that lunar quakes in particular were responsible for the displacement of boulders. The new global map of rockfalls indicates that impacts from asteroids may play a much more important role. They are apparently – directly or indirectly – responsible for more than 80 percent of all observed rockfalls.
“Most of the rockfalls are found near crater walls,” says Prof. Dr. Simon Loew of ETH Zurich. Some of the boulders are displaced soon after the impact, others much later. The researchers hypothesize that impacts cause a network of cracks that extend in the underlying bedrock. Parts of the surface can thus become unstable even after very long periods of time.
Surprisingly, even in the oldest lunar landscapes, which formed up to 4 billion years ago or even earlier, traces of rockfall events can be found. Since such imprints would typically disappear after a few million years, these surfaces are apparently still subject to erosion through rockfall, even billions of years after they were formed.
“Apparently, impacts influence and modify the geology of a region over very, very long time scales,” says Bickel. The results also suggest that very old surfaces on other airless bodies such as Mercury or the large asteroid Vesta may still be evolving as well.
###
Media Contact
Valentin Bickel
[email protected]
Original Source
https:/
Related Journal Article
http://dx.